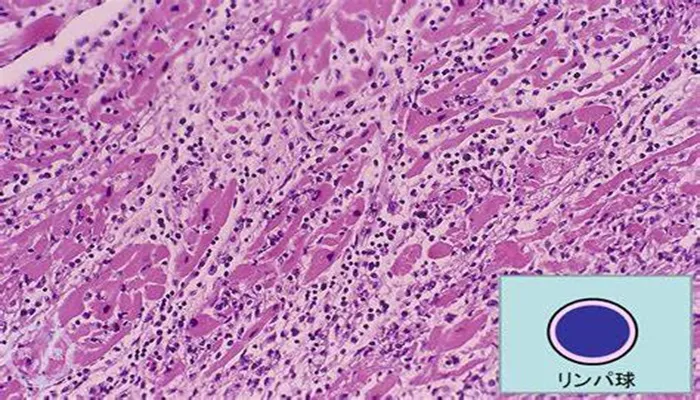
Viral myocarditis is an inflammation of the heart muscle caused by a viral infection. This condition can affect the heart’s ability to pump blood, leading to a range of symptoms that may be mild or severe. In this article, we will explore what viral myocarditis is, its causes, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment options, and preventive measures. The aim is to provide a clear and comprehensive understanding of this condition to help both healthcare professionals and the general public be aware of its implications.
What Is Viral Myocarditis?
Viral myocarditis occurs when a viral infection leads to inflammation of the myocardium, which is the middle layer of the heart’s wall. The inflammation damages the heart muscle, which can impair the heart’s ability to pump blood effectively. As a result, viral myocarditis can lead to serious complications, including heart failure, arrhythmias (irregular heartbeats), and in extreme cases, sudden cardiac death.
The condition can affect individuals of any age but is more common in younger people and in those with weakened immune systems. Early diagnosis and appropriate treatment are essential to prevent long-term damage and improve the chances of recovery.
Causes of Viral Myocarditis
Viral infections are the primary cause of myocarditis. Various viruses can invade the heart muscle and trigger an immune response that causes inflammation. Some of the most common viruses associated with viral myocarditis include:
1. Coxsackievirus B
Coxsackievirus B, a member of the enterovirus family, is one of the most common causes of viral myocarditis, especially in children and young adults. The virus spreads through respiratory droplets and contaminated surfaces.
2. Adenovirus
Adenoviruses are a group of viruses that can cause respiratory, gastrointestinal, and eye infections. These viruses are also linked to myocarditis, particularly in people with weakened immune systems.
3. Parvovirus B19
Parvovirus B19 is a common cause of viral myocarditis, particularly in children. It is often associated with a condition called “fifth disease,” which causes a mild rash and fever. In rare cases, the virus can spread to the heart and cause inflammation.
4. Herpesviruses
Herpesviruses, including Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) and cytomegalovirus (CMV), are known to cause myocarditis. These viruses often affect people with compromised immune systems, such as those with HIV/AIDS or organ transplant recipients.
5. Influenza Virus
The influenza virus, or flu, is another common cause of viral myocarditis, particularly during flu season. In some cases, a severe flu infection can lead to complications like myocarditis, especially in individuals with pre-existing heart conditions.
6. Other Viruses
Other viruses that can cause viral myocarditis include HIV, hepatitis C, and certain types of coronavirus. In recent years, the COVID-19 pandemic has also been associated with cases of viral myocarditis, particularly in individuals who have contracted the virus.
Symptoms of Viral Myocarditis
The symptoms of viral myocarditis can range from mild to severe, and in some cases, the condition may not cause noticeable symptoms at all. The severity of symptoms depends on the extent of inflammation and damage to the heart muscle. Common symptoms of viral myocarditis include:
1. Fatigue and Weakness
One of the most common symptoms is extreme fatigue and weakness, especially during physical activity. This happens because the heart is not able to pump blood efficiently due to the inflammation.
2. Chest Pain
Chest pain, which may feel sharp or pressure-like, is another common symptom. This can occur as a result of inflammation in the heart muscle or due to reduced blood flow to the heart.
3. Shortness of Breath
Shortness of breath, especially during exertion, is a typical symptom of viral myocarditis. This happens when the heart’s reduced pumping ability makes it difficult for the body to get enough oxygenated blood.
4. Irregular Heartbeat (Arrhythmias)
People with viral myocarditis may experience irregular heartbeats, which can feel like palpitations, fluttering, or skipped beats. In severe cases, arrhythmias can be life-threatening.
5. Swelling in the Legs, Ankles, and Feet
Due to poor heart function, blood may back up in the body, causing swelling (edema) in the lower extremities. This can be particularly noticeable in the legs, ankles, and feet.
6. Lightheadedness and Fainting
In severe cases, the reduced blood flow to the brain can lead to dizziness or fainting spells. This is more common when standing up quickly or engaging in physical activity.
7. Flu-like Symptoms
In some cases, viral myocarditis may begin with flu-like symptoms such as fever, sore throat, or muscle aches. These symptoms usually appear before the more serious heart-related symptoms.
Diagnosis of Viral Myocarditis
Viral myocarditis can be difficult to diagnose because its symptoms often overlap with other heart conditions. To diagnose viral myocarditis, healthcare providers rely on a combination of patient history, physical examination, and diagnostic tests.
1. Medical History and Physical Exam
The first step in diagnosis is a thorough medical history and physical examination. The healthcare provider will ask about recent viral infections, symptoms, and any family history of heart disease. A physical exam will focus on signs of heart failure or abnormal heart rhythms.
2. Blood Tests
Blood tests can help detect signs of inflammation and assess heart function. Elevated levels of cardiac enzymes, such as troponin, can indicate heart muscle damage, which may suggest myocarditis.
3. Electrocardiogram (ECG or EKG)
An electrocardiogram (ECG) is a non-invasive test that records the electrical activity of the heart. In patients with viral myocarditis, an ECG may show abnormal rhythms, such as tachycardia (fast heart rate) or arrhythmias.
4. Echocardiogram
An echocardiogram uses sound waves to create a picture of the heart’s structure and function. It can help detect abnormal heart movement, poor heart pumping, or fluid buildup around the heart.
5. Cardiac MRI
A cardiac magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scan is a more advanced imaging technique that can provide detailed images of the heart muscle. This test can help detect inflammation and other structural changes in the heart.
6. Endomyocardial Biopsy
In rare cases, a small tissue sample from the heart muscle may be taken for analysis. This procedure, called an endomyocardial biopsy, can help confirm the diagnosis and identify the specific virus causing the myocarditis.
Treatment of Viral Myocarditis
The treatment of viral myocarditis aims to reduce inflammation, support heart function, and manage symptoms. The approach depends on the severity of the condition and the specific virus involved. Treatment options may include:
1. Medications
Anti-inflammatory Drugs: Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) or corticosteroids may be prescribed to reduce inflammation in the heart muscle. However, corticosteroids are generally used with caution as they may have side effects in certain patients.
Antiviral Medications: In some cases, antiviral medications may be used if a specific virus is identified and there is evidence that the antiviral treatment is effective.
Diuretics: These medications help reduce fluid buildup in the body and can alleviate symptoms of heart failure, such as swelling in the legs and difficulty breathing.
ACE Inhibitors: Angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors can help relax blood vessels, making it easier for the heart to pump blood.
Beta-blockers: These drugs help reduce the heart’s workload and manage abnormal heart rhythms.
2. Hospitalization and Monitoring
In severe cases of viral myocarditis, hospitalization may be required to closely monitor heart function and provide supportive care, such as intravenous medications or mechanical circulatory support (e.g., a ventricular assist device).
3. Implantable Devices
In some cases, patients with severe arrhythmias may require the implantation of a device like a pacemaker or an implantable cardioverter-defibrillator (ICD) to regulate the heart’s electrical activity.
4. Heart Transplant
In cases where viral myocarditis leads to severe heart failure that does not respond to treatment, a heart transplant may be considered as a last resort.
Preventive Measures for Viral Myocarditis
Although viral myocarditis cannot always be prevented, there are certain steps individuals can take to reduce the risk of developing the condition:
1. Vaccination
Vaccines, such as the flu vaccine, can help prevent infections caused by viruses that may lead to myocarditis. Vaccinating against viruses like influenza, COVID-19, and others can reduce the risk of viral infections that can affect the heart.
2. Good Hygiene Practices
Practicing good hygiene, such as frequent hand washing and avoiding close contact with people who are sick, can reduce the risk of contracting viral infections.
3. Timely Treatment of Infections
Prompt treatment of viral infections, such as respiratory infections, can help prevent complications like myocarditis.
Seeking medical attention early when symptoms of a viral infection appear is crucial.
4. Managing Risk Factors
Maintaining a healthy lifestyle, managing chronic conditions like hypertension and diabetes, and avoiding smoking and excessive alcohol consumption can improve overall heart health and reduce the risk of developing myocarditis.
Conclusion
Viral myocarditis is a serious condition that can cause significant damage to the heart if left untreated. While the condition is often associated with viral infections, the severity of symptoms and potential for recovery vary from person to person.
Early diagnosis and appropriate treatment are key to managing viral myocarditis and improving outcomes for affected individuals. By understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for viral myocarditis, patients and healthcare providers can work together to prevent complications and promote heart health.
Related topics: