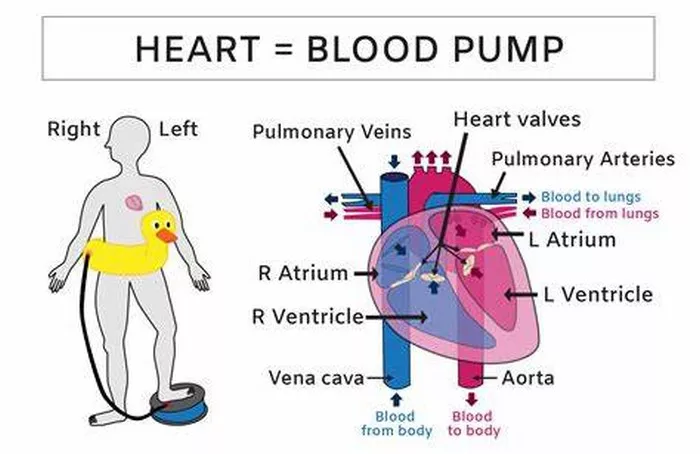
Heart function is a critical aspect of overall health and well-being, with the heart playing a vital role in circulating oxygen-rich blood throughout the body. When discussing heart function, one common metric used is the ejection fraction (EF), which measures the percentage of blood pumped out of the heart’s left ventricle with each heartbeat. A normal EF typically ranges from 55% to 70%. However, when the EF drops to 40%, it indicates a reduction in the heart’s pumping ability and can raise concerns about the individual’s longevity and quality of life.
Understanding Heart Function and Ejection Fraction
To understand the implications of a 40% heart function, it’s essential to delve into the basics of heart function and the significance of ejection fraction. The heart is a muscular organ responsible for pumping blood throughout the body, delivering oxygen and nutrients to tissues and organs while removing waste products. This pumping action is crucial for maintaining vital functions and overall health.
The ejection fraction specifically refers to the percentage of blood pumped out of the left ventricle of the heart during each contraction. It is a key indicator of heart health and function, with a lower EF indicating reduced pumping capacity. A 40% EF suggests that the heart is not effectively pumping as much blood as it should with each heartbeat, which can lead to various cardiovascular issues and impact life expectancy.
Implications of 40% Heart Function
A 40% heart function raises several important considerations regarding an individual’s health and longevity. Here are some key points to understand:
1. Reduced Cardiac Output: With a lower ejection fraction, the heart’s ability to pump an adequate amount of blood to meet the body’s demands is compromised. This can lead to symptoms such as fatigue, shortness of breath, and reduced exercise tolerance.
2. Risk of Heart Failure: A 40% EF is indicative of heart failure, a condition where the heart is unable to pump blood effectively. Heart failure can significantly impact quality of life and increase the risk of complications such as fluid buildup in the lungs (pulmonary edema) and other organs.
3. Increased Mortality Risk: Studies have shown that individuals with a 40% EF or lower have a higher risk of mortality compared to those with a normal EF. The severity of heart dysfunction, presence of underlying conditions, and response to treatment can influence life expectancy.
4. Treatment and Management: Managing heart function at 40% involves a comprehensive approach that may include medications, lifestyle modifications (such as a heart-healthy diet, regular exercise, and smoking cessation), monitoring for complications, and possibly interventions like implantable devices or surgery in advanced cases.
Factors Influencing Prognosis
While a 40% heart function is a concerning indication of cardiac health, several factors can influence an individual’s prognosis and life expectancy:
1. Underlying Conditions: The presence of underlying heart conditions such as coronary artery disease, hypertension, valvular heart disease, or previous heart attacks can impact prognosis and treatment outcomes.
2. Response to Treatment: How well an individual responds to medications, lifestyle changes, and other interventions can play a significant role in managing symptoms, improving heart function, and potentially extending life expectancy.
3. Comorbidities: The presence of other health issues such as diabetes, kidney disease, or respiratory conditions can complicate management and contribute to overall health outcomes.
4. Age and Overall Health: Age and general health status also influence prognosis. Younger individuals with fewer comorbidities may have better outcomes compared to older adults with multiple health challenges.
Improving Quality of Life
While the prognosis for individuals with 40% heart function can vary depending on multiple factors, there are strategies to improve quality of life and optimize health outcomes:
1. Medication Adherence: It’s crucial for individuals to adhere to prescribed medications, including those for heart function, blood pressure management, and cholesterol control, to help stabilize heart function and reduce complications.
2. Healthy Lifestyle: Adopting a heart-healthy lifestyle that includes a balanced diet, regular exercise, maintaining a healthy weight, managing stress, and avoiding tobacco and excessive alcohol can positively impact heart health and overall well-being.
3. Regular Monitoring: Routine medical check-ups, monitoring of heart function, and timely adjustments to treatment plans based on medical assessments are essential for managing heart function and addressing any changes or concerns promptly.
4. Support and Education: Accessing support from healthcare providers, cardiac rehabilitation programs, and educational resources can empower individuals with information, tools, and guidance to navigate their heart health journey effectively.
Conclusion
In conclusion, a 40% heart function indicates a reduced ejection fraction that can significantly impact cardiovascular health, quality of life, and life expectancy. While it raises concerns about heart failure and mortality risk, proactive management strategies focusing on medication adherence, healthy lifestyle choices, regular monitoring, and comprehensive medical care can help improve outcomes and enhance overall well-being for individuals with this condition. Early diagnosis, timely interventions, and ongoing support are key elements in optimizing heart function and promoting a better quality of life.