Atrial flutter is a type of arrhythmia, or irregular heartbeat, that originates in the upper chambers of the heart, known as the atria. It’s characterized by rapid but regular electrical activity, which leads to inefficient contraction of the heart. This condition can lead to symptoms such as dizziness, shortness of breath, fatigue, and chest discomfort. While atrial flutter can be managed and treated effectively, certain practices or behaviors can exacerbate the condition or make it harder to control.
Understanding what not to do when dealing with atrial flutter is crucial to avoiding complications and ensuring optimal treatment outcomes.
What Is Atrial Flutter?
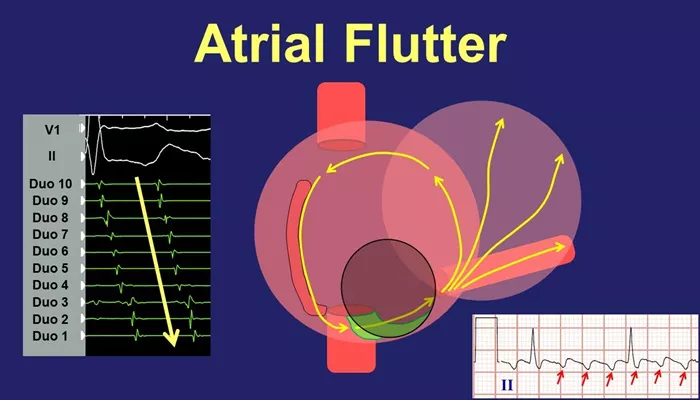
Before delving into the dos and don’ts, it is important to have a clear understanding of atrial flutter. This condition typically arises due to a problem with the electrical signals in the heart, leading to rapid, irregular atrial contractions. Unlike atrial fibrillation, another type of irregular heart rhythm, atrial flutter tends to occur in a more regular pattern.
In atrial flutter, the electrical signals in the atria loop rapidly, often at a rate of 250-350 beats per minute. However, the ventricles (lower chambers of the heart) don’t beat at such a fast rate because they cannot keep up with the rapid signals.
This causes the heart to beat irregularly and inefficiently, impairing its ability to pump blood effectively.
Treatment typically includes medications, cardioversion (a procedure to restore normal rhythm), or catheter ablation to modify the electrical pathways in the heart. However, certain behaviors can worsen the condition, make treatments less effective, or cause further health complications.
What Not to Do with Atrial Flutter
1. Do Not Ignore Symptoms or Delay Treatment
One of the most critical things not to do when dealing with atrial flutter is to ignore or delay seeking treatment. Symptoms such as dizziness, shortness of breath, fatigue, or palpitations are signals from the body that something is wrong. Even if the symptoms appear mild or occasional, they should not be disregarded.
Ignoring symptoms can lead to the worsening of the condition, increased risk of stroke, or heart failure over time. If you suspect that you are experiencing atrial flutter, it’s essential to seek medical advice promptly. Early diagnosis and treatment can prevent complications and help to manage the condition more effectively.
2. Do Not Self-Medicate with Over-the-Counter Medications
Some people with atrial flutter may attempt to treat their symptoms on their own, often by self-medicating with over-the-counter (OTC) medications such as decongestants, cough medicines, or pain relievers. While these medications may seem harmless, they can actually worsen the situation.
Certain OTC medications, especially those containing stimulants, can increase the heart rate and blood pressure, which may trigger or worsen arrhythmias. Additionally, some non-prescription drugs can interact with prescribed medications, reducing their effectiveness. Always consult your healthcare provider before taking any medication, whether prescription or over-the-counter.
3. Do Not Skip Medications Prescribed by Your Doctor
For patients with atrial flutter, doctors often prescribe medications to control heart rate, restore normal rhythm, or prevent blood clots. Skipping these medications or taking them incorrectly can lead to dangerous complications, including increased risk of stroke or heart failure.
It’s crucial to take all prescribed medications as directed, even if you feel better or notice a reduction in symptoms. Stopping or altering your medication regimen without consulting your healthcare provider could result in a recurrence of atrial flutter or other complications. If you experience side effects from a medication, speak to your doctor about possible alternatives.
4. Avoid Excessive Alcohol Consumption
Alcohol is a known trigger for many types of arrhythmias, including atrial flutter. Excessive alcohol intake can lead to electrolyte imbalances, dehydration, and increased heart rate, all of which can worsen atrial flutter.
While moderate alcohol consumption may be safe for some individuals with atrial flutter, it’s important to avoid excessive drinking. Even small amounts of alcohol can disrupt the electrical balance of the heart and trigger arrhythmias in some individuals. If you have atrial flutter, it’s best to limit or avoid alcohol altogether.
5. Do Not Engage in Excessive Physical Activity Without Medical Guidance
Exercise is an important part of maintaining overall health, but for individuals with atrial flutter, excessive physical activity can put additional strain on the heart and worsen symptoms. High-intensity workouts, especially those that involve lifting heavy weights or rapid cardiovascular exertion, can increase the risk of an arrhythmia episode.
Before starting or modifying an exercise routine, it’s crucial to consult with your healthcare provider. They can recommend a safe level of physical activity that won’t exacerbate your condition. In many cases, moderate aerobic exercises, such as walking or swimming, may be appropriate, but high-intensity activities should be avoided unless cleared by your doctor.
6. Do Not Engage in Stressful Situations Without Coping Mechanisms
Stress is another common trigger for atrial flutter. High-stress situations can lead to an increase in adrenaline, which can disrupt the heart’s normal rhythm. Chronic stress has also been associated with the development of various heart conditions, including arrhythmias.
It’s important to learn and adopt effective stress-management techniques, such as meditation, deep breathing exercises, or yoga. These methods can help reduce the impact of stress on your body and minimize the risk of triggering an arrhythmia. If stress becomes overwhelming, seeking support from a mental health professional can also be beneficial.
7. Do Not Skip Regular Follow-Up Appointments
Even if your symptoms seem to be under control, it’s important not to neglect follow-up appointments with your cardiologist. Atrial flutter is a condition that can change over time, and regular check-ups allow your doctor to monitor your heart’s health and adjust your treatment plan as necessary.
During these appointments, your doctor may perform tests such as an electrocardiogram (ECG), Holter monitor, or echocardiogram to assess the electrical activity and overall function of your heart. Regular monitoring can help detect any changes early and prevent complications from arising.
8. Avoid Dehydration and Electrolyte Imbalances
Maintaining proper hydration and balanced electrolyte levels is crucial for individuals with atrial flutter. Dehydration or an imbalance in electrolytes (such as potassium or magnesium) can lead to disturbances in the electrical activity of the heart, increasing the likelihood of arrhythmia episodes.
Ensure that you drink enough water throughout the day and consume a diet rich in potassium and magnesium. If you are on medications such as diuretics, which can cause dehydration or electrolyte imbalances, your doctor may recommend supplements to restore balance. Always follow your healthcare provider’s advice regarding hydration and nutrition.
9. Do Not Neglect the Risk of Stroke
Atrial flutter significantly increases the risk of stroke, as the irregular atrial contractions can lead to blood clots forming in the heart. These clots can travel to the brain and block blood flow, resulting in a stroke. Therefore, it’s essential to take measures to prevent stroke when living with atrial flutter.
Your doctor may prescribe blood thinners (anticoagulants) to reduce the risk of blood clots. It’s critical to take these medications as prescribed and follow up with your healthcare provider regularly to monitor for any potential side effects. Lifestyle modifications, such as maintaining a healthy weight, managing blood pressure, and avoiding smoking, can also help lower the risk of stroke.
10. Do Not Ignore the Signs of Other Heart Conditions
Atrial flutter often occurs alongside other heart conditions, such as heart failure, coronary artery disease, or hypertension. If you have a history of these conditions or experience symptoms such as chest pain or palpitations, it’s essential to get evaluated by a cardiologist.
Ignoring these symptoms can lead to the worsening of both atrial flutter and other underlying heart problems. Early detection and treatment of coexisting conditions can help reduce the overall burden on the heart and improve outcomes.
Conclusion
Atrial flutter is a serious condition that requires careful management and attention. By understanding what not to do and following medical advice, individuals can reduce the risk of complications and improve their quality of life. Avoiding behaviors that worsen the condition, such as ignoring symptoms, self-medicating, excessive alcohol consumption, and engaging in high-intensity exercise without guidance, is crucial for successful treatment.
Related topics: