Atrial fibrillation (Afib) and atrial flutter are two common types of cardiac arrhythmias that affect millions of people worldwide. While both conditions involve abnormal heart rhythms originating in the atria, they have distinct characteristics and potential risks. Understanding the differences and assessing their respective dangers is crucial for effective management and treatment. In this article, we delve into the debate of which is more dangerous – Afib or Aflutter – exploring their mechanisms, complications, management strategies, and long-term implications.
Understanding Atrial Fibrillation (Afib)
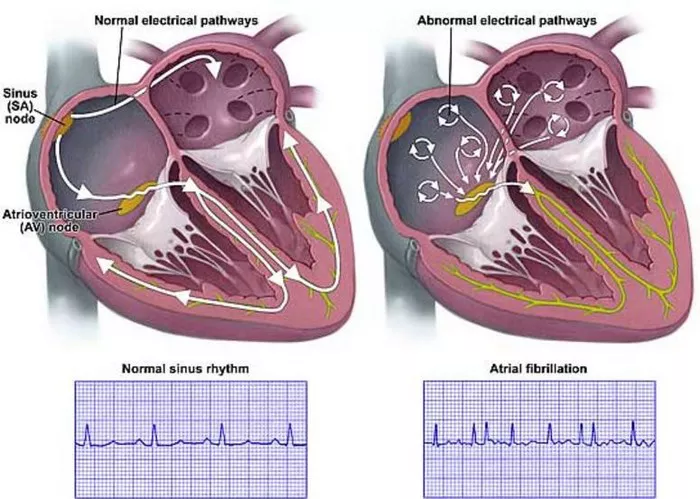
Atrial fibrillation is a cardiac arrhythmia characterized by rapid and irregular electrical impulses in the atria, leading to an erratic heartbeat. This condition can result in ineffective atrial contractions, leading to reduced cardiac output and potential complications such as stroke, heart failure, and other cardiovascular issues. Afib can be classified into several types based on its duration and onset:
1. Paroxysmal Afib: Occasional episodes that start and stop on their own within 7 days.
2. Persistent Afib: Episodes that last longer than 7 days and require medical intervention to restore normal rhythm.
3. Long-standing Persistent Afib: Continuous Afib lasting for more than a year.
4. Permanent Afib: Afib that persists despite attempts to restore normal rhythm.
Potential Dangers of Afib
Afib is associated with several potential dangers and complications:
1. Increased Stroke Risk: The irregular heartbeat in Afib can lead to blood clots forming in the atria, increasing the risk of stroke if these clots travel to the brain.
2. Heart Failure: Prolonged Afib can weaken the heart muscle and contribute to heart failure over time.
3. Cardiovascular Events: Afib is linked to an increased risk of other cardiovascular events such as myocardial infarction (heart attack) and cardiovascular mortality.
4. Reduced Quality of Life: Symptoms such as palpitations, fatigue, shortness of breath, and dizziness can significantly impact a person’s quality of life.
Management of Afib
The management of Afib involves several approaches aimed at controlling symptoms, reducing complications, and improving overall heart health:
1. Medications: Anticoagulants to reduce stroke risk, rhythm-control medications, and rate-control medications to manage heart rate.
2. Cardioversion: Electrical cardioversion or pharmacological cardioversion may be used to restore normal heart rhythm.
3. Ablation Therapy: Catheter ablation to target and eliminate abnormal electrical pathways in the heart.
4. Lifestyle Modifications: Healthy diet, regular exercise, stress management, and avoiding triggers such as alcohol and caffeine.
Understanding Atrial Flutter
Atrial flutter is another type of cardiac arrhythmia characterized by a rapid but regular heartbeat originating from the atria. Unlike Afib, atrial flutter typically presents as a regular pattern of atrial contractions at a rate higher than the normal heart rate. However, it can also lead to similar complications and risks if left untreated.
Potential Dangers of Atrial Flutter
While atrial flutter shares some similarities with Afib, it also presents unique dangers and complications:
1. Stroke Risk: Like Afib, atrial flutter can increase the risk of stroke due to the formation of blood clots in the atria.
2. Heart Failure: Prolonged atrial flutter can contribute to heart failure and other cardiovascular issues.
3. Symptoms: Atrial flutter can cause symptoms such as palpitations, chest discomfort, fatigue, and shortness of breath, affecting daily life and well-being.
4. Arrhythmia Progression: In some cases, atrial flutter can progress to atrial fibrillation or other more serious arrhythmias.
Management of Atrial Flutter
The management of atrial flutter is similar to that of Afib and includes:
1. Medications: Anticoagulants, rate-control medications, and rhythm-control medications as needed.
2. Cardioversion: Electrical or pharmacological cardioversion to restore normal heart rhythm.
3. Ablation Therapy: Catheter ablation to target and correct abnormal electrical pathways in the heart.
4. Lifestyle Changes: Healthy lifestyle habits to support heart health and reduce the risk of complications.
Comparing the Dangers: Afib vs. Aflutter
When comparing the dangers of Afib and atrial flutter, several factors come into play:
1. Stroke Risk: Both conditions carry an increased risk of stroke due to blood clot formation in the atria. The risk may vary based on individual factors such as age, overall health, and presence of other risk factors like hypertension and diabetes.
2. Complication Rates: While both Afib and atrial flutter can lead to similar complications such as heart failure and cardiovascular events, the rates and severity of these complications can vary among individuals.
3. Management Challenges: Managing Afib and atrial flutter requires a comprehensive approach that may include medications, procedures, and lifestyle changes. The effectiveness of treatment may vary depending on the specific arrhythmia pattern and underlying heart conditions.
4. Long-Term Outlook: The long-term outlook for individuals with Afib or atrial flutter depends on various factors, including how well the condition is managed, adherence to treatment plans, and overall heart health.
Conclusion
In conclusion, both atrial fibrillation (Afib) and atrial flutter are serious cardiac arrhythmias that require careful management and monitoring. While they share similarities in terms of potential dangers such as stroke risk and heart-related complications, the specific risks and management strategies may vary based on individual factors. Consultation with a healthcare provider is essential for accurate diagnosis, personalized treatment plans, and ongoing care to mitigate the dangers associated with these arrhythmias.