Cholesterol levels play a crucial role in maintaining overall health, especially cardiovascular health. Understanding what constitutes normal cholesterol levels across different age groups is essential for managing and preventing various heart-related conditions. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the specifics of normal cholesterol levels based on age, including recommended ranges and factors that can influence cholesterol levels.
Understanding Cholesterol: A Brief Overview
Cholesterol is a fatty substance produced by the liver and also obtained from certain foods. It is essential for building cell membranes, producing hormones, and aiding in the digestion of fats. However, elevated levels of cholesterol, particularly low-density lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol, can lead to the buildup of plaque in the arteries, increasing the risk of heart disease and stroke.
Cholesterol levels are typically measured through a blood test known as a lipid panel. This test measures various types of cholesterol, including:
1. Total Cholesterol: This includes both LDL cholesterol (often referred to as “bad” cholesterol) and high-density lipoprotein (HDL) cholesterol (“good” cholesterol).
2. LDL Cholesterol: This type of cholesterol contributes to plaque buildup in the arteries.
3. HDL Cholesterol: HDL cholesterol helps remove LDL cholesterol from the bloodstream, reducing the risk of artery blockages.
4. Triglycerides: These are another type of fat found in the blood. Elevated triglyceride levels can also increase the risk of heart disease.
Normal Cholesterol Levels by Age
Cholesterol levels can vary based on age, sex, genetics, and lifestyle factors. The following are general guidelines for normal cholesterol levels based on age:
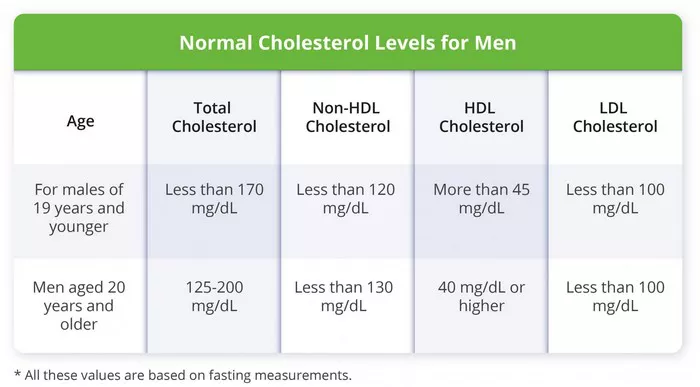
Children (Ages 2-19):
1. Total Cholesterol: Less than 170 mg/dL
2. LDL Cholesterol: Less than 110 mg/dL
3. HDL Cholesterol: Greater than 45 mg/dL
4. Triglycerides: Less than 75 mg/dL (ages 0-9), less than 90 mg/dL (ages 10-19)
Adults (Ages 20-39):
1. Total Cholesterol: Less than 200 mg/dL
2. LDL Cholesterol: Less than 130 mg/dL
3. HDL Cholesterol: Greater than 40 mg/dL (men), greater than 50 mg/dL (women)
4. Triglycerides: Less than 150 mg/dL
Adults (Ages 40-59):
1. Total Cholesterol: Less than 200 mg/dL
2. LDL Cholesterol: Less than 130 mg/dL
3. HDL Cholesterol: Greater than 40 mg/dL (men), greater than 50 mg/dL (women)
4. Triglycerides: Less than 150 mg/dL
Adults (Ages 60 and older):
1. Total Cholesterol: Less than 200 mg/dL
2. LDL Cholesterol: Less than 130 mg/dL
3. HDL Cholesterol: Greater than 40 mg/dL (men), greater than 50 mg/dL (women)
4. Triglycerides: Less than 150 mg/dL
Factors Affecting Cholesterol Levels
Several factors can influence cholesterol levels, including:
1. Diet: Consuming a diet high in saturated and trans fats can increase LDL cholesterol levels.
2. Physical Activity: Regular exercise can help raise HDL cholesterol levels and lower LDL cholesterol levels.
3. Weight: Being overweight or obese can lead to higher LDL cholesterol and triglyceride levels.
4. Genetics: Family history plays a significant role in cholesterol levels. Some individuals may have genetically high cholesterol levels despite a healthy lifestyle.
5. Smoking: Smoking can lower HDL cholesterol levels and damage blood vessels, increasing the risk of plaque buildup.
Managing Cholesterol Levels
Maintaining healthy cholesterol levels is crucial for overall heart health. Here are some tips for managing cholesterol levels:
1. Eat a Healthy Diet: Focus on consuming fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats such as those found in olive oil and nuts. Limit intake of saturated and trans fats.
2. Exercise Regularly: Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise per week.
3. Maintain a Healthy Weight: Losing excess weight can help improve cholesterol levels.
4. Quit Smoking: If you smoke, quitting can have a positive impact on cholesterol levels and overall cardiovascular health.
5. Limit Alcohol Intake: Excessive alcohol consumption can raise triglyceride levels. Limit alcohol intake to moderate levels.
Consulting a Healthcare Professional
It’s essential to consult a healthcare professional for personalized guidance on managing cholesterol levels. They can perform lipid panels, assess overall heart health, and recommend lifestyle changes or medications if necessary.
Conclusion
Understanding normal cholesterol levels by age is key to maintaining optimal cardiovascular health. By adopting a healthy lifestyle, including a nutritious diet, regular exercise, maintaining a healthy weight, and avoiding smoking and excessive alcohol consumption, individuals can help manage their cholesterol levels and reduce their risk of heart disease and stroke. Regular monitoring and guidance from healthcare professionals are vital for overall heart health and well-being.