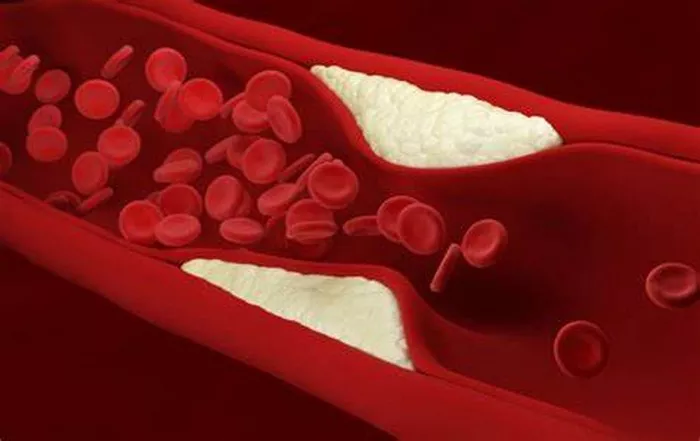
Arterial plaque is a build-up of substances like cholesterol, fatty deposits, calcium, and other elements within the walls of the arteries. This condition, known as atherosclerosis, can lead to reduced blood flow, increasing the risk of heart attacks, strokes, and other cardiovascular diseases. Many people wonder whether it’s possible to reduce or reverse this plaque build-up and improve arterial health. Fortunately, while eliminating all existing plaque might not be entirely feasible, there are several ways to significantly reduce plaque formation, stabilize existing plaques, and enhance overall cardiovascular health.
This article explores whether arterial plaque can be reduced, how it is formed, and details various methods to manage and lower plaque levels effectively.
How Plaque Develops in Arteries
Arterial plaque begins to form when the inner lining of the arteries, known as the endothelium, gets damaged. Factors like high cholesterol, high blood pressure, smoking, diabetes, and a poor diet contribute to this damage. Once damaged, cholesterol and other particles accumulate in the artery wall, creating a plaque. Over time, these plaques harden and narrow the arteries, restricting blood flow and potentially leading to blockages.
The development of arterial plaque is a slow, progressive process that can start in early adulthood and gradually worsen.
While the complete elimination of plaque is difficult, certain strategies can halt its progression and improve arterial function.
Can You Reduce Plaque in The Arteries?
Yes, it is possible to reduce the amount of plaque in the arteries to some extent. More importantly, even if the plaque is not entirely removed, it can be stabilized and prevented from causing further damage. Lifestyle changes, medications, and certain medical procedures can play a role in reducing plaque or at least managing its effects. The key is to adopt a holistic approach that includes healthy habits, dietary modifications, physical activity, and sometimes pharmaceutical interventions.
Methods to Reduce Plaque in The Arteries
1. Adopt a Heart-Healthy Diet
Diet plays a crucial role in managing cholesterol levels, reducing blood pressure, and minimizing the risk of plaque build-up. Eating the right foods can help prevent new plaque from forming and stabilize existing plaque.
Key Dietary Changes Include:
Increase Intake of Fruits and Vegetables: High in vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants, fruits and vegetables help reduce inflammation and oxidative stress, which contribute to plaque formation.
Consume Whole Grains: Foods like oatmeal, brown rice, and whole wheat bread are rich in fiber, which helps lower bad cholesterol (LDL) levels.
Add Healthy Fats: Replace saturated and trans fats with monounsaturated and polyunsaturated fats found in olive oil, avocados, nuts, seeds, and fatty fish like salmon. Omega-3 fatty acids, in particular, have been shown to reduce inflammation and improve cholesterol profiles.
Limit Sugar and Processed Foods: High sugar intake can lead to weight gain, insulin resistance, and higher levels of bad cholesterol, all of which contribute to atherosclerosis.
SEE ALSO: What Is Coronary Atherosclerosis of Native Coronary Artery?
2. Engage in Regular Physical Activity
Exercise is one of the most effective ways to improve heart health and reduce the risk of atherosclerosis. Physical activity helps improve blood circulation, promotes weight loss, and enhances the body’s ability to manage cholesterol and blood sugar levels.
Recommended Exercises Include:
Aerobic Exercise: Activities like walking, running, cycling, and swimming help increase cardiovascular fitness and promote overall heart health.
Strength Training: Lifting weights or doing resistance exercises helps improve muscle mass and metabolism, aiding in better weight and cholesterol management.
Flexibility and Balance Exercises: Yoga and stretching can lower stress levels, which in turn helps manage blood pressure.
Experts recommend at least 150 minutes of moderate aerobic exercise or 75 minutes of vigorous exercise per week, along with strength training exercises twice a week.
3. Quit Smoking
Smoking is a major risk factor for atherosclerosis. The chemicals in tobacco smoke damage the blood vessels, making it easier for plaque to build up. Quitting smoking can slow down or stop the progression of arterial plaque and improve overall cardiovascular health.
Benefits of Quitting Smoking:
Improved Circulation: Blood vessels start to heal, and circulation improves within weeks of quitting.
Lower Blood Pressure: Nicotine raises blood pressure, so quitting helps reduce this risk factor.
Better Cholesterol Profile: Quitting smoking improves HDL (good) cholesterol levels, which helps remove excess cholesterol from the bloodstream.
4. Manage Stress Effectively
Chronic stress can lead to high blood pressure, elevated cholesterol levels, and inflammation, all of which contribute to the build-up of plaque. Stress management techniques can help reduce these risks and improve heart health.
Effective Stress Management Strategies Include:
Meditation and Deep Breathing Exercises: These activities help reduce stress hormones and lower blood pressure.
Engaging in Hobbies and Social Activities: Spending time with friends and family, or engaging in hobbies, can reduce stress and improve mental well-being.
Regular Physical Activity: Exercise not only improves physical health but also acts as a stress reliever by releasing endorphins.
5. Medication for Plaque Management
In some cases, lifestyle changes may not be enough, and medications might be needed to manage plaque levels. Doctors prescribe medications to lower cholesterol, reduce blood pressure, or prevent blood clots, all of which help reduce the risk of heart disease.
Common Medications Include:
Statins: These drugs lower LDL cholesterol levels, which are primarily responsible for plaque build-up. Examples include atorvastatin, simvastatin, and rosuvastatin.
Antihypertensive Drugs: Managing blood pressure is crucial for preventing further arterial damage. Common medications include ACE inhibitors, beta-blockers, and diuretics.
Antiplatelet Drugs: Aspirin and other antiplatelet agents help prevent the formation of blood clots, which can block arteries narrowed by plaque.
6. Consider Medical Procedures if Necessary
In severe cases where lifestyle changes and medication are not sufficient, doctors may recommend medical procedures to reduce plaque or improve blood flow.
Common Medical Procedures:
Angioplasty and Stenting: In this procedure, a balloon is used to widen the narrowed artery, and a stent is placed to keep it open. This improves blood flow and reduces the risk of a heart attack.
Coronary Artery Bypass Surgery (CABG): For more severe blockages, this surgery creates a bypass around the blocked arteries, improving blood flow to the heart.
Atherectomy: This procedure involves removing plaque from the arteries using a catheter with a cutting device at the tip. It is less commonly performed but can be effective in certain cases.
Conclusion
Reducing plaque in the arteries is not only about reversing existing build-up but also about preventing new deposits from forming. While lifestyle changes like a healthy diet, regular exercise, quitting smoking, and managing stress can significantly reduce the risk of atherosclerosis, medications and medical procedures may be required for more advanced cases.
Related topics:
- How Long Can You Live with Mild Tricuspid Regurgitation?
- Does Ischemic Heart Disease Cause Atrial Fibrillation?
- How Do You Clear Blocked Arteries Without Surgery