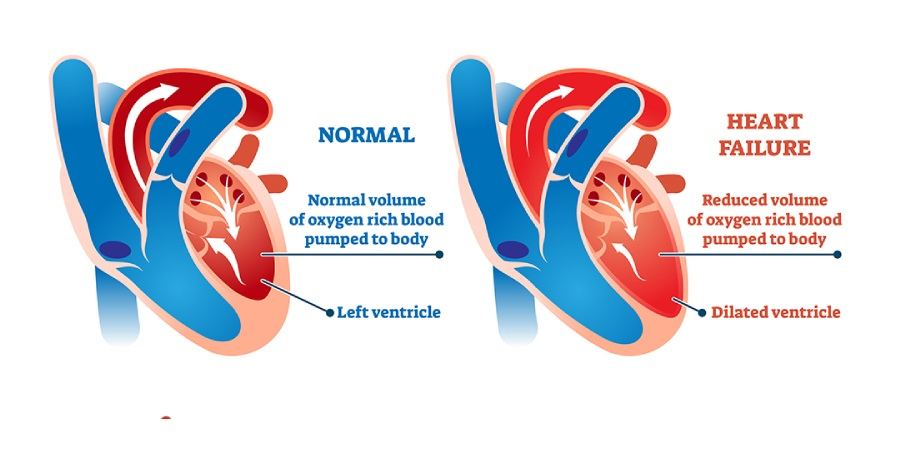
The right ventricle plays a crucial role in the heart’s function by pumping deoxygenated blood to the lungs for oxygenation.
When the right ventricle fails, it can lead to significant health issues and complications. This article will explore the causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment of right ventricular failure, providing a comprehensive understanding of this condition.
The Function of The Right Ventricle
The heart is divided into four chambers: the left atrium, left ventricle, right atrium, and right ventricle. Each chamber has a specific role in ensuring blood circulates efficiently throughout the body. The right ventricle receives deoxygenated blood from the right atrium and pumps it into the pulmonary arteries, leading to the lungs. In the lungs, the blood receives oxygen and releases carbon dioxide. This oxygen-rich blood then returns to the left atrium, ready to be pumped to the rest of the body by the left ventricle.
SEE ALSO: What Is Ventricular Systolic Dysfunction
Causes of Right Ventricular Failure
Right ventricular failure, also known as right-sided heart failure, can be caused by various conditions that put excessive strain on the right ventricle or impede its function. Some common causes include:
1. Left-Sided Heart Failure
Left-sided heart failure is one of the most common causes of right ventricular failure. When the left ventricle fails, it leads to an accumulation of blood in the lungs, increasing the pressure in the pulmonary circulation. This increased pressure puts a strain on the right ventricle, eventually leading to its failure.
2. Pulmonary Hypertension
Pulmonary hypertension is a condition characterized by high blood pressure in the pulmonary arteries. It can result from chronic lung diseases, such as chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) or interstitial lung disease, or it can be idiopathic. The increased pressure in the pulmonary arteries forces the right ventricle to work harder to pump blood, which can cause it to fail over time.
3. Myocardial Infarction
A myocardial infarction, commonly known as a heart attack, occurs when the blood flow to a part of the heart muscle is blocked, causing tissue damage. If the right coronary artery, which supplies blood to the right ventricle, is affected, it can lead to right ventricular failure.
4. Congenital Heart Defects
Certain congenital heart defects, such as tetralogy of Fallot or tricuspid atresia, can cause right ventricular failure. These defects often involve abnormalities in the structure or function of the right ventricle, leading to its inadequate performance.
5. Cardiomyopathy
Cardiomyopathy is a group of diseases that affect the heart muscle, leading to its weakening or stiffening. Dilated cardiomyopathy, hypertrophic cardiomyopathy, and restrictive cardiomyopathy can all result in right ventricular failure if the right ventricle is significantly affected.
Symptoms of Right Ventricular Failure
The symptoms of right ventricular failure can vary depending on the severity of the condition and the underlying cause.
Some common symptoms include:
1. Edema
One of the hallmark symptoms of right ventricular failure is peripheral edema, which is the swelling of the legs, ankles, and feet. This occurs because the failing right ventricle is unable to effectively pump blood out of the heart, leading to a buildup of fluid in the body’s tissues.
2. Ascites
Ascites is the accumulation of fluid in the abdominal cavity. It can cause abdominal swelling and discomfort, and is often associated with advanced right ventricular failure.
3. Jugular Venous Distention
Jugular venous distention (JVD) is the visible swelling of the jugular veins in the neck. It occurs because the increased pressure in the right atrium is transmitted to the veins, causing them to become engorged.
4. Fatigue and Weakness
Patients with right ventricular failure often experience fatigue and weakness due to the decreased cardiac output and reduced oxygen delivery to the body’s tissues.
5. Shortness of Breath
Shortness of breath, or dyspnea, can occur in right ventricular failure, particularly if it is associated with left-sided heart failure or pulmonary hypertension. The buildup of fluid in the lungs and the increased pressure in the pulmonary circulation can make breathing difficult.
Treatment of Right Ventricular Failure
The treatment of right ventricular failure aims to address the underlying cause, relieve symptoms, and improve the patient’s quality of life. Treatment options may include:
1. Medications
Medications are often used to manage right ventricular failure. These may include:
Diuretics: Diuretics help reduce fluid buildup in the body by increasing urine output. This can help relieve symptoms such as edema and ascites.
ACE Inhibitors and ARBs: Angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors and angiotensin II receptor blockers (ARBs) help relax blood vessels and reduce the workload on the heart.
Beta-Blockers: Beta-blockers can help slow the heart rate and reduce blood pressure, improving the efficiency of the heart’s pumping action.
Pulmonary Vasodilators: In cases of pulmonary hypertension, medications such as sildenafil or bosentan can help relax the pulmonary arteries and reduce the pressure in the pulmonary circulation.
2. Lifestyle Modifications
Lifestyle modifications can play a significant role in managing right ventricular failure. Patients may be advised to:
Follow a Low-Sodium Diet: Reducing sodium intake can help prevent fluid retention and decrease the workload on the heart.
Limit Fluid Intake: Monitoring and limiting fluid intake can help prevent fluid overload and reduce symptoms.
Engage in Regular Physical Activity: Regular exercise, as recommended by a healthcare provider, can improve overall cardiovascular health and reduce symptoms of heart failure.
Avoid Alcohol and Tobacco: Alcohol and tobacco can worsen heart failure symptoms and should be avoided.
3. Surgical Interventions
In some cases, surgical interventions may be necessary to treat the underlying cause of right ventricular failure. These may include:
Heart Valve Surgery: If right ventricular failure is caused by a malfunctioning heart valve, surgery to repair or replace the valve may be required.
Coronary Artery Bypass Grafting (CABG): In cases of myocardial infarction affecting the right ventricle, CABG surgery can improve blood flow to the heart muscle.
Ventricular Assist Devices (VADs): VADs are mechanical devices that help the heart pump blood. They may be used as a temporary measure or as a long-term solution for patients with severe heart failure.
4. Heart Transplant
For patients with end-stage right ventricular failure who do not respond to other treatments, a heart transplant may be considered. A heart transplant involves replacing the failing heart with a healthy donor heart. This option is typically reserved for patients with severe symptoms and a poor prognosis.
Prognosis And Management
The prognosis for right ventricular failure varies depending on the underlying cause, the severity of the condition, and the patient’s overall health. With appropriate treatment and management, many patients can achieve significant symptom relief and an improved quality of life.
Ongoing monitoring and follow-up with a healthcare provider are essential to ensure optimal management of the condition.
1. Regular Follow-Up
Patients with right ventricular failure should have regular follow-up appointments with their healthcare provider to monitor their condition, adjust medications, and address any new or worsening symptoms.
2. Cardiac Rehabilitation
Cardiac rehabilitation programs can provide structured exercise, education, and support to help patients with right ventricular failure improve their cardiovascular health and manage their condition effectively.
3. Support Groups
Joining a support group for heart failure patients can provide emotional support, practical advice, and a sense of community for individuals living with right ventricular failure.
Conclusion
Right ventricular failure is a serious condition that can significantly impact a patient’s health and quality of life.
Understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options is essential for effective management. By addressing the underlying causes, making lifestyle modifications, and following medical advice, patients with right ventricular failure can achieve better symptom control and improve their overall well-being.