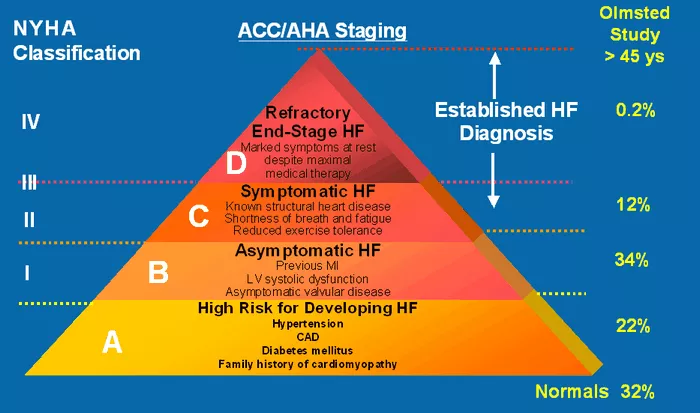
Heart failure is a serious medical condition that affects millions of people worldwide. It occurs when the heart is unable to pump blood efficiently, leading to symptoms such as shortness of breath, fatigue, and swelling in the legs and abdomen. The severity of heart failure is often categorized into stages, with stage 4 representing the most advanced and severe form of the condition. In this article, we will explore what stage 4 heart failure entails and discuss life expectancy and prognosis for individuals diagnosed with this stage of heart failure.
Understanding Stage 4 Heart Failure
Stage 4 heart failure, also known as end-stage heart failure or advanced heart failure, is characterized by severe symptoms that significantly impact a person’s quality of life. At this stage, the heart’s pumping function is severely impaired, leading to persistent and debilitating symptoms despite optimal medical therapy. These symptoms may include:
- Severe shortness of breath, even at rest
- Inability to perform daily activities without experiencing symptoms
- Recurrent hospitalizations for heart failure exacerbations
- Marked limitations in physical activity
- Poor kidney function due to reduced blood flow
- Fluid retention leading to significant swelling (edema) in the legs, abdomen, and other parts of the body
- Fatigue and weakness
Patients with stage 4 heart failure often require advanced medical interventions, such as implantable devices like left ventricular assist devices (LVADs) or heart transplants, to improve their prognosis and quality of life. These interventions are considered when conventional treatments have not been effective in managing symptoms and improving heart function.
Life Expectancy in Stage 4 Heart Failure
The life expectancy for individuals with stage 4 heart failure varies depending on several factors, including the underlying cause of heart failure, the presence of other medical conditions, the individual’s overall health, and the effectiveness of medical treatments and interventions. It is important to note that stage 4 heart failure is a serious and life-threatening condition, and the prognosis can be challenging to predict with certainty.
1. Underlying Cause: The underlying cause of heart failure can influence life expectancy. For example, heart failure due to ischemic heart disease (coronary artery disease) may have a different prognosis compared to heart failure caused by cardiomyopathy or other structural heart diseases.
2. Medical History: Patients with a history of recurrent hospitalizations for heart failure exacerbations or other significant medical comorbidities, such as diabetes, kidney disease, or lung disease, may have a poorer prognosis.
3. Response to Treatment: The response to medical treatments and interventions, including medications, lifestyle modifications, and advanced therapies like LVADs or heart transplantation, can impact life expectancy. Patients who respond well to treatment and experience symptom improvement may have a better prognosis.
4. Quality of Life: The impact of heart failure on a person’s quality of life, including physical, emotional, and social aspects, can also influence life expectancy. Patients with severe symptoms and functional limitations may have a reduced life expectancy compared to those with milder symptoms and better functional status.
Prognosis and Advanced Therapies
Despite the challenges associated with stage 4 heart failure, advancements in medical technology and treatment options have improved outcomes for some patients. Advanced therapies such as LVADs and heart transplantation can extend life expectancy and improve quality of life for select individuals with stage 4 heart failure.
1. Left Ventricular Assist Devices (LVADs): LVADs are mechanical devices implanted in the chest to help the heart pump blood more effectively. They can be used as a bridge to transplantation for patients awaiting a heart transplant or as destination therapy for those who are not eligible for transplantation.
2. Heart Transplantation: Heart transplantation is considered the gold standard treatment for end-stage heart failure in eligible patients. It involves surgically replacing the diseased heart with a healthy donor heart. However, the availability of donor organs and eligibility criteria for transplantation can impact access to this treatment option.
3. Palliative Care: For patients with advanced heart failure who may not be candidates for advanced therapies or who choose a more conservative approach, palliative care can provide symptom management, emotional support, and assistance with end-of-life planning.
Conclusion
In conclusion, stage 4 heart failure represents the most advanced and severe form of the condition, characterized by debilitating symptoms and impaired heart function. Life expectancy in stage 4 heart failure is influenced by various factors, including the underlying cause, medical history, treatment response, and quality of life. Advanced therapies such as LVADs and heart transplantation can improve outcomes and extend life expectancy for some patients. However, it is essential for individuals with stage 4 heart failure to work closely with their healthcare providers to determine the most appropriate treatment plan based on their unique medical needs and goals of care.