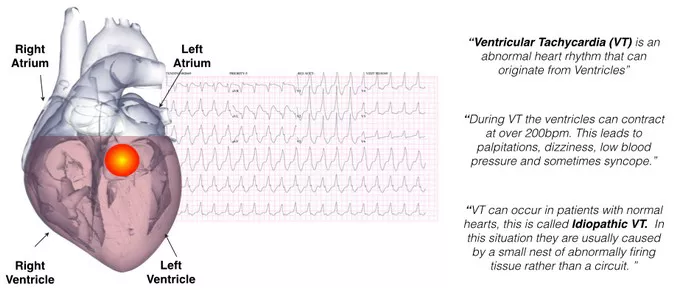
Left ventricular tachycardia (LVT) is a potentially life-threatening cardiac arrhythmia characterized by rapid heartbeats originating from the left ventricle of the heart. This condition can lead to various complications, including heart failure and sudden cardiac arrest. Understanding the causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment options for LVT is crucial for effective management and prevention of adverse outcomes.
Causes of Left Ventricular Tachycardia
Left ventricular tachycardia can arise from a variety of underlying cardiac conditions. One common cause is structural heart disease, such as coronary artery disease, myocardial infarction (heart attack), or cardiomyopathy. These conditions can lead to abnormalities in the electrical conduction system of the heart, predisposing individuals to LVT.
Other potential causes include:
1. Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy: A genetic condition characterized by abnormal thickening of the heart muscle, which can disrupt normal electrical activity.
2. Dilated Cardiomyopathy: A condition where the heart chambers become enlarged and weakened, increasing the risk of arrhythmias like LVT.
3. Valvular Heart Disease: Malfunctioning heart valves can alter blood flow and contribute to the development of arrhythmias.
4. Myocarditis: Inflammation of the heart muscle can disrupt electrical impulses and trigger arrhythmias.
5. Electrolyte Imbalance: Abnormal levels of potassium, sodium, or calcium in the blood can affect the heart’s electrical activity and lead to tachycardia.
6. Drug-induced: Certain medications, such as antiarrhythmics, can inadvertently trigger LVT in susceptible individuals.
Symptoms of Left Ventricular Tachycardia
The symptoms of LVT can vary depending on the individual’s overall health, the underlying cause of the arrhythmia, and the rate at which the heart is beating. Some common symptoms include:
1. Palpitations: A rapid, pounding, or irregular heartbeat sensation.
2. Dizziness or Lightheadedness: Due to decreased blood flow to the brain during periods of rapid heart rate.
3. Shortness of Breath: Difficulty breathing, especially during physical activity or exertion.
4. Chest Pain or Discomfort: Typically described as a tightness, pressure, or squeezing sensation in the chest.
5. Fainting (Syncope): Loss of consciousness may occur in severe cases, particularly if the arrhythmia leads to a sudden drop in blood pressure.
It’s important to note that some individuals with LVT may not experience any symptoms, especially if the arrhythmia is intermittent or occurs at a relatively low heart rate. However, even asymptomatic individuals are at risk of complications and should seek medical evaluation if LVT is suspected.
Diagnosis of Left Ventricular Tachycardia
Diagnosing left ventricular tachycardia typically involves a combination of medical history review, physical examination, and various diagnostic tests. Key steps in the diagnostic process may include:
1. Medical History: The healthcare provider will inquire about the patient’s symptoms, medical history, family history of cardiac conditions, and any medications or substances they may be taking.
2. Physical Examination: This may include measuring vital signs, listening to the heart with a stethoscope, and assessing for signs of heart failure or other cardiac abnormalities.
3. Electrocardiogram (ECG or EKG): A non-invasive test that records the electrical activity of the heart. An ECG can reveal characteristic patterns associated with LVT, such as widened QRS complexes and abnormal T-wave morphology.
