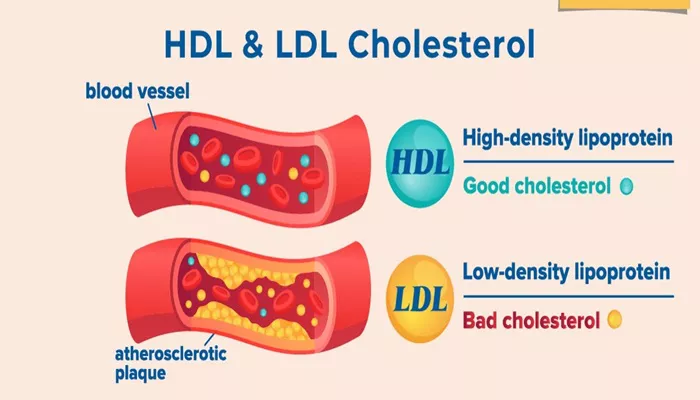
High-Density Lipoprotein (HDL) is often referred to as the “good” cholesterol, due to its protective effects on cardiovascular health. In the world of lipids, cholesterol is a key component, and its levels in the bloodstream play a critical role in determining overall heart health.
While we typically hear about low-density lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol and its association with heart disease, HDL cholesterol is just as important in understanding a person’s risk of developing cardiovascular conditions. This comprehensive guide will explore HDL in detail, explaining what it is, how it works, why it’s beneficial, and how you can manage its levels.
What Is High-Density Lipoprotein (HDL)?
High-Density Lipoprotein (HDL) is a type of cholesterol-carrying particle in the blood. It plays an essential role in maintaining cardiovascular health by helping to remove excess cholesterol from the bloodstream and transporting it to the liver for excretion. This process helps to prevent cholesterol buildup in the arteries, which can lead to atherosclerosis, a condition that increases the risk of heart attack and stroke.
HDL is considered “good” cholesterol because it helps reduce the risk of heart disease by facilitating the removal of LDL (“bad” cholesterol) from the bloodstream. Higher levels of HDL are associated with a lower risk of developing heart disease, while lower levels of HDL can increase the likelihood of cardiovascular problems.
The Structure of HDL
HDL is a complex molecule consisting of proteins and lipids. It is composed mainly of phospholipids and apolipoproteins, which give it its unique structure and allow it to function as a cholesterol transporter. The protein component of HDL is primarily apolipoprotein A-I (apoA-I), which acts as the primary vehicle for transporting cholesterol from the arteries to the liver for processing.
The lipoprotein is called “high-density” because it has a higher proportion of protein compared to lipids, which gives it a denser structure compared to other lipoproteins, like LDL or very low-density lipoprotein (VLDL).
How HDL Works in the Body
HDL’s primary function is to facilitate reverse cholesterol transport. In this process, HDL particles bind to excess cholesterol found in the bloodstream or within the walls of blood vessels. The HDL particles then transport this cholesterol to the liver, where it can be metabolized and either used for the production of bile acids or excreted from the body.
By effectively removing excess cholesterol, HDL prevents the accumulation of cholesterol plaques in the arteries, helping to maintain healthy blood flow. This action reduces the likelihood of developing conditions such as atherosclerosis, coronary artery disease, and other cardiovascular issues. In essence, HDL works to “clean up” the bloodstream, ensuring that cholesterol is removed before it has a chance to do damage to the arteries.
The Role of HDL in Cardiovascular Health
HDL plays an essential protective role in heart health. A higher concentration of HDL in the blood has been linked to a reduced risk of developing coronary artery disease, heart attacks, and strokes. This is due to its ability to reverse the process of cholesterol buildup in the arteries.
1. Protecting Against Atherosclerosis
Atherosclerosis is a condition in which plaque builds up in the arteries, narrowing and hardening the blood vessels. This can restrict blood flow and increase the risk of heart disease, strokes, and peripheral artery disease. HDL helps protect against atherosclerosis by removing excess cholesterol from the blood vessels, thus reducing plaque formation.
HDL’s role in preventing atherosclerosis is particularly important in people who have high levels of LDL cholesterol, as this “bad” cholesterol can contribute to plaque buildup. By counteracting the harmful effects of LDL, HDL reduces the risk of plaque rupture and clot formation, which can lead to heart attacks or strokes.
