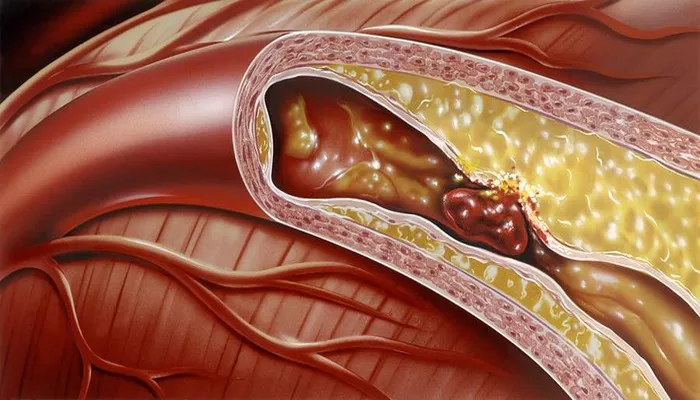
Partial blockage of the heart artery is a serious condition that can lead to significant health issues. This article discusses the symptoms associated with this condition, providing a detailed understanding of what individuals may experience.
Recognizing these symptoms early can be crucial for timely medical intervention.
Introduction
The heart is a vital organ responsible for pumping blood throughout the body. It relies on a network of arteries to supply oxygen-rich blood to its tissues. When these arteries become partially blocked, the flow of blood is reduced. This condition often results from a buildup of plaque, which consists of fats, cholesterol, and other substances. Over time, this buildup can narrow the arteries, leading to coronary artery disease (CAD).
While some individuals with partial blockage may not experience noticeable symptoms, many do. Understanding these symptoms is essential for early detection and treatment. This article will explore the various symptoms associated with partial blockage of the heart artery in detail.
Understanding Partial Blockage
Partial blockage occurs when an artery supplying blood to the heart is narrowed but not completely obstructed. This can happen gradually over time due to atherosclerosis, a process where plaque builds up in the arterial walls. Factors contributing to this condition include high cholesterol, high blood pressure, smoking, diabetes, and a sedentary lifestyle.
As the blockage worsens, the heart may struggle to receive enough blood, especially during physical activity or stress. This can lead to various symptoms that indicate the heart is not getting the oxygen it needs.
Common Symptoms of Partial Blockage
Individuals with partial blockage of the heart artery may experience a range of symptoms. These symptoms can vary in severity and frequency based on the extent of the blockage and individual health conditions. Here are some common symptoms associated with this condition:
1. Chest Pain or Discomfort (Angina)
Chest pain or discomfort is one of the most common symptoms of partial blockage. This pain may feel like:
- A squeezing sensation
- Pressure or tightness
- A burning feeling
Angina typically occurs during physical exertion or emotional stress when the heart demands more oxygen than usual. It may subside with rest or medication.
2. Shortness of Breath
Shortness of breath can occur during physical activity or even at rest in some cases. Individuals may feel as though they cannot catch their breath or may experience difficulty breathing deeply. This symptom often accompanies chest pain and indicates that the heart is struggling to pump enough blood.
3. Fatigue
Unexplained fatigue is another symptom that individuals with partial blockage might notice. People may feel unusually tired even after minimal activity. This fatigue can result from reduced blood flow and oxygen delivery to muscles and tissues.
4. Dizziness or Lightheadedness
Dizziness or lightheadedness can occur due to insufficient blood flow to the brain. Individuals may feel faint or unsteady, especially when standing up quickly or engaging in physical activity.
5. Heart Palpitations
Some individuals may experience heart palpitations, which are sensations of an irregular heartbeat or a racing heart. These palpitations can be alarming and may occur during periods of stress or physical exertion.
6. Nausea
Nausea is less common but can occur in individuals experiencing chest pain or discomfort. Some people may also experience gastrointestinal symptoms such as indigestion or bloating alongside other cardiovascular symptoms.
7. Sweating
Excessive sweating, particularly cold sweats, can be a sign that something is wrong with the heart. This symptom often accompanies chest pain and indicates that the body is under stress.
8. Pain in Other Areas
Pain from partial blockage may radiate beyond the chest area. Individuals might experience discomfort in:
- The arms (especially the left arm)
- Shoulders
- Neck
- Jaw
- Back
This referred pain can often be mistaken for other conditions but should always be evaluated by a healthcare professional.
Severity of Symptoms
The severity and frequency of these symptoms can vary widely among individuals with partial blockage of the heart artery:
Mild Blockage: Some people may have mild blockages without any noticeable symptoms until they engage in strenuous activities.
Moderate Blockage: Individuals with moderate blockages may experience angina during exercise or emotional stress but find relief with rest.
Severe Blockage: Severe blockages can lead to frequent angina episodes and more pronounced symptoms like shortness of breath and fatigue even at rest.
When to Seek Medical Attention
It is crucial for individuals experiencing any combination of these symptoms to seek medical attention promptly. Early diagnosis and treatment can prevent further complications, including complete blockage and potentially life-threatening conditions such as heart attacks.
If you experience:
Severe chest pain lasting more than a few minutes
Shortness of breath that worsens
Dizziness accompanied by chest discomfort
Any sudden changes in your usual health status
You should seek emergency medical care immediately.
Diagnosis of Partial Blockage
Healthcare providers use various methods to diagnose partial blockage of coronary arteries:
Medical History: A thorough review of your medical history and symptom description.
Physical Examination: A healthcare provider will check for signs such as high blood pressure or abnormal heart sounds.
Electrocardiogram (ECG): This test measures electrical activity in your heart and helps identify irregularities.
Stress Testing: Patients exercise on a treadmill while monitoring their heart’s response.
Imaging Tests: Tests such as echocardiograms, CT scans, or angiograms help visualize blood flow through the coronary arteries.
Treatment Options
Treatment for partial blockage focuses on improving blood flow and reducing risk factors for further artery damage:
Lifestyle Changes: Adopting a heart-healthy diet, engaging in regular exercise, quitting smoking, and managing stress are crucial steps.
Medications: Doctors often prescribe medications to manage cholesterol levels, reduce blood pressure, and prevent blood clots.
Surgical Interventions: In severe cases, procedures like angioplasty (widening narrowed arteries) or coronary artery bypass grafting (CABG) may be necessary.
Conclusion
Partial blockage of the heart artery is a significant health concern that can lead to serious complications if left untreated.
Recognizing the symptoms early—such as chest pain, shortness of breath, fatigue, dizziness, and others—can facilitate timely medical intervention and improve outcomes for affected individuals.
Related topics:
- How Long to Cardiac Stents Last?
- How Long A Person Can Live After Angioplasty?
- How Long Can You Live with Left Ventricular Hypertrophy?