Cardiomyopathy and heart failure are terms commonly used in discussions related to heart health, but many people often confuse them or use them interchangeably. While they share similarities and are closely related, they refer to different medical conditions. This article will help clarify the differences between cardiomyopathy and heart failure, providing a comprehensive understanding of these conditions, their causes, symptoms, and treatments.
Understanding Cardiomyopathy
Cardiomyopathy is a disease of the heart muscle that affects the ability of the heart to pump blood efficiently. It can occur as a result of various factors, including genetic conditions, infections, drug use, and other health problems. There are several types of cardiomyopathy, each with unique characteristics:
Dilated Cardiomyopathy (DCM): This is the most common form of cardiomyopathy, where the heart’s chambers become enlarged, weakening the heart muscle and impairing its ability to pump blood effectively.
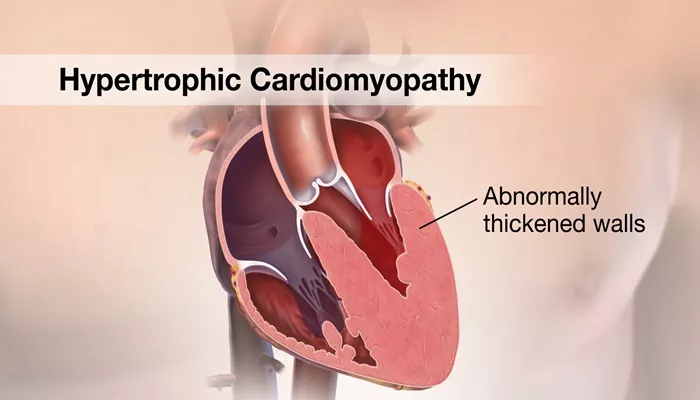
Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy (HCM): In this type, the heart muscle becomes abnormally thickened, making it harder for the heart to fill with blood and pump it efficiently. It can be hereditary and is often associated with sudden cardiac arrest in young athletes.
Restrictive Cardiomyopathy (RCM): This is a less common form where the heart muscle becomes stiff, preventing the heart chambers from expanding and filling properly with blood.
Arrhythmogenic Right Ventricular Cardiomyopathy (ARVC): In ARVC, the muscle tissue of the right ventricle is replaced with fatty or fibrous tissue, which disrupts the heart’s electrical signals and can cause arrhythmias.
Causes of Cardiomyopathy
Cardiomyopathy can be caused by various factors, including:
Genetic Factors: Inherited forms of cardiomyopathy are common, particularly in hypertrophic and arrhythmogenic types.
Chronic High Blood Pressure (Hypertension): Long-term high blood pressure can weaken and enlarge the heart muscle.
Heart Valve Problems: Certain heart valve diseases, like mitral valve prolapse, can lead to cardiomyopathy.
Myocarditis: Infections, particularly viral infections, can cause inflammation of the heart muscle.
Excessive Alcohol Use: Chronic alcohol consumption can damage the heart muscle, leading to cardiomyopathy.
Pregnancy: Some women develop cardiomyopathy during or after pregnancy, a condition known as peripartum cardiomyopathy.
Chemotherapy Drugs: Certain medications used in cancer treatment can damage the heart muscle.
Symptoms of Cardiomyopathy
The symptoms of cardiomyopathy vary depending on the type and severity of the condition. Common signs include:
- Shortness of breath, especially with exertion
- Fatigue and weakness
- Swelling in the legs, ankles, or abdomen
- Dizziness or lightheadedness
- Palpitations or irregular heartbeats
- Fainting or near-fainting episodes
Understanding Heart Failure
Heart failure is a condition where the heart is unable to pump blood effectively to meet the body’s needs. It doesn’t mean the heart has stopped working, but rather that it is not working as efficiently as it should. Heart failure can result from various underlying conditions, including coronary artery disease, high blood pressure, and heart valve problems.
Cardiomyopathy is one of the leading causes of heart failure.
Heart failure is categorized into two main types:
Left-sided heart failure: This occurs when the left side of the heart (which pumps blood to the rest of the body) is unable to pump blood effectively. This can lead to fluid buildup in the lungs, causing shortness of breath and fatigue.
Right-sided heart failure: In this type, the right side of the heart (which pumps blood to the lungs) fails, leading to fluid buildup in the body, particularly in the abdomen, legs, and ankles.
Causes of Heart Failure
The main causes of heart failure include:
Coronary Artery Disease: Blockages in the coronary arteries reduce the heart’s blood supply, causing damage to the heart muscle.
High Blood Pressure: Chronic high blood pressure makes the heart work harder, eventually leading to heart failure.
Heart Valve Problems: Defective heart valves can prevent proper blood flow and strain the heart.
Heart Attack (Myocardial Infarction): Damage from a heart attack can weaken the heart muscle, leading to heart failure.
Cardiomyopathy: This condition, whether dilated, hypertrophic, or restrictive, can lead to heart failure as it weakens the heart muscle and impairs its ability to pump blood effectively.
Symptoms of Heart Failure
Symptoms of heart failure include:
- Shortness of breath
- Fatigue and weakness
- Swelling in the legs, ankles, or abdomen
- Reduced ability to exercise or perform daily activities
- Persistent cough or wheezing
- Weight gain due to fluid retention
Relationship Between Cardiomyopathy and Heart Failure
Cardiomyopathy is one of the most common causes of heart failure. The damage to the heart muscle from cardiomyopathy can impair the heart’s ability to pump blood efficiently, leading to heart failure. However, not all cases of cardiomyopathy lead to heart failure, and not all heart failure cases are caused by cardiomyopathy.
Here’s how they are related:
Cardiomyopathy can lead to heart failure: If cardiomyopathy is left untreated, the weakened heart muscle may eventually lead to heart failure. As the heart muscle deteriorates, it becomes less able to pump blood to the rest of the body, causing the symptoms of heart failure.
Heart failure can result from many causes, not just cardiomyopathy: While cardiomyopathy is a significant cause of heart failure, other conditions, such as coronary artery disease, high blood pressure, and heart valve problems, can also lead to heart failure. Therefore, heart failure can occur without cardiomyopathy.
Key Differences Between Cardiomyopathy and Heart Failure
Definition:
Cardiomyopathy refers to a disease of the heart muscle that impairs its ability to pump blood.
Heart failure refers to a condition where the heart is unable to pump blood effectively, which may result from cardiomyopathy or other conditions.
Causes:
Cardiomyopathy is caused by factors such as genetics, infections, drugs, and high blood pressure.
Heart failure can result from multiple causes, including coronary artery disease, high blood pressure, heart attacks, and cardiomyopathy.
Symptoms:
Both conditions share similar symptoms, such as shortness of breath, fatigue, and swelling, but heart failure typically leads to more severe symptoms due to the heart’s inability to meet the body’s demands.
Progression:
Cardiomyopathy can develop slowly, and not all cases progress to heart failure.
Heart failure is a progressive condition that can result from cardiomyopathy or other underlying heart diseases, often leading to worsening symptoms over time.
Treatment:
Treatment for cardiomyopathy often focuses on addressing the underlying cause (e.g., controlling blood pressure, managing alcohol intake, or treating infections) and medications to improve heart function.
Treatment for heart failure involves lifestyle changes, medications, and possibly devices like pacemakers or implantable cardioverter-defibrillators (ICDs). In severe cases, heart transplantation may be necessary.
Conclusion
Cardiomyopathy and heart failure are related but distinct conditions. While cardiomyopathy refers to a disease of the heart muscle, heart failure refers to a condition where the heart cannot pump blood effectively. Cardiomyopathy can lead to heart failure, but not all cases of heart failure are caused by cardiomyopathy. Understanding these conditions, their causes, symptoms, and treatment options can help individuals manage their heart health more effectively.
Early diagnosis and treatment are crucial in both conditions to prevent complications and improve the quality of life. If you or someone you know is experiencing symptoms such as shortness of breath, fatigue, or swelling, it’s important to consult a healthcare provider for evaluation and appropriate management.
Related topics: