Hyperlipidemia, a condition characterized by abnormally elevated levels of lipids (fats) in the blood, is a significant risk factor for cardiovascular diseases, including stroke. Strokes occur when the blood supply to part of the brain is interrupted or reduced, preventing brain tissue from getting oxygen and nutrients. This can lead to brain cells dying within minutes. Among the numerous risk factors for stroke, hyperlipidemia stands out due to its direct impact on the vascular system. In this article, we will delve into the five primary ways hyperlipidemia can lead to stroke, providing a comprehensive understanding of the mechanisms involved and the importance of managing lipid levels to prevent this life-threatening event.
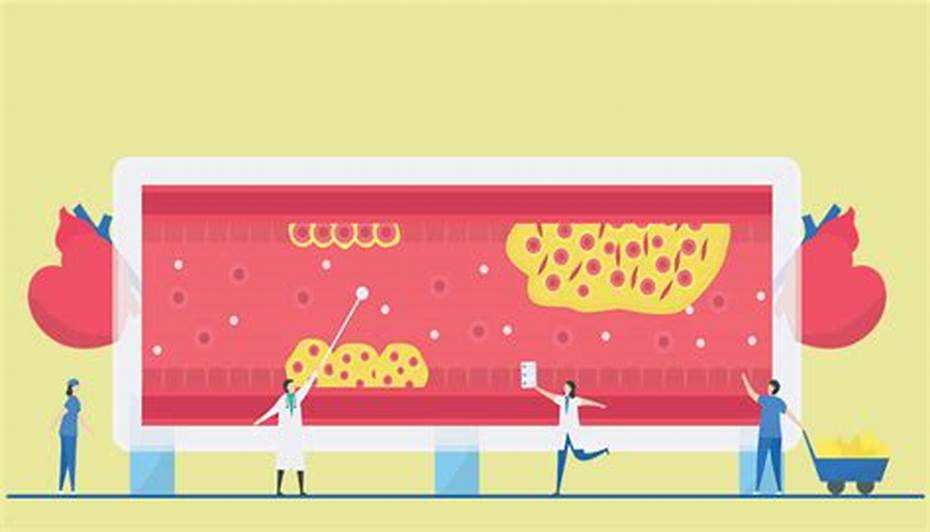
1. Atherosclerosis
How Atherosclerosis Develops
Atherosclerosis is a condition where plaques, composed of fat, cholesterol, calcium, and other substances, build up in the walls of arteries. This plaque formation is significantly influenced by high levels of low-density lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol and triglycerides, common in individuals with hyperlipidemia. Over time, these plaques harden and narrow the arteries, restricting blood flow to vital organs, including the brain.
SEE ALSO: When to Start Drug Therapy for Hyperlipidemia
The Connection to Stroke
When atherosclerosis affects the arteries supplying the brain, it can lead to ischemic strokes. These strokes occur when a blood clot forms on the plaque’s surface or when a piece of the plaque breaks off, traveling through the bloodstream and lodging in a smaller artery in the brain. This blockage disrupts the blood flow, causing an ischemic stroke.
Preventive Measures
Managing hyperlipidemia through lifestyle changes, such as adopting a heart-healthy diet, regular physical activity, and medications like statins, can significantly reduce the risk of atherosclerosis and subsequent stroke.
2. Thrombosis
Understanding Thrombosis
Thrombosis refers to the formation of a blood clot within a blood vessel. Hyperlipidemia contributes to thrombosis by increasing the concentration of lipids in the blood, which can cause the blood to become more viscous (thicker). This increased viscosity makes it easier for clots to form, especially in arteries already narrowed by atherosclerosis.
Thrombosis and Stroke Risk
When a blood clot forms in an artery leading to the brain (cerebral thrombosis), it can obstruct blood flow, causing an ischemic stroke.
Thrombosis is particularly dangerous because clots can form suddenly and without warning, leading to rapid and severe interruption of blood supply to the brain.
Preventive Measures
To reduce the risk of thrombosis, individuals with hyperlipidemia should focus on maintaining optimal lipid levels through diet, exercise, and medication. Anticoagulant or antiplatelet medications may also be prescribed to prevent clot formation.
3. Embolism
The Process of Embolism
An embolism occurs when a blood clot or other debris travels from one part of the body to another. In the context of hyperlipidemia, plaques or clots can dislodge from atherosclerotic sites in the arteries and travel through the bloodstream.
If these emboli reach the brain, they can cause an embolic stroke.
Hyperlipidemia and Embolic Stroke
Hyperlipidemia increases the likelihood of plaque formation and clotting, thereby raising the risk of embolism. An embolic stroke can occur suddenly and can be particularly severe, depending on the size and location of the blockage.
SEE ALSO: What Drugs Can Be Taken to Combat Hyperlipidemia
Preventive Measures
Controlling hyperlipidemia is crucial to prevent plaque formation and embolism. Regular monitoring of lipid levels, adherence to prescribed medications, and healthy lifestyle choices are essential strategies to minimize the risk of embolic stroke.
4. Small Vessel Disease
What is Small Vessel Disease?
Small vessel disease (SVD) affects the tiny arteries in the brain, causing them to become narrowed or blocked. This condition is often linked to chronic hyperlipidemia, which can damage the walls of these small arteries, leading to inflammation and scarring.
SVD and Stroke
SVD can lead to lacunar strokes, which are small, deep infarcts in the brain caused by the blockage of a single, small penetrating artery.
Although lacunar strokes are smaller than other types, they can accumulate over time, leading to significant neurological deficits and cognitive decline.
Preventive Measures
Effective management of hyperlipidemia through medication, diet, and exercise is vital to prevent SVD. Regular check-ups with a healthcare provider to monitor blood pressure and lipid levels can help in early detection and management of SVD.
5. Inflammation and Endothelial Dysfunction
The Role of Inflammation
Chronic hyperlipidemia can lead to systemic inflammation, which plays a crucial role in the development of atherosclerosis and other vascular conditions. High levels of LDL cholesterol can trigger an inflammatory response, damaging the endothelium, the inner lining of blood vessels.
Endothelial Dysfunction and Stroke
Endothelial dysfunction impairs the ability of blood vessels to dilate properly, increasing the risk of hypertension (high blood pressure) and promoting a pro-thrombotic state, where blood clots are more likely to form. Both hypertension and a pro-thrombotic state significantly elevate the risk of stroke.
Preventive Measures
Reducing inflammation through lifestyle changes and medications is essential for individuals with hyperlipidemia. Anti-inflammatory diets, rich in omega-3 fatty acids, antioxidants, and fiber, along with medications like statins, can help manage inflammation and endothelial dysfunction.
Conclusion
Hyperlipidemia is a major contributor to the development of stroke through various mechanisms, including atherosclerosis, thrombosis, embolism, small vessel disease, and inflammation-induced endothelial dysfunction. Understanding these pathways is crucial for preventing strokes in individuals with high lipid levels.