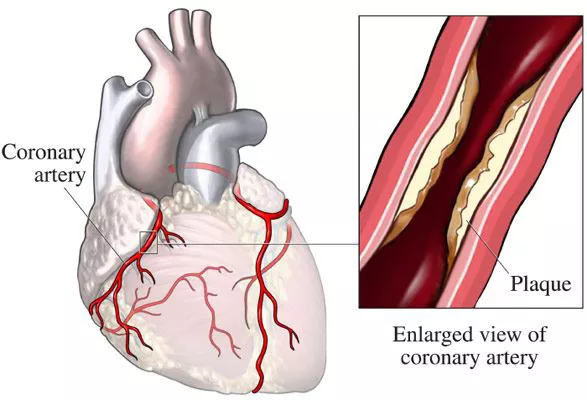
Coronary heart disease (CHD) is a leading cause of death globally. It occurs when the coronary arteries, which supply blood to the heart muscle, become narrowed or blocked due to the buildup of plaque—a combination of fat, cholesterol, and other substances. This condition can lead to angina (chest pain), heart attacks, and other serious cardiovascular events. While genetics and other factors play a role in the development of CHD, diet is a critical modifiable risk factor that significantly influences heart health. This article explores how various dietary patterns and specific foods affect coronary heart disease.
The Role of Diet in Coronary Heart Disease
Saturated and Trans Fats
Saturated and trans fats are well-known contributors to the development of coronary heart disease. These fats raise low-density lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol levels in the blood, leading to plaque buildup in the arteries. Common sources of saturated fats include:
- Red meat
- Full-fat dairy products
- Butter
- Palm and coconut oils
Trans fats, often found in partially hydrogenated oils, are present in many processed and fried foods, such as:
- Commercially baked goods (cookies, cakes, pastries)
- Fried fast foods
- Margarine
Impact on Heart Health: High intake of saturated and trans fats increases the risk of developing atherosclerosis (hardening and narrowing of the arteries), thereby elevating the risk of CHD. Reducing consumption of these fats and replacing them with healthier fats can help improve cholesterol levels and reduce heart disease risk.
see also: What Fruits Can A Heart Patient Eat
Unsaturated Fats
Unsaturated fats, including monounsaturated and polyunsaturated fats, are beneficial for heart health. They can help reduce LDL cholesterol levels and increase high-density lipoprotein (HDL) cholesterol levels, which protect against heart disease. Sources of unsaturated fats include:
- Olive oil
- Avocado
- Nuts and seeds
- Fatty fish (such as salmon, mackerel, and sardines)
- Vegetable oils (such as canola, sunflower, and safflower oils)
Impact on Heart Health: Replacing saturated and trans fats with unsaturated fats can significantly lower the risk of CHD.
For example, the Mediterranean diet, which is rich in unsaturated fats from olive oil, nuts, and fish, has been associated with a reduced incidence of heart disease.
Dietary Cholesterol
For many years, dietary cholesterol was believed to be a major contributor to high blood cholesterol levels and CHD.
However, recent research suggests that for most people, dietary cholesterol has a smaller impact on blood cholesterol than previously thought. Foods high in dietary cholesterol include:
- Egg yolks
- Shellfish (such as shrimp and lobster)
- Organ meats (such as liver)
Impact on Heart Health: While moderate consumption of cholesterol-rich foods may not significantly affect heart disease risk for most people, those with certain conditions, such as familial hypercholesterolemia, may need to limit their intake. It is more important to focus on the overall quality of the diet rather than just cholesterol content.
Fiber-Rich Foods
Dietary fiber, particularly soluble fiber, can help lower cholesterol levels and reduce the risk of CHD. Soluble fiber binds to cholesterol in the digestive system and helps remove it from the body. High-fiber foods include:
- Oats and barley
- Fruits (such as apples, oranges, and berries)
- Vegetables (such as carrots, broccoli, and Brussels sprouts)
- Legumes (such as beans, lentils, and peas)
- Whole grains
Impact on Heart Health: A diet rich in fiber can help lower LDL cholesterol levels and improve overall heart health. Studies have shown that individuals who consume high amounts of fiber have a lower risk of developing CHD.
Sugar and Refined Carbohydrates
High consumption of sugar and refined carbohydrates can lead to weight gain, increased triglyceride levels, and higher blood pressure—all risk factors for CHD. Foods high in sugar and refined carbs include:
Sugary beverages (such as soda and sweetened coffee drinks)
Candy and sweets
White bread and pastries
Processed snack foods
Impact on Heart Health: Diets high in sugar and refined carbohydrates can contribute to insulin resistance, obesity, and metabolic syndrome, all of which increase the risk of CHD. Reducing intake of these foods and choosing whole grains and complex carbohydrates can help mitigate these risks.
Sodium
Excessive sodium intake is linked to high blood pressure (hypertension), a major risk factor for CHD. High-sodium foods include:
Processed and packaged foods
Canned soups and vegetables
Deli meats
Fast foods
Salty snacks
Impact on Heart Health: Reducing sodium intake can help lower blood pressure and reduce the risk of CHD. The American Heart Association recommends limiting sodium intake to no more than 2,300 milligrams per day, with an ideal limit of 1,500 milligrams for most adults.
Antioxidant-Rich Foods
Antioxidants, found in a variety of fruits and vegetables, help protect the body from oxidative stress and inflammation, both of which are implicated in the development of CHD. Key antioxidant-rich foods include:
- Berries (such as blueberries, strawberries, and raspberries)
- Leafy greens (such as spinach and kale)
- Nuts and seeds
- Dark chocolate (in moderation)
- Green tea
Impact on Heart Health: Consuming a diet rich in antioxidants can help reduce inflammation and protect against the oxidative damage that contributes to plaque formation in the arteries. This can lower the risk of CHD.
Plant-Based Diets
Plant-based diets, which emphasize fruits, vegetables, whole grains, legumes, nuts, and seeds, are associated with numerous health benefits, including a reduced risk of CHD. These diets are typically low in saturated fats and high in fiber, antioxidants, and healthy fats.
Impact on Heart Health: Studies have shown that plant-based diets can help lower cholesterol levels, reduce blood pressure, and improve overall heart health. For example, the DASH (Dietary Approaches to Stop Hypertension) diet, which is rich in fruits, vegetables, and low-fat dairy, has been shown to reduce blood pressure and lower the risk of CHD.
Alcohol
Moderate alcohol consumption has been linked to a reduced risk of CHD, potentially due to its effects on raising HDL cholesterol levels and providing antioxidants (such as resveratrol in red wine). However, excessive alcohol intake can lead to high blood pressure, obesity, and other health issues.
Impact on Heart Health: While moderate alcohol consumption (one drink per day for women and up to two drinks per day for men) may have some protective effects, it is not recommended to start drinking alcohol for heart health benefits due to the potential risks associated with excessive consumption.
The Mediterranean Diet
The Mediterranean diet is often cited as one of the healthiest dietary patterns for heart health. It emphasizes:
High consumption of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and legumes
Healthy fats from olive oil and nuts
Moderate consumption of fish and poultry
Low intake of red meat and processed foods
Moderate consumption of red wine
Impact on Heart Health: Numerous studies have shown that the Mediterranean diet is associated with a lower risk of CHD, improved cholesterol levels, and reduced inflammation. This diet’s emphasis on healthy fats, fiber, and antioxidants contributes to its cardiovascular benefits.
The DASH Diet
The DASH diet is designed to combat hypertension and promote heart health. It focuses on:
- High intake of fruits, vegetables, and whole grains
- Low-fat dairy products
- Lean proteins (such as fish, poultry, and legumes)
- Limited intake of saturated fats, red meat, and sweets
- Reduced sodium intake
Impact on Heart Health: The DASH diet has been shown to lower blood pressure, improve cholesterol levels, and reduce the risk of CHD. Its emphasis on nutrient-dense foods and low sodium intake makes it an effective dietary approach for heart health.
Conclusion
Diet plays a crucial role in the prevention and management of coronary heart disease. Consuming a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, healthy fats, and lean proteins while limiting saturated and trans fats, sugar, refined carbohydrates, and sodium can significantly reduce the risk of CHD. Adopting dietary patterns such as the Mediterranean diet or the DASH diet can further enhance heart health. By making informed dietary choices, individuals can take proactive steps to protect their heart and overall well-being.