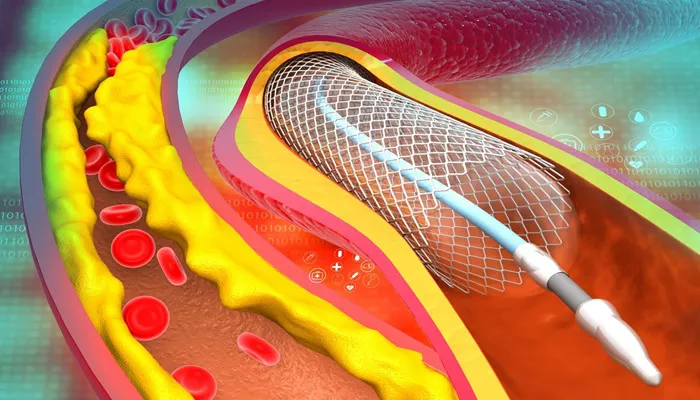
Heart stents are small, mesh-like tubes placed in narrowed or blocked coronary arteries to improve blood flow to the heart.
They are a common treatment for coronary artery disease (CAD) and have saved countless lives since their introduction.
While stents are designed to be permanent implants, their longevity and effectiveness can vary based on several factors.
This article will explore how long heart stents can last, the factors influencing their lifespan, and the importance of post-procedure care.
What Are Heart Stents?
Heart stents are typically made of metal or polymer materials. They are inserted into the coronary arteries during a procedure known as percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI), commonly referred to as angioplasty. During this procedure, a catheter with a balloon at its tip is used to open the blocked artery. Once the artery is widened, the balloon is deflated, and the stent remains in place to keep the artery open.
Stents can be classified into two main types:
Bare-metal stents (BMS): These are simple metal tubes that provide structural support to keep the artery open.
Drug-eluting stents (DES): These stents are coated with medication that helps prevent restenosis, or re-narrowing of the artery.
How Long Do Heart Stents Last?
The longevity of heart stents can vary significantly based on several factors. Generally, heart stents are designed to remain in place indefinitely, but their effectiveness over time can be influenced by both patient-specific and procedural factors.
Type of Stent: Drug-eluting stents tend to last longer than bare-metal stents. This is primarily due to the medication coating that reduces the risk of restenosis. Studies have shown that drug-eluting stents have lower rates of re-narrowing compared to bare-metal stents.
SEE ALSO: Which Artery Is The Most Common to Have Blockage?
Patient Health: The overall health of a patient plays a crucial role in how long a heart stent lasts. Conditions such as diabetes, hypertension, and high cholesterol can adversely affect stent durability.
Well-managed health conditions contribute to longer-lasting stents.
Lifestyle Choices: Lifestyle factors significantly influence the lifespan of heart stents. Smoking cessation, maintaining a healthy diet, and engaging in regular exercise are essential for extending the life of a stent.
Medication Adherence: After receiving a heart stent, patients must adhere to prescribed antiplatelet medications to prevent blood clots from forming within the stent. Failure to take these medications as directed can lead to serious complications, including heart attacks.
Factors Affecting Stent Longevity
Several factors can impact how long a heart stent remains effective:
Restenosis: Restenosis refers to the re-narrowing of an artery after it has been treated with a stent. While drug-eluting stents significantly reduce this risk compared to bare-metal options, it can still occur due to various reasons such as inflammation or excessive scar tissue formation.
Patient Compliance: Following medical advice after receiving a stent is critical for its longevity. Patients should adhere strictly to their prescribed medication regimen and attend regular follow-up appointments with their healthcare providers.
Health Management: Managing underlying health issues is vital for maintaining good cardiovascular health and ensuring that the stent functions effectively over time. Regular monitoring of blood pressure, cholesterol levels, and blood sugar levels is essential for patients with diabetes or other chronic conditions.
Surgical Technique: The skill and experience of the interventional cardiologist performing the procedure can also impact outcomes. Proper placement of the stent is crucial for minimizing complications and ensuring long-term success.
The Role of Lifestyle Changes
Making positive lifestyle changes after receiving a heart stent can significantly enhance its longevity:
Diet: A heart-healthy diet is essential for all patients with coronary artery disease. This includes consuming plenty of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats while limiting saturated fats, trans fats, sodium, and added sugars.
Exercise: Regular physical activity helps improve cardiovascular health and maintain a healthy weight. Patients should consult their healthcare provider before starting any exercise program.
Smoking Cessation: Quitting smoking is one of the most important steps patients can take to improve their overall health and prolong the life of their heart stent.
Stress Management: Chronic stress can negatively impact heart health. Techniques such as mindfulness meditation, yoga, or deep breathing exercises can help manage stress levels effectively.
Post-Procedure Care
Proper post-procedure care is crucial for ensuring that heart stents function effectively over time:
Medication Adherence: Patients must take prescribed antiplatelet medications as directed by their doctor to prevent blood clots within the stent.
Regular Follow-Ups: Routine check-ups with healthcare providers allow for monitoring of heart health and assessment of any potential complications related to the stent.
Awareness of Symptoms: Patients should be aware of symptoms that may indicate complications related to their stent, such as chest pain or shortness of breath, and seek medical attention promptly if they occur.
Stent Identification Card: Carrying a card that identifies that a patient has a heart stent is important for emergency situations where medical personnel need this information quickly.
Conclusion
Heart stents are designed to be permanent solutions for treating coronary artery disease by keeping arteries open and ensuring adequate blood flow to the heart. While they can last indefinitely when properly managed, several factors influence their longevity and effectiveness over time.
Patients play an active role in extending the life of their heart stents through lifestyle changes, adherence to medication regimens, and regular follow-ups with healthcare providers. By understanding these factors and taking proactive steps towards maintaining cardiovascular health, patients can optimize their outcomes after receiving a heart stent.
Related topics:
- How Long A Person Can Live After Angioplasty?
- How Long Can You Live with Left Ventricular Hypertrophy?
- How Long Can You Live with A Leaky Aortic Valve?