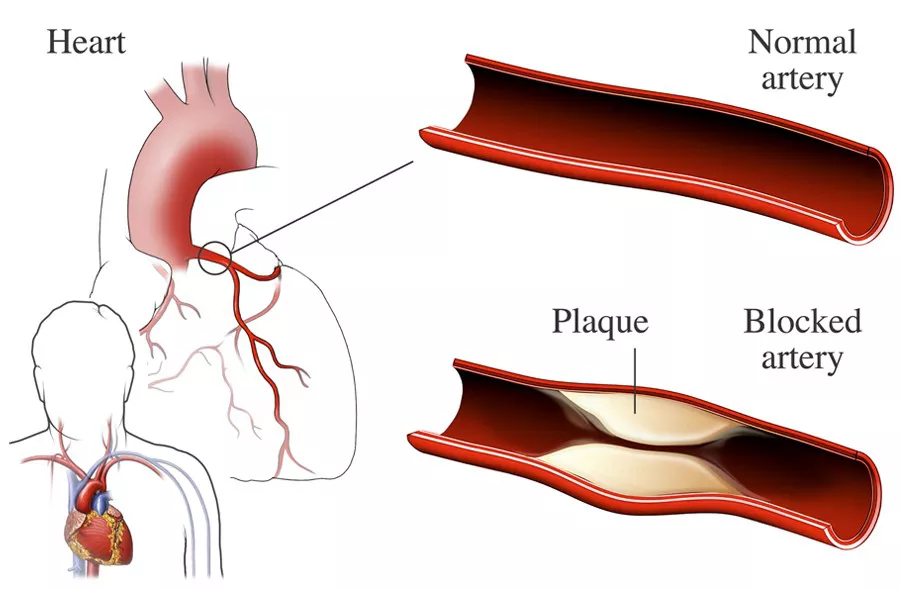
The Left Anterior Descending (LAD) artery is a critical vessel responsible for supplying oxygen-rich blood to a significant portion of the heart muscle. When this artery becomes obstructed, it can lead to severe consequences such as heart attacks and other cardiovascular complications. Understanding the underlying causes of LAD artery blockage is essential for effective prevention and treatment strategies. In this article, we delve into the various factors that contribute to LAD artery blockage, ranging from lifestyle choices to genetic predispositions.
Anatomy and Function of the LAD Artery
Before delving into the causes of LAD artery blockage, it’s crucial to understand the anatomy and function of this vital coronary artery. The LAD artery, also known as the “widow-maker,” is located on the front surface of the heart and runs down the anterior interventricular groove. It supplies blood to a large portion of the left ventricle, septum, and portions of the right ventricle.
The LAD artery plays a pivotal role in myocardial perfusion, ensuring that the heart receives an adequate supply of oxygen and nutrients to function optimally. Any obstruction or blockage in this artery can lead to ischemia (lack of blood flow) and subsequent damage to the heart muscle.
Contributing Factors to LAD Artery Blockage
Several factors contribute to the development of LAD artery blockage, ranging from modifiable lifestyle choices to genetic predispositions. Understanding these factors is crucial for implementing preventive measures and adopting a holistic approach to cardiovascular health. Below are some of the primary causes of LAD artery blockage:
1. Atherosclerosis: Atherosclerosis is a progressive condition characterized by the buildup of plaque within the arterial walls. This plaque is composed of cholesterol, fatty substances, cellular waste, calcium, and other substances. Over time, the plaque can harden and narrow the arterial lumen, restricting blood flow. The LAD artery is particularly susceptible to atherosclerosis due to its critical role in myocardial perfusion.
2. Smoking: Tobacco smoke contains numerous toxic chemicals that can damage the endothelial lining of blood vessels, promoting inflammation and the formation of atherosclerotic plaque. Smoking is a significant risk factor for LAD artery blockage and cardiovascular disease. It accelerates the progression of atherosclerosis and increases the likelihood of blood clot formation.
3. High Cholesterol: Elevated levels of LDL (low-density lipoprotein) cholesterol, often referred to as “bad” cholesterol, contribute to the development of atherosclerosis. LDL cholesterol can infiltrate the arterial walls, triggering an inflammatory response and promoting plaque formation. Individuals with high cholesterol levels are at increased risk of LAD artery blockage and coronary artery disease.
4. Hypertension: High blood pressure imposes excessive stress on the arterial walls, leading to endothelial dysfunction and arterial remodeling. Chronic hypertension accelerates the progression of atherosclerosis and increases the likelihood of plaque rupture and thrombosis. Proper blood pressure management is essential for preserving the integrity of the LAD artery and preventing blockage.
5. Diabetes Mellitus: Diabetes is a metabolic disorder characterized by elevated blood sugar levels. Prolonged hyperglycemia can damage blood vessels and impair endothelial function, predisposing individuals to atherosclerosis and cardiovascular complications. Diabetic patients are at increased risk of LAD artery blockage and myocardial infarction.
6. Sedentary Lifestyle: Physical inactivity is a significant risk factor for cardiovascular disease, including LAD artery blockage. Regular exercise helps maintain optimal cardiovascular health by promoting weight management, improving lipid profiles, and enhancing endothelial function. Sedentary individuals are more likely to develop atherosclerosis and experience coronary events.
7. Poor Dietary Habits: A diet high in saturated fats, trans fats, refined carbohydrates, and sodium contributes to dyslipidemia, insulin resistance, and hypertension—all of which are risk factors for LAD artery blockage. A balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats can mitigate the risk of cardiovascular disease.
8. Obesity: Excess body weight, especially abdominal obesity, is associated with insulin resistance, dyslipidemia, inflammation, and hypertension—key drivers of atherosclerosis and LAD artery blockage. Obesity increases the workload on the heart and exacerbates cardiovascular risk factors, necessitating comprehensive lifestyle interventions.
9. Genetic Predisposition: While lifestyle factors play a significant role in the development of LAD artery blockage, genetic predispositions also contribute to individual susceptibility. Familial hypercholesterolemia, familial combined hyperlipidemia, and other inherited lipid disorders can accelerate the progression of atherosclerosis and increase the risk of coronary artery disease.
10. Stress and Psychosocial Factors: Chronic stress, depression, anxiety, and social isolation have been linked to adverse cardiovascular outcomes, including LAD artery blockage. Psychological distress can trigger inflammation, dysregulate the autonomic nervous system, and promote unhealthy coping behaviors such as smoking, overeating, and sedentary behavior.
Conclusion
LAD artery blockage is a serious cardiovascular condition with potentially life-threatening consequences. While certain risk factors such as genetics cannot be modified, many contributing factors are modifiable through lifestyle interventions and medical management. By addressing risk factors such as smoking, high cholesterol, hypertension, diabetes, sedentary behavior, poor dietary habits, obesity, and psychosocial stress, individuals can reduce their likelihood of developing LAD artery blockage and improve their overall cardiovascular health. A multidisciplinary approach involving healthcare professionals, lifestyle modifications, and patient education is essential for mitigating the burden of LAD artery disease and enhancing long-term outcomes.