Left Ventricular Systolic Dysfunction (LVSD), also known as systolic heart failure, is a condition that affects the heart’s ability to pump blood effectively. This article delves into the medical intricacies of LVSD, including its causes, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment options, and prognosis.
What Is LVSD?
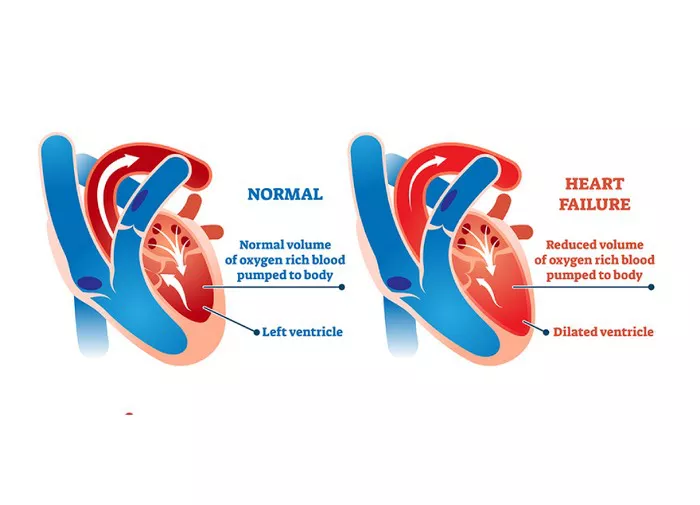
LVSD refers to a condition where the left ventricle of the heart, responsible for pumping oxygen-rich blood to the body, doesn’t contract properly during each heartbeat. This impaired contraction leads to reduced cardiac output, causing symptoms such as fatigue, shortness of breath, and fluid retention.
Causes of LVSD
LVSD can result from various underlying conditions, including:
1. Coronary Artery Disease (CAD): Blockages in the coronary arteries can lead to myocardial infarction (heart attack), causing damage to the heart muscle and impairing its function.
2. Hypertension (High Blood Pressure): Prolonged high blood pressure can strain the heart muscle, leading to LVSD over time.
3. Cardiomyopathy: This includes conditions where the heart muscle becomes weakened or stiff, affecting its ability to pump blood effectively.
4. Valvular Heart Disease: Malfunctioning heart valves can disrupt blood flow, contributing to LVSD.
5. Myocarditis: Inflammation of the heart muscle due to infections or autoimmune disorders can cause LVSD.
6. Congenital Heart Defects: Some individuals may be born with structural abnormalities in the heart that predispose them to LVSD later in life.
Symptoms of LVSD
The symptoms of LVSD can vary depending on the severity of the condition but commonly include:
- Fatigue and weakness, especially during physical activity
- Shortness of breath, particularly with exertion or when lying down
- Swelling in the legs, ankles, or abdomen due to fluid retention (edema)
- Persistent coughing or wheezing, especially at night
- Rapid or irregular heartbeat (palpitations)
- Reduced exercise tolerance
Diagnosis of LVSD
Diagnosing LVSD typically involves a combination of medical history assessment, physical examination, and diagnostic tests, including:
1. Echocardiogram: This imaging test uses sound waves to create a detailed picture of the heart’s structure and function, allowing healthcare providers to assess ventricular function and detect abnormalities.
2. Electrocardiogram (ECG or EKG): This test records the heart’s electrical activity, helping identify abnormal heart rhythms and signs of myocardial damage.
3. Blood Tests: These can reveal elevated levels of certain enzymes or proteins indicative of heart muscle damage or stress.
4.Cardiac MRI or CT Scan: These imaging techniques provide detailed images of the heart and can help diagnose underlying conditions contributing to LVSD.
Treatment Options for LVSD
The management of LVSD aims to alleviate symptoms, improve quality of life, and slow disease progression. Treatment strategies may include:
Medications:
1. ACE Inhibitors or ARBs: These drugs help relax blood vessels, reduce blood pressure, and improve heart function.
Beta-Blockers: They lower heart rate and blood pressure, reducing the heart’s workload.
Diuretics: These medications help eliminate excess fluid from the body, reducing edema and relieving symptoms of fluid retention.
2. Aldosterone Antagonists: They help regulate salt and water balance in the body, reducing strain on the heart.
Digoxin: In some cases, this medication may be used to improve heart function and reduce symptoms.
Lifestyle Modifications:
1. Dietary Changes: Following a heart-healthy diet low in sodium and saturated fats can help manage LVSD.
2. Regular Exercise: Engaging in supervised exercise programs can improve cardiovascular fitness and overall health.
3. Smoking Cessation: Quitting smoking is crucial in reducing further damage to the heart and blood vessels.
4. Weight Management: Maintaining a healthy weight can reduce strain on the heart.
Interventional Procedures:
1. Implantable Cardioverter-Defibrillator (ICD): This device can detect and correct abnormal heart rhythms, reducing the risk of sudden cardiac arrest.
2. Cardiac Resynchronization Therapy (CRT): In select cases, CRT devices can help synchronize the heart’s contractions, improving its efficiency.
Surgical Options:
1. Coronary Artery Bypass Grafting (CABG): For individuals with significant coronary artery disease, CABG surgery may improve blood flow to the heart muscle.
2. Heart Valve Repair or Replacement: In cases of valvular heart disease contributing to LVSD, surgical repair or replacement of the affected valve may be necessary.
Prognosis and Outlook
The prognosis for LVSD can vary depending on factors such as the underlying cause, the severity of the condition, and the individual’s response to treatment. With appropriate medical management, lifestyle modifications, and regular follow-up care, many individuals with LVSD can lead fulfilling lives and effectively manage their symptoms.
Conclusion
LVSD is a complex cardiovascular condition that requires comprehensive evaluation, timely diagnosis, and multidisciplinary management. Through a combination of medication, lifestyle changes, and, in some cases, interventional or surgical interventions, healthcare providers can help improve outcomes and enhance the quality of life for individuals living with LVSD.