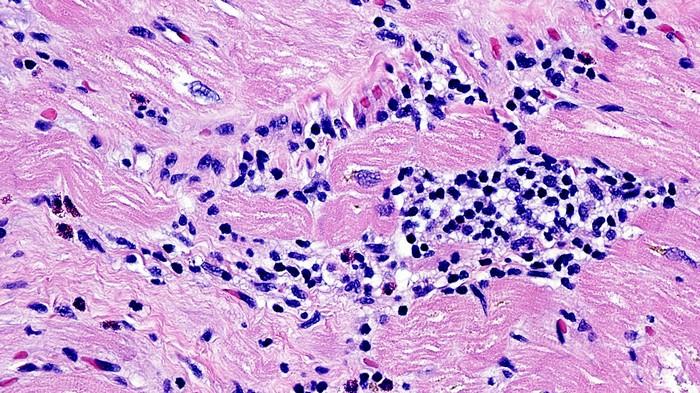
Lymphocytic myocarditis is a challenging condition characterized by inflammation of the heart muscle, primarily driven by infiltration of lymphocytes into myocardial tissue. This inflammatory process can lead to a spectrum of clinical manifestations, ranging from mild symptoms to life-threatening heart failure. Understanding the complex interplay of factors contributing to the development of lymphocytic myocarditis is crucial for accurate diagnosis, effective management, and prevention strategies. In this article, we delve into the multifaceted etiology of lymphocytic myocarditis, exploring the various genetic, environmental, infectious, and immune-mediated factors implicated in its pathogenesis.
Genetic Predisposition: Unraveling the Genetic Basis
Genetic predisposition plays a significant role in the susceptibility to lymphocytic myocarditis. Several genetic variations have been implicated in the development and progression of the disease. Variants in genes encoding proteins involved in immune regulation, such as human leukocyte antigen (HLA) genes, have been associated with an increased risk of myocarditis. Additionally, mutations in genes encoding components of the cardiac muscle structure or proteins involved in inflammatory signaling pathways can predispose individuals to myocarditis. Genome-wide association studies (GWAS) have identified specific genetic loci linked to an elevated risk of myocarditis, shedding light on the underlying genetic architecture of the disease.
Environmental Triggers: Uncovering External Influences
Environmental factors play a critical role in triggering or exacerbating lymphocytic myocarditis in genetically susceptible individuals. Exposure to certain environmental toxins, such as heavy metals or chemicals, has been implicated in the development of myocarditis by inducing oxidative stress and immune dysregulation. Furthermore, environmental pollutants and infectious agents can act as triggers for autoimmune responses, leading to myocardial inflammation. Understanding the impact of environmental factors on myocarditis risk can inform preventive strategies aimed at minimizing exposure to potential triggers.
Infectious Agents: Exploring Microbial Contributors
Infectious agents represent a significant category of triggers for lymphocytic myocarditis. Viruses, including enteroviruses, adenoviruses, and human herpesvirus 6 (HHV-6), are among the most common pathogens associated with myocarditis. These viruses can directly infect cardiac myocytes, triggering an inflammatory response mediated by both innate and adaptive immune mechanisms. Bacterial infections, such as those caused by Borrelia burgdorferi (Lyme disease) or Chlamydia pneumoniae, have also been implicated in the pathogenesis of myocarditis. The identification of specific microbial agents responsible for myocarditis can guide targeted diagnostic approaches and therapeutic interventions, including antiviral or antimicrobial treatments.
Immune Dysregulation: Unveiling Autoimmune Mechanisms
Dysregulation of the immune system plays a central role in the pathogenesis of lymphocytic myocarditis. Autoimmune mechanisms, wherein the immune system mistakenly targets self-antigens present in cardiac tissue, contribute to the perpetuation of myocardial inflammation. Molecular mimicry, wherein microbial antigens share structural similarities with host antigens, can trigger cross-reactive immune responses leading to myocarditis. Additionally, defects in immune tolerance mechanisms, such as regulatory T cell dysfunction or impaired central tolerance, can result in the breakdown of self-tolerance and the development of autoimmunity. Elucidating the precise mechanisms underlying immune dysregulation in myocarditis holds promise for the development of targeted immunomodulatory therapies aimed at restoring immune homeostasis.
Inflammatory Signaling Pathways: Insights into Pathophysiology
Inflammatory signaling pathways orchestrate the immune response in lymphocytic myocarditis, driving myocardial inflammation and tissue damage. Activation of pro-inflammatory cytokines, such as tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α), interleukin-1 (IL-1), and interferon-gamma (IFN-γ), amplifies the inflammatory cascade within the myocardium. Chemokines recruit circulating immune cells, including lymphocytes, monocytes, and neutrophils, to the site of inflammation, further propagating tissue injury. In addition, the complement system, a key component of innate immunity, contributes to myocardial damage through complement-mediated cytotoxicity and immune complex deposition. Targeting specific inflammatory pathways implicated in myocarditis pathophysiology holds therapeutic potential for mitigating myocardial injury and improving clinical outcomes.
Conclusion
Lymphocytic myocarditis is a multifactorial disease characterized by inflammation of the heart muscle, with diverse genetic, environmental, infectious, and immune-mediated factors contributing to its etiology. The interplay between these factors determines individual susceptibility to myocarditis and influences disease severity and progression. Advancements in genomic technologies, such as next-generation sequencing and gene expression profiling, hold promise for unraveling the genetic basis of myocarditis and identifying novel therapeutic targets. Moreover, a deeper understanding of the environmental triggers and immune dysregulation underlying myocarditis pathogenesis is essential for developing personalized treatment strategies and preventive interventions. Collaborative efforts integrating basic science research, clinical investigation, and translational approaches are crucial for advancing our knowledge of lymphocytic myocarditis and improving patient outcomes in this complex and challenging disease.
By comprehensively elucidating the intricate mechanisms driving lymphocytic myocarditis, we can pave the way for more effective diagnostic, therapeutic, and preventive strategies, ultimately improving the prognosis and quality of life for affected individuals.