2. Reducing Inflammation
Inflammation is another key factor in the development of cardiovascular disease. Chronic low-grade inflammation can lead to the formation of plaques in the arteries and increase the risk of cardiovascular events. HDL has anti-inflammatory properties that help reduce the inflammation associated with atherosclerosis. In fact, studies suggest that HDL can suppress the inflammatory response in the blood vessels, further lowering the risk of cardiovascular disease.
3. Antioxidant Effects
HDL also acts as an antioxidant. This means that it helps neutralize free radicals—unstable molecules that can damage blood vessel walls and increase the risk of heart disease. By reducing oxidative stress, HDL helps protect the cardiovascular system from damage.
What Is the Ideal HDL Level?
The ideal level of HDL cholesterol varies depending on a person’s overall cardiovascular risk. In general, higher levels of HDL are better for heart health. According to the American Heart Association:
Low HDL: Below 40 mg/dL for men and below 50 mg/dL for women.
Normal HDL: 40-59 mg/dL for men and 50-59 mg/dL for women.
High HDL: 60 mg/dL and above for both men and women. Higher HDL levels are associated with a lower risk of heart disease.
While raising HDL levels is beneficial, it’s essential to focus on achieving a balanced lipid profile, which includes maintaining healthy levels of LDL cholesterol and triglycerides. In some cases, your healthcare provider may recommend medication to help manage cholesterol levels, in addition to lifestyle changes.
How to Increase HDL Cholesterol
Having adequate levels of HDL cholesterol is crucial for maintaining heart health. While genetics play a role in determining HDL levels, lifestyle factors can have a significant impact. Below are some key strategies to increase HDL levels and improve overall cardiovascular health.
1. Exercise Regularly
Regular physical activity is one of the most effective ways to increase HDL cholesterol. Aerobic exercises such as walking, running, swimming, or cycling can boost HDL levels. Studies show that even moderate-intensity exercise, such as 30 minutes of brisk walking most days of the week, can help raise HDL levels.
Exercise not only increases HDL but also helps lower LDL cholesterol and triglycerides, contributing to a healthier lipid profile overall.
2. Adopt a Heart-Healthy Diet
Diet plays a critical role in managing cholesterol levels. To increase HDL cholesterol, consider incorporating the following foods into your diet:
Healthy fats: Monounsaturated and polyunsaturated fats, found in foods like olive oil, avocados, and fatty fish (salmon, mackerel, sardines), can help increase HDL cholesterol.
Fiber-rich foods: Soluble fiber, found in foods like oats, beans, and vegetables, can help improve your cholesterol profile by lowering LDL levels and supporting overall heart health.
Nuts and seeds: Almonds, walnuts, and flaxseeds are rich in healthy fats and fiber, which can promote healthy cholesterol levels.
Fruits and vegetables: A diet high in fruits and vegetables provides essential antioxidants, vitamins, and minerals that support heart health.
3. Quit Smoking
Smoking lowers HDL cholesterol levels and accelerates the development of cardiovascular disease. Quitting smoking can lead to significant improvements in HDL cholesterol levels and overall cardiovascular health. In fact, research shows that within just a few weeks of quitting, HDL levels can start to rise.
4. Moderate Alcohol Consumption
Moderate alcohol consumption has been shown to increase HDL cholesterol. However, it’s important to emphasize moderation—excessive alcohol intake can lead to various health problems, including high blood pressure and liver damage.
Stick to one drink per day for women and two drinks per day for men to experience the heart-healthy benefits of alcohol without the risks.
5. Maintain a Healthy Weight
Carrying excess weight, particularly around the abdomen, can lower HDL levels and increase the risk of heart disease.
Losing weight through a combination of a balanced diet and regular exercise can help raise HDL cholesterol and reduce LDL cholesterol and triglyceride levels.
Conclusion
High-Density Lipoprotein (HDL) is an essential component of heart health, acting as a protector against atherosclerosis and cardiovascular disease. By understanding how HDL functions and taking steps to increase its levels through exercise, diet, and lifestyle changes, individuals can reduce their risk of heart disease and improve overall cardiovascular health.
Related topics: