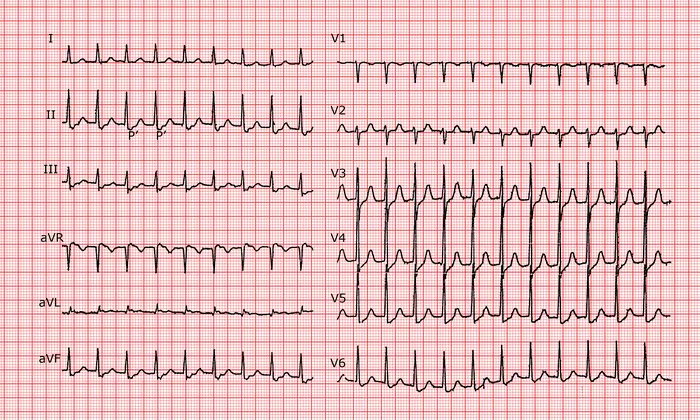
Atrioventricular nodal reentrant tachycardia (AVNRT) is a common type of supraventricular tachycardia characterized by a rapid heart rate originating from the atrioventricular (AV) node. It affects individuals of all ages and can lead to significant morbidity if not properly managed. One of the key aspects in understanding and managing AVNRT is identifying its triggers. In this article, we delve into the various factors that can precipitate AVNRT episodes, shedding light on the mechanisms behind this condition and strategies for prevention and treatment.
Understanding AVNRT
Before delving into the triggers of AVNRT, it’s crucial to have a basic understanding of the condition itself. AVNRT is a reentrant arrhythmia involving dual pathways within the AV node. These pathways, known as fast and slow pathways, create a loop of electrical activity that results in a rapid heartbeat. The precise triggers that initiate this reentrant circuit can vary among individuals, making it essential to identify and address specific triggers for effective management.
Common Triggers of AVNRT
Emotional Stress
Emotional stress is a well-recognized trigger for AVNRT episodes. The physiological response to stress, such as increased sympathetic activity and the release of stress hormones like adrenaline, can stimulate the AV node and facilitate the initiation of reentrant circuits. Patients with AVNRT may notice an increase in episodes during times of stress, anxiety, or emotional upheaval.
Caffeine and Stimulants
Caffeine, found in coffee, tea, energy drinks, and certain medications, is a known stimulant that can trigger AVNRT in susceptible individuals. Stimulants like caffeine enhance sympathetic activity, leading to increased heart rate and potential arrhythmias. Patients with AVNRT are often advised to limit their intake of caffeinated beverages and monitor their response to stimulant-containing substances.
Alcohol Consumption
Alcohol consumption is another common trigger for AVNRT episodes. The exact mechanism is not fully understood but is thought to involve alterations in autonomic tone and electrolyte balance. Some individuals may experience palpitations, rapid heartbeat, and AVNRT episodes after consuming alcohol. Limiting alcohol intake or avoiding it altogether can be beneficial for managing AVNRT.
Tobacco Use
Tobacco use, particularly smoking, has been associated with an increased risk of arrhythmias, including AVNRT. The nicotine in tobacco products can stimulate the sympathetic nervous system and promote arrhythmogenicity. Quitting smoking and avoiding exposure to secondhand smoke are important steps in reducing the triggers for AVNRT.
Medications
Certain medications can trigger or exacerbate AVNRT in susceptible individuals. These may include stimulants, decongestants, some asthma medications, and certain over-the-counter cold remedies. Patients with AVNRT should inform their healthcare providers about all medications they are taking to assess potential triggers and make necessary adjustments.
Electrolyte Imbalances
Electrolyte imbalances, particularly low potassium (hypokalemia) and low magnesium (hypomagnesemia), can disrupt cardiac conduction and trigger arrhythmias like AVNRT. Patients with electrolyte abnormalities should receive appropriate treatment and monitoring to prevent arrhythmia recurrence.
Physical Activity and Exertion
Intense physical activity or exertion can sometimes trigger AVNRT episodes, especially in individuals with underlying heart conditions or predisposing factors. Vigorous exercise can stimulate sympathetic activity and alter cardiac conduction, potentially leading to arrhythmias. Patients with AVNRT may benefit from a tailored exercise plan and monitoring during physical activity.
Other Cardiac Conditions
Underlying cardiac conditions, such as structural heart defects, ischemic heart disease, or other arrhythmias, can increase the risk of AVNRT episodes. Identifying and managing these conditions is essential in comprehensive arrhythmia management and may help reduce the frequency of AVNRT triggers.
Hormonal Changes
Hormonal changes, such as those occurring during menstruation, pregnancy, or menopause, can influence cardiac function and electrical conduction, potentially triggering AVNRT in susceptible individuals. Women with AVNRT may notice fluctuations in symptom severity related to hormonal cycles and should discuss management strategies with their healthcare providers.
Sleep Disruptions
Sleep disruptions, including insufficient sleep, irregular sleep patterns, and sleep disorders like sleep apnea, can impact autonomic function and increase the risk of