High cholesterol is a pervasive health concern worldwide, contributing significantly to the burden of cardiovascular diseases. Often termed the “silent killer,” it manifests subtly, making awareness and early detection crucial. Understanding the signs of high cholesterol can empower individuals to seek timely medical intervention, thereby mitigating associated health risks.
Understanding Cholesterol and Its Impact
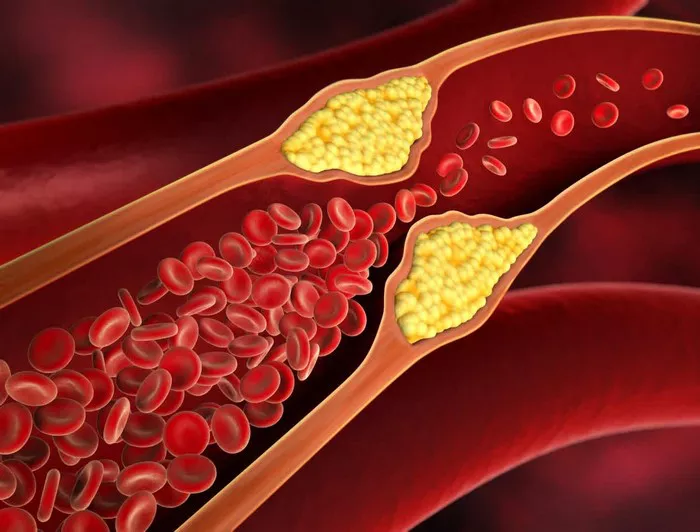
Before delving into the signs, it’s essential to grasp what cholesterol is and why it matters. Cholesterol, a waxy substance found in the blood, is vital for building healthy cells. However, when its levels elevate, it poses significant health risks, including heart disease and stroke. The body has two main types of cholesterol: Low-Density Lipoprotein (LDL), often dubbed “bad” cholesterol, and High-Density Lipoprotein (HDL), known as “good” cholesterol. An imbalance in these levels, particularly high LDL or low HDL, signals trouble.
1. Physical Signs on the Body
Xanthelasmas and Xanthomas
Xanthelasmas are yellowish deposits of cholesterol under the skin, typically around the eyelids. Xanthomas, similarly, are fatty deposits that can appear anywhere on the body but are most commonly found on the elbows, joints, tendons, knees, hands, feet, and buttocks. These physical manifestations can be early indicators of elevated cholesterol levels, particularly if they appear without other underlying causes.
Example:
John, a 52-year-old male with no previous history of skin conditions, noticed yellowish patches around his eyes and small, bump-like deposits on his elbows. Upon dermatological examination, these were identified as xanthelasmas and xanthomas, leading to further cardiovascular evaluation and the diagnosis of high cholesterol.
2. Corneal Arcus
Corneal arcus is a condition characterized by a gray or white arc visible around the cornea of the eye. While it can be a normal aging phenomenon, in individuals under the age of 40, it may be an indicator of elevated cholesterol levels.
Example:
Lisa, a 35-year-old female, observed a grayish ring around the iris of her eyes during a routine eye examination. Her optometrist recommended a lipid profile test, which revealed significantly high cholesterol levels, prompting immediate lifestyle and dietary interventions.
3. Unexplained Pains and Aches
High cholesterol can lead to the formation of plaques in the arteries, restricting blood flow and potentially causing pain. This is often noticed in the legs due to peripheral artery disease (PAD).
Example:
Ahmed, a 48-year-old office worker with a sedentary lifestyle, experienced cramping and discomfort in his calves while walking or climbing stairs. Initially attributing it to lack of exercise, he consulted a doctor after persistent symptoms, which led to the discovery of PAD caused by high cholesterol levels.
4. Stroke or Transient Ischemic Attacks (TIAs)
Though a more severe manifestation, experiencing a stroke or TIAs, often referred to as mini-strokes, can be a wake-up call to undiagnosed high cholesterol. These occur when cholesterol plaques cause a blockage in the arteries supplying the brain.
Example:
Maria, a 60-year-old woman with no significant medical history, suffered a TIA characterized by sudden weakness in her left arm and slurred speech. Emergency tests showed no permanent damage, but further investigations revealed high cholesterol, a key contributor to her condition.
5. Angina and Heart Attack
Chest pain (angina) or discomfort may signify that your heart is not receiving enough blood and oxygen due to cholesterol buildup in the coronary arteries. This can escalate to a heart attack if not addressed.
Example:
Kevin, a 45-year-old smoker, experienced chest pain during physical exertion. He initially dismissed it as heartburn but sought medical attention when the pain became more frequent. Tests revealed significant blockages in his coronary arteries due to high cholesterol, necessitating immediate medical intervention.
Prevention and Management
Understanding the signs of high cholesterol is just the beginning. It’s crucial to engage in preventive measures, including regular screenings, maintaining a healthy diet, regular physical activity, and, when necessary, medication. Early detection and lifestyle adjustments can significantly reduce the risk of severe cardiovascular events.
Conclusion
High cholesterol can remain unnoticed until it manifests through more severe health issues. Recognizing these signs and symptoms, as illustrated by the examples provided, can play a pivotal role in early detection and management. Regular health check-ups and being attuned to your body’s signals are essential steps toward maintaining cardiovascular health and overall well-being.