4. Holter Monitoring: A portable device worn by the patient for 24 to 48 hours to continuously record the heart’s electrical activity. This can help detect intermittent arrhythmias that may not be captured during a standard ECG.
5. Echocardiogram: An ultrasound imaging test that provides detailed images of the heart’s structure and function. It can identify structural abnormalities, such as cardiomyopathy or valve disease, that may contribute to LVT.
6. Electrophysiology Study (EPS): An invasive procedure performed in a specialized cardiac catheterization lab. During an EPS, thin, flexible wires (electrodes) are inserted through blood vessels and positioned within the heart to map its electrical pathways. This test can pinpoint the site of arrhythmia origin and guide treatment decisions.
Treatment Options for Left Ventricular Tachycardia
The management of left ventricular tachycardia aims to control symptoms, prevent complications, and reduce the risk of sudden cardiac death. Treatment strategies may include:
1. Medications: Antiarrhythmic drugs, such as beta-blockers, calcium channel blockers, and sodium channel blockers, are commonly prescribed to stabilize the heart’s electrical activity and prevent tachycardia episodes. In some cases, additional medications to manage underlying heart conditions (e.g., heart failure, hypertension) may also be recommended.
2. Implantable Cardioverter-Defibrillator (ICD): For individuals at high risk of life-threatening arrhythmias or sudden cardiac arrest, an ICD may be implanted under the skin to continuously monitor the heart’s rhythm. If ventricular tachycardia or fibrillation is detected, the device delivers a shock to restore normal rhythm.
3. Catheter Ablation: An invasive procedure performed by an electrophysiologist to selectively destroy (ablate) abnormal heart tissue responsible for triggering or sustaining LVT. Radiofrequency energy or cryotherapy may be used to create scar tissue and disrupt the abnormal electrical pathways.
4. Cardiac Resynchronization Therapy (CRT): In patients with heart failure and conduction abnormalities, CRT involves implanting a special pacemaker that coordinates the contractions of the heart’s chambers to improve overall function and reduce the risk of arrhythmias.
5. Lifestyle Modifications: Adopting heart-healthy habits, such as maintaining a balanced diet, engaging in regular exercise, avoiding tobacco and excessive alcohol consumption, and managing stress, can help reduce the risk of arrhythmias and improve overall cardiovascular health.
Prognosis and Complications
The prognosis for individuals with left ventricular tachycardia depends on various factors, including the underlying cause, the frequency and severity of arrhythmia episodes, the presence of other cardiac conditions, and the effectiveness of treatment interventions. With appropriate management, many patients can achieve symptom control and maintain a good quality of life.
However, left ventricular tachycardia can lead to serious complications if left untreated or poorly managed, including:
1. Sudden Cardiac Arrest: A life-threatening condition characterized by abrupt loss of heart function, resulting in loss of consciousness and cessation of breathing. Prompt intervention with CPR and defibrillation is essential to improve outcomes.
2. Heart Failure: Chronic or recurrent LVT can weaken the heart muscle over time, impairing its ability to pump blood effectively and leading to symptoms of heart failure, such as fatigue, fluid retention, and shortness of breath.
3. Stroke: Prolonged periods of rapid heart rate can increase the risk of blood clots forming in the heart chambers and traveling to the brain, causing a stroke.
4. Decreased Quality of Life: Frequent arrhythmia episodes and associated symptoms can significantly impact an individual’s physical and emotional well-being, limiting daily activities and impairing overall quality of life.
Conclusion
Left ventricular tachycardia is a serious cardiac arrhythmia that requires prompt diagnosis and appropriate management to prevent complications and improve outcomes. By understanding the underlying causes, recognizing common symptoms, and implementing effective treatment strategies, healthcare providers can help individuals with LVT achieve better control of their condition and enjoy a higher quality of life. Ongoing research into the mechanisms of arrhythmia formation and the development of novel therapeutic approaches holds promise for further advancements in the field of cardiac electrophysiology.