Heart valve replacement is a critical surgical procedure aimed at treating various heart valve diseases, including stenosis and regurgitation. Despite the advancements in surgical techniques and prosthetic materials, heart valve replacement failure can still occur. Recognizing the signs of valve failure early is essential for timely intervention and management. This article explores the key signs of heart valve replacement failure, providing insights for both medical professionals and patients.
Introduction to Heart Valve Replacement
Heart valves play a crucial role in maintaining unidirectional blood flow through the heart. When these valves become diseased or damaged, they can significantly impair cardiac function and lead to severe health consequences. Valve replacement surgery involves substituting the faulty valve with a mechanical or bioprosthetic valve. While this procedure can restore normal cardiac function, it is not without risks. Valve replacement failure can result from various factors, including valve degeneration, thrombosis, infection, or structural issues.
see also: What Are The Treatments for Low Ejection Fraction?
Types of Heart Valve Replacement Failures
Before delving into the specific signs of valve replacement failure, it is important to understand the different types of failures that can occur:
Structural Valve Deterioration (SVD): This involves the degeneration of the valve material, leading to tears, calcification, or other structural issues that impede valve function.
Non-Structural Dysfunction: This includes issues such as valve malposition, paravalvular leak (leakage around the valve), and other problems not related to the valve material itself.
Thrombosis: The formation of blood clots on or around the valve, which can obstruct blood flow and impair valve function.
Endocarditis: Infection of the valve, which can lead to valve destruction and failure.
Hemolysis: Destruction of red blood cells due to abnormal shear forces across the valve, leading to anemia and other complications.
Common Signs of Heart Valve Replacement Failure
1. Shortness of Breath
One of the earliest and most common signs of heart valve replacement failure is shortness of breath, or dyspnea. This symptom may occur during physical activity or even at rest, depending on the severity of the valve dysfunction. It results from the heart’s inability to efficiently pump blood, leading to pulmonary congestion and reduced oxygen delivery to tissues.
2. Fatigue and Weakness
Patients experiencing heart valve replacement failure often report a marked decrease in energy levels. Fatigue and general weakness can be attributed to the heart’s reduced capacity to maintain adequate circulation, thereby compromising the delivery of oxygen and nutrients to the body’s tissues.
3. Swelling (Edema)
Edema, or swelling, particularly in the lower extremities (legs, ankles, and feet), can indicate heart valve replacement failure. This occurs due to the accumulation of fluid in the tissues, resulting from increased pressure in the veins and capillaries as the heart struggles to maintain efficient blood flow.
4. Palpitations
Patients may experience palpitations, or the sensation of an irregular or rapid heartbeat. This can be a sign of valve dysfunction, as the heart may develop arrhythmias in response to the altered hemodynamics caused by the failing valve.
5. Chest Pain or Discomfort
Chest pain or discomfort, also known as angina, can occur in cases of heart valve replacement failure. This symptom is typically due to increased strain on the heart muscle as it attempts to compensate for the defective valve. It may also result from inadequate blood flow to the coronary arteries.
6. Heart Murmurs
A new or changing heart murmur detected during a physical examination can be indicative of valve replacement failure.
Heart murmurs are sounds produced by turbulent blood flow through a malfunctioning valve. These sounds can provide clues about the nature and severity of the valve dysfunction.
7. Syncope (Fainting)
Syncope, or fainting, can be a serious sign of heart valve replacement failure. It may occur due to a sudden drop in blood pressure or inadequate blood flow to the brain, often as a result of severe valve dysfunction or associated arrhythmias.
8. Weight Gain
Unexpected weight gain, particularly due to fluid retention, can be a sign of heart valve replacement failure. This is often accompanied by swelling and may indicate worsening heart failure symptoms.
9. Coughing and Wheezing
Persistent coughing or wheezing, especially when lying down, can suggest pulmonary congestion due to heart valve replacement failure.
This occurs as fluid accumulates in the lungs, leading to respiratory symptoms.
Specific Signs Based on Valve Type
The signs of heart valve replacement failure can also vary depending on the type of valve (mechanical or bioprosthetic) and the location of the valve (aortic, mitral, tricuspid, or pulmonary).
Aortic Valve Replacement Failure
Severe Aortic Regurgitation: If the aortic valve replacement fails, it can lead to severe aortic regurgitation, where blood leaks back into the left ventricle. This can cause symptoms such as shortness of breath, fatigue, and chest pain.
Aortic Stenosis Recurrence: Recurrence of aortic stenosis, characterized by narrowing of the valve opening, can lead to symptoms like chest pain, syncope, and heart failure.
Mitral Valve Replacement Failure
Mitral Regurgitation: Failure of the mitral valve replacement can result in mitral regurgitation, where blood flows backward into the left atrium.
Symptoms include shortness of breath, palpitations, and edema.
Mitral Stenosis: Recurrence of mitral stenosis can cause symptoms such as fatigue, shortness of breath, and palpitations.
Tricuspid Valve Replacement Failure
Tricuspid Regurgitation: If the tricuspid valve replacement fails, it can lead to tricuspid regurgitation, causing symptoms like swelling, fatigue, and abdominal discomfort due to liver congestion.
Tricuspid Stenosis: Recurrence of tricuspid stenosis can result in symptoms such as swelling, fatigue, and jugular venous distention.
Pulmonary Valve Replacement Failure
Pulmonary Regurgitation: Failure of the pulmonary valve replacement can cause pulmonary regurgitation, leading to symptoms like shortness of breath, fatigue, and right-sided heart failure.
Pulmonary Stenosis: Recurrence of pulmonary stenosis can result in symptoms such as shortness of breath, fatigue, and chest pain.
Diagnostic Approaches
Identifying the signs of heart valve replacement failure requires a comprehensive approach, including a thorough clinical evaluation and diagnostic testing. Key diagnostic tools include:
Echocardiography: This imaging technique uses ultrasound waves to visualize the heart valves and assess their function. It can detect structural abnormalities, valve leaks, and measure the pressure gradients across the valves.
Cardiac Catheterization: This invasive procedure provides detailed information about the heart’s hemodynamics and can help identify valve dysfunction, especially in complex cases.
Chest X-ray: This imaging modality can reveal signs of heart enlargement, pulmonary congestion, and other complications associated with valve failure.
Electrocardiogram (ECG): An ECG can detect arrhythmias, heart block, and other electrical abnormalities that may accompany valve replacement failure.
Blood Tests: Biomarkers such as B-type natriuretic peptide (BNP) can help assess heart failure severity and monitor the response to treatment.
Management And Treatment
The management of heart valve replacement failure depends on the underlying cause and severity of the dysfunction.
Treatment options include:
Medical Management: Medications such as diuretics, beta-blockers, and anticoagulants can help manage symptoms and prevent complications.
Valve Repair or Replacement: In cases of significant valve dysfunction, repeat surgery may be necessary to repair or replace the failing valve.
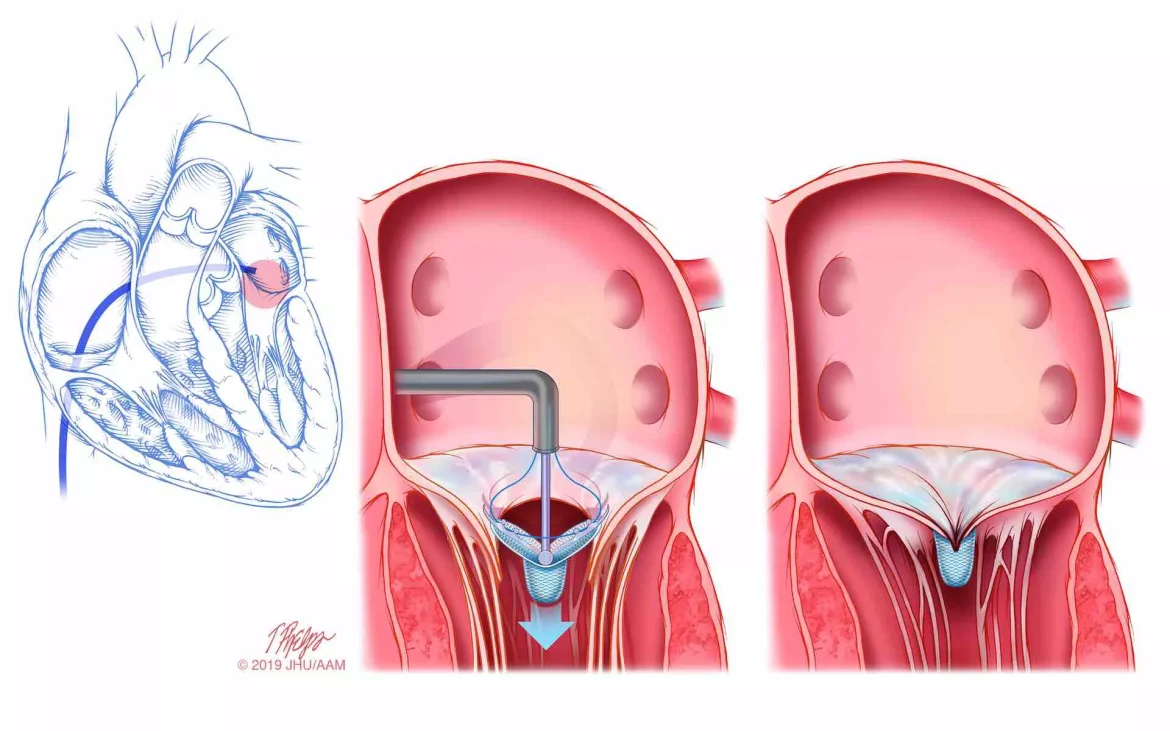
Interventional Procedures: Minimally invasive procedures, such as transcatheter valve replacement, can be considered for high-risk patients.
Conclusion
Heart valve replacement failure is a serious complication that requires prompt recognition and management. By understanding the signs of valve failure, healthcare providers can ensure timely intervention and improve patient outcomes. Patients with valve replacements should be vigilant about monitoring their symptoms and seeking medical attention if they experience any signs of valve dysfunction. With advancements in diagnostic and therapeutic techniques, the prognosis for patients with heart valve replacement failure continues to improve.