Cholesterol-lowering medications, also known as statins, play a crucial role in managing cardiovascular health by reducing the levels of LDL (low-density lipoprotein) cholesterol in the blood. However, concerns about potential side effects, particularly on the liver, have led to discussions and research about which cholesterol drug is safest for liver function. In this article, we will explore the various types of cholesterol-lowering drugs, their effects on liver health, and which ones are considered safest for individuals concerned about liver function.
Understanding Cholesterol and Its Management
Before delving into the specifics of cholesterol-lowering medications, it’s important to understand the role of cholesterol in the body and why its management is crucial for overall health. Cholesterol is a fatty substance that is essential for building cells and producing certain hormones. However, elevated levels of LDL cholesterol, often referred to as “bad” cholesterol, can lead to plaque buildup in the arteries, increasing the risk of heart disease and stroke.
To manage cholesterol levels, healthcare providers often recommend lifestyle changes such as a healthy diet, regular exercise, and weight management. In cases where lifestyle modifications are insufficient, medications such as statins may be prescribed to lower LDL cholesterol levels and reduce cardiovascular risk.
Types of Cholesterol-Lowering Medications
There are several types of cholesterol-lowering medications available, each with its mechanism of action and potential impact on liver function. These medications include:
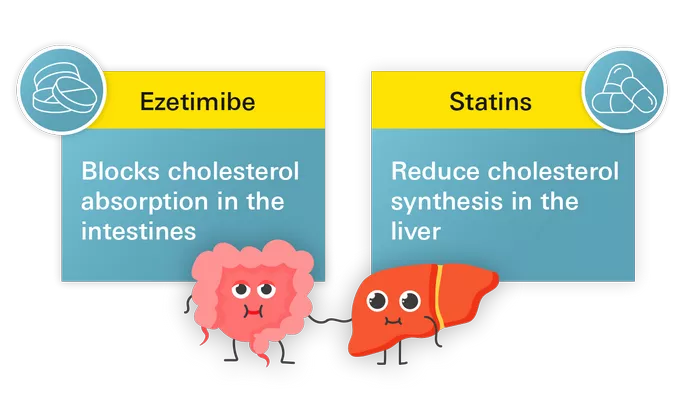
1. Statins: Statins are the most commonly prescribed cholesterol-lowering drugs. They work by blocking an enzyme in the liver that is involved in cholesterol production. Examples of statins include atorvastatin (Lipitor), simvastatin (Zocor), and rosuvastatin (Crestor).
2. Ezetimibe: Ezetimibe (Zetia) is a medication that reduces the absorption of cholesterol from the diet. It is often used in combination with statins to further lower LDL cholesterol levels.
3. PCSK9 Inhibitors: PCSK9 inhibitors are a newer class of medications that work by increasing the liver’s ability to remove LDL cholesterol from the blood. Examples include evolocumab (Repatha) and alirocumab (Praluent).
4. Bile Acid Sequestrants: These medications, such as cholestyramine (Questran) and colesevelam (Welchol), work by binding to bile acids in the intestine, leading to increased excretion of cholesterol.
5. Fibrates: Fibrates, such as fenofibrate (TriCor) and gemfibrozil (Lopid), primarily target triglyceride levels but can also have a modest effect on LDL cholesterol.
Safety Considerations for Liver Function
Liver function is a critical consideration when prescribing cholesterol-lowering medications, as some drugs can affect liver enzymes and potentially lead to liver damage. Monitoring liver function tests, including alanine aminotransferase (ALT) and aspartate aminotransferase (AST) levels, is important for patients taking these medications.
Among the cholesterol-lowering drugs, statins have been extensively studied regarding their impact on liver function. While they can cause mild elevations in liver enzymes in some individuals, severe liver damage is rare. Ezetimibe and PCSK9 inhibitors have also shown favorable safety profiles regarding liver function.
On the other hand, bile acid sequestrants and fibrates may have a higher risk of affecting liver enzymes, although serious liver problems are uncommon with these medications.
Choosing the Safest Cholesterol Drug for Liver Health
When considering which cholesterol drug is safest for liver function, several factors come into play:
1. Baseline Liver Health: Patients with pre-existing liver conditions may require closer monitoring when taking cholesterol-lowering medications. A thorough assessment of liver function before starting treatment is essential.
2. Drug Interactions: Some cholesterol-lowering drugs can interact with other medications, including those metabolized by the liver. Healthcare providers must consider potential drug interactions when prescribing these medications.
3. Individual Risk Factors: Each patient’s overall health status, including factors such as age, other medical conditions, and medication history, influences the choice of cholesterol-lowering medication.
4. Monitoring: Regular monitoring of liver function tests is crucial for patients taking cholesterol-lowering medications, especially during the initial stages of treatment and when adjusting doses.
Conclusion
In conclusion, while all cholesterol-lowering medications have the potential to affect liver function to some extent, statins, ezetimibe, and PCSK9 inhibitors are generally considered safer options with a low risk of serious liver problems. However, individualized treatment plans, careful monitoring, and collaboration between patients and healthcare providers are essential for optimizing cholesterol management while safeguarding liver health.