Coronary heart disease (CHD), also known as coronary artery disease (CAD), is a condition that affects millions of people worldwide. It occurs when the coronary arteries, which supply oxygen-rich blood to the heart muscle, become narrowed or blocked due to the buildup of plaque—a combination of cholesterol, calcium, and other substances. This narrowing or blockage can lead to chest pain (angina), heart attacks, and other serious cardiovascular events. One of the common treatments for coronary heart disease is the use of stents. In this article, we will delve into the details of how stents work to treat CHD, their types, benefits, risks, and the overall impact on patients’ quality of life.
What Are Stents?
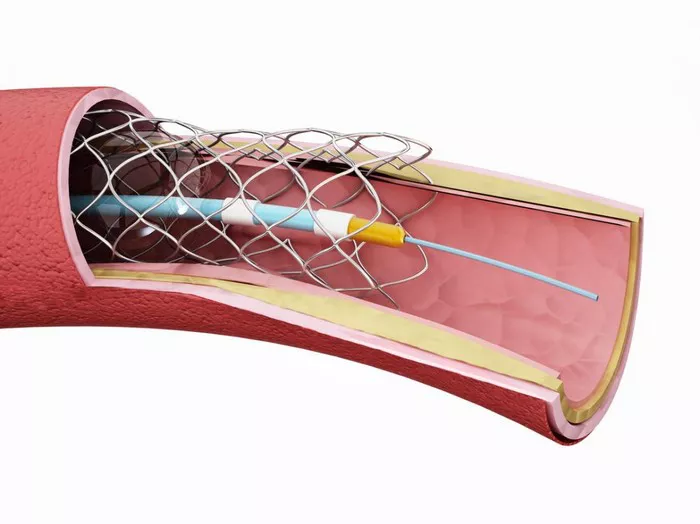
Stents are small, expandable tubes typically made of metal (such as stainless steel or cobalt-chromium) or polymer materials. They are designed to be inserted into narrowed or blocked coronary arteries to help keep them open and restore blood flow to the heart muscle. Stents act as scaffolds, providing structural support to prevent arteries from collapsing or becoming blocked again.
Types of Stents
There are two main types of stents used in the treatment of coronary heart disease: bare-metal stents (BMS) and drug-eluting stents (DES).
1. Bare-Metal Stents (BMS): These stents are made of metal and do not contain any medication. They work by physically holding open the blocked artery. While effective in improving blood flow, bare-metal stents have a higher risk of restenosis (re-narrowing of the artery) compared to drug-eluting stents.
2. Drug-Eluting Stents (DES): These stents are coated with medications that help prevent the growth of scar tissue inside the artery. This reduces the risk of restenosis and improves long-term outcomes. DES are the preferred choice in many cases due to their lower restenosis rates.
How Do Stents Treat Coronary Heart Disease?
The placement of stents is typically done through a minimally invasive procedure called percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) or angioplasty. Here is an overview of how stents treat coronary heart disease:
1. Diagnosis and Assessment: Before stent placement, patients undergo diagnostic tests such as coronary angiography to identify the location and severity of coronary artery blockages. This information helps cardiologists determine the appropriate treatment strategy.
2. Angioplasty: During the angioplasty procedure, a catheter with a deflated balloon at its tip is inserted into the blocked artery. The balloon is then inflated to compress the plaque against the artery walls, widening the artery and restoring blood flow. This process is known as balloon angioplasty.
3. Stent Placement: After the balloon angioplasty, the stent is placed in the newly widened artery. The stent is delivered to the site of the blockage on a balloon catheter. When the balloon is inflated, the stent expands and locks into place, holding the artery open. The balloon is then deflated and removed, leaving the stent in position.
4. Healing and Recovery: Once the stent is in place, the inner lining of the artery begins to heal around it. Over time, the stent becomes integrated into the artery wall, providing long-term support and maintaining improved blood flow to the heart.
Benefits of Stents in Treating Coronary Heart Disease
Stents offer several benefits in the treatment of coronary heart disease:
1. Improved Blood Flow: By keeping narrowed arteries open, stents restore adequate blood flow to the heart muscle, relieving symptoms such as chest pain and reducing the risk of heart attacks.
2. Minimally Invasive: Stent placement is a minimally invasive procedure compared to traditional open-heart surgery. It involves smaller incisions, shorter recovery times, and reduced risk of complications.
3. Customizable Treatment: Stents come in different sizes and types, allowing cardiologists to tailor the treatment to each patient’s specific needs based on the location and severity of coronary artery blockages.
4. Long-Term Effectiveness: Drug-eluting stents, in particular, have shown to be effective in reducing the need for repeat procedures (such as revascularization) due to their ability to prevent restenosis.
Risks and Considerations
While stents are generally safe and effective, there are potential risks and considerations associated with their use:
1. Restenosis: In some cases, the treated artery may narrow again over time, leading to restenosis. This risk is higher with bare-metal stents compared to drug-eluting stents.
2. Stent Thrombosis: Rarely, blood clots (thrombosis) can form inside the stent, potentially causing a heart attack or other complications. To reduce this risk, patients are often prescribed antiplatelet medications (such as aspirin and clopidogrel) after stent placement.
3. Allergic Reactions: Some patients may have allergic reactions to the stent materials or the medications used in drug-eluting stents. It’s essential for healthcare providers to consider individual patient factors and medical history when selecting stents.
4. Follow-Up Care: Patients who receive stents require regular follow-up appointments with their cardiologists to monitor stent function, assess blood flow, and manage risk factors such as high blood pressure, diabetes, and high cholesterol.
Conclusion
Stents play a crucial role in the management of coronary heart disease by restoring blood flow to narrowed or blocked arteries. They offer significant benefits in terms of symptom relief, minimally invasive treatment, and long-term effectiveness. While stents are associated with potential risks, advancements in stent technology and patient care have improved outcomes and quality of life for many individuals with coronary heart disease. It’s important for patients to work closely with their healthcare providers to understand the benefits, risks, and ongoing management of stents as part of their cardiovascular care plan.