Heart failure (HF) is a chronic condition where the heart is unable to pump blood efficiently to meet the body’s needs. This can lead to symptoms like shortness of breath, fatigue, swelling in the legs, and difficulty performing physical activities.
Heart failure can occur due to various causes such as coronary artery disease, high blood pressure, or heart muscle damage.
The management of heart failure typically involves medications, lifestyle changes, and sometimes surgical procedures.
Medications are central to controlling symptoms, preventing disease progression, and improving the quality of life for patients. One class of medication that plays a significant role in heart failure management is beta-blockers, specifically metoprolol succinate.
What Is Metoprolol Succinate?
Metoprolol succinate is a long-acting form of metoprolol, a beta-blocker used to manage various cardiovascular conditions.
Unlike other medications that provide short-term effects, metoprolol succinate releases the drug slowly over time, ensuring continuous blood pressure control and heart rate management.
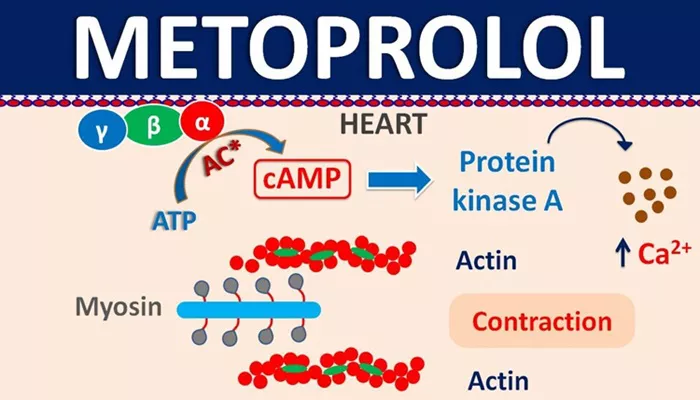
Beta-blockers, like metoprolol succinate, work by blocking the effects of adrenaline on the heart’s beta receptors.
Adrenaline typically increases the heart rate and force of contraction, which can be harmful in conditions like heart failure.
By reducing the heart rate and the force of contraction, metoprolol succinate helps the heart pump more efficiently and reduces the workload on the heart.
Why Is Metoprolol Succinate Important in Heart Failure?
Metoprolol succinate is often prescribed for patients with heart failure because it helps manage the condition in several ways. The benefits of this medication have been well documented, particularly in patients with heart failure with reduced ejection fraction (HFrEF), which is a type of heart failure where the heart’s ability to pump blood is significantly impaired.
Improving Heart Function
In heart failure, the heart’s pumping capacity decreases, leading to less efficient blood circulation. Metoprolol succinate works by slowing the heart rate and reducing the heart’s workload. By doing so, it gives the heart more time to fill with blood before pumping it out. This helps improve the overall efficiency of the heart and allows it to pump more effectively.
Over time, this can improve the ejection fraction, which is the percentage of blood the heart pumps out with each beat.
Reducing the Risk of Heart Arrhythmias
One of the key issues in heart failure is the development of irregular heart rhythms, or arrhythmias. These arrhythmias can further worsen heart function and increase the risk of sudden cardiac arrest. Metoprolol succinate reduces the heart rate and stabilizes the electrical activity of the heart, making arrhythmias less likely. This is especially important in heart failure patients, who are at a higher risk of these life-threatening conditions.
Reducing Mortality in Heart Failure Patients
Numerous clinical studies have shown that beta-blockers like metoprolol succinate can significantly reduce the mortality rate in heart failure patients. The benefit is primarily due to the medication’s ability to improve heart function, reduce arrhythmias, and decrease the risk of hospitalization for heart failure exacerbations. In fact, metoprolol succinate is considered one of the cornerstone therapies for heart failure with reduced ejection fraction, alongside other medications like ACE inhibitors and diuretics.
Preventing Hospitalization and Disease Progression
One of the main goals in managing heart failure is preventing hospitalizations and slowing the progression of the disease.
Metoprolol succinate has been shown to reduce the frequency of hospitalizations for heart failure-related issues. By improving heart function and reducing symptoms, it helps keep patients stable and reduces the likelihood of requiring emergency care. This leads to better long-term outcomes and an improved quality of life for patients.
Symptom Control
Heart failure symptoms, including fatigue, shortness of breath, and fluid retention, can significantly impact a patient’s quality of life.
Metoprolol succinate can help control these symptoms by improving the heart’s pumping ability and reducing fluid buildup.
By decreasing the workload on the heart and improving circulation, it can help alleviate some of the physical strain that patients with heart failure experience. This improvement in symptoms can make daily activities easier and less exhausting.
How Does Metoprolol Succinate Compare to Other Beta-Blockers?
While there are several types of beta-blockers available, metoprolol succinate is often preferred for heart failure due to its long-acting formulation. The extended-release nature of metoprolol succinate ensures that patients receive consistent medication effects throughout the day, reducing the need for frequent dosing.
In comparison to other beta-blockers, metoprolol succinate has been found to have specific benefits in heart failure management. For instance, it is generally better tolerated by patients with heart failure, especially those who may be more sensitive to other forms of beta-blockers. Its proven ability to improve ejection fraction and reduce mortality makes it a first-line choice in the management of heart failure with reduced ejection fraction.
How Is Metoprolol Succinate Administered?
Metoprolol succinate is typically administered in oral form, taken once a day. The dosage may vary depending on the patient’s specific condition, response to treatment, and the severity of their heart failure. Initially, a lower dose may be prescribed, with gradual adjustments made over time to ensure the medication is effective while minimizing side effects.
It is essential for patients to take metoprolol succinate exactly as prescribed by their healthcare provider. Missing doses or abruptly stopping the medication can lead to worsening heart failure symptoms and other complications. Patients should also be monitored regularly by their doctor to track their progress and adjust the treatment as needed.
Possible Side Effects of Metoprolol Succinate
Like any medication, metoprolol succinate can cause side effects. Common side effects include fatigue, dizziness, and a slow heart rate. These side effects are usually mild and may decrease over time as the body adjusts to the medication.
In some cases, patients may experience more serious side effects, such as shortness of breath, swelling of the feet or ankles, or severe dizziness. These side effects should be reported to a healthcare provider immediately.
Patients with asthma, certain heart conditions, or low blood pressure should inform their doctor before starting metoprolol succinate, as it may not be suitable for them.
Conclusion
Metoprolol succinate is a key medication in the management of heart failure, particularly for patients with reduced ejection fraction. Its benefits, such as improving heart function, reducing the risk of arrhythmias, and lowering mortality rates, make it an essential part of heart failure treatment. By improving symptoms and preventing hospitalizations, metoprolol succinate helps enhance the quality of life for patients living with heart failure. As with any medication, it is crucial for patients to follow their doctor’s instructions and report any side effects to ensure the best possible outcomes.
Related topics: