As individuals age, monitoring and understanding blood pressure becomes increasingly crucial. Blood pressure is a key indicator of cardiovascular health and can significantly impact overall well-being, particularly in seniors. In this article, we delve into the concept of normal blood pressure for seniors, exploring what it means, how it is measured, factors influencing it, and why maintaining healthy blood pressure levels is essential for older adults.
What Is Blood Pressure?
Blood pressure refers to the force of blood pushing against the walls of the arteries as the heart pumps it around the body. It is typically measured in millimeters of mercury (mm Hg) and recorded as two numbers:
1. Systolic Pressure: The top number represents systolic pressure, which is the pressure in the arteries when the heart beats and pumps blood out.
2. Diastolic Pressure: The bottom number represents diastolic pressure, which is the pressure in the arteries when the heart rests between beats.
For example, a blood pressure reading of 120/80 mm Hg indicates a systolic pressure of 120 mm Hg and a diastolic pressure of 80 mm Hg.
Normal Blood Pressure for Seniors
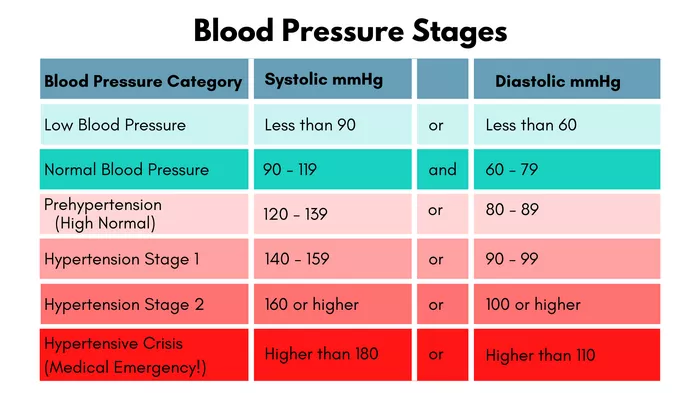
The definition of normal blood pressure can vary slightly depending on the source, but generally, it is categorized into the following ranges:
1. Normal: Systolic less than 120 mm Hg and diastolic less than 80 mm Hg.
2. Elevated: Systolic between 120-129 mm Hg and diastolic less than 80 mm Hg.
3. Stage 1 Hypertension: Systolic between 130-139 mm Hg or diastolic between 80-89 mm Hg.
4. Stage 2 Hypertension: Systolic 140 mm Hg or higher or diastolic 90 mm Hg or higher.
5. Hypertensive Crisis: Systolic over 180 mm Hg and/or diastolic over 120 mm Hg.
These categories are based on guidelines from organizations such as the American Heart Association (AHA) and the National Institutes of Health (NIH). However, for seniors, especially those over 65, the interpretation of normal blood pressure can be more nuanced.
Understanding Blood Pressure Changes with Age
Blood pressure tends to increase with age due to changes in blood vessels, heart function, and other physiological factors. It is not uncommon for older adults to have slightly higher blood pressure readings compared to younger individuals. However, there is a distinction between normal age-related changes and hypertension, which requires medical attention and management.
The following are some key points to consider regarding blood pressure changes in seniors:
1. Arterial Stiffness: As people age, their arteries may become stiffer, leading to increased systolic blood pressure.
2. Atherosclerosis: The buildup of plaque in the arteries can contribute to higher blood pressure.
3. Reduced Elasticity: Blood vessels may lose some of their elasticity over time, affecting blood pressure regulation.
4. Heart Changes: Age-related changes in the heart, such as thickening of the heart muscle, can influence blood pressure levels.
5. Other Health Conditions: Chronic conditions like diabetes, kidney disease, and obesity can also impact blood pressure in seniors.
Factors Affecting Blood Pressure Readings
Several factors can influence blood pressure readings, and understanding these variables is essential for accurately assessing an individual’s cardiovascular health. Some of the key factors affecting blood pressure measurements include:
1. Physical Activity: Regular exercise can help maintain healthy blood pressure levels.
2. Dietary Habits: A diet high in sodium, saturated fats, and processed foods can contribute to hypertension.
3. Weight: Being overweight or obese can increase the risk of high blood pressure.
4. Smoking and Alcohol: Tobacco use and excessive alcohol consumption can elevate blood pressure.
5. Stress Levels: Chronic stress can impact blood pressure over time.
6. Medications: Certain medications, such as decongestants and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), can affect blood pressure.
7. Sleep Quality: Poor sleep patterns and sleep disorders may influence blood pressure readings.
Healthcare providers consider these factors when evaluating blood pressure readings and determining the appropriate management approach for seniors.
Importance of Maintaining Normal Blood Pressure
Maintaining normal blood pressure levels is crucial for seniors due to its significant impact on overall health and well-being. Here are some reasons why healthy blood pressure is essential:
1. Reduced Risk of Cardiovascular Disease: High blood pressure is a major risk factor for heart disease, stroke, and other cardiovascular conditions. Keeping blood pressure within normal ranges helps reduce these risks.
2. Preservation of Organ Health: Normal blood pressure supports the health of vital organs such as the heart, kidneys, and brain.
3. Prevention of Complications: Lowering blood pressure can help prevent complications such as heart attacks, strokes, kidney disease, and vision problems.
4. Improved Quality of Life: Maintaining healthy blood pressure levels contributes to better overall quality of life, including increased energy, better cognitive function, and enhanced mobility.
Monitoring and Managing Blood Pressure in Seniors
Regular monitoring of blood pressure is essential for seniors to detect any abnormalities early and take appropriate actions. Healthcare providers may recommend the following strategies for monitoring and managing blood pressure in older adults:
1. Home Blood Pressure Monitoring: Seniors can use home blood pressure monitors to track their blood pressure regularly and share the readings with their healthcare team.
2. Medication Management: If prescribed, taking blood pressure medications as directed is crucial for controlling hypertension.
3. Lifestyle Modifications: Adopting a healthy lifestyle, including a balanced diet, regular exercise, stress management techniques, and avoiding tobacco and excessive alcohol, can help lower blood pressure naturally.
4. Regular Medical Checkups: Seniors should schedule regular checkups with their healthcare provider to monitor blood pressure, assess overall health, and make any necessary adjustments to their treatment plan.
5. Education and Support: Providing seniors with education about blood pressure management and offering support in making lifestyle changes can improve outcomes.
Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding normal blood pressure levels for seniors is essential for promoting healthy aging and reducing the risk of cardiovascular complications. While blood pressure naturally tends to rise with age, maintaining it within normal ranges through lifestyle modifications, regular monitoring, and appropriate medical interventions can significantly improve seniors’ quality of life and longevity. Healthcare providers play a vital role in educating seniors about blood pressure management and providing personalized care to optimize their cardiovascular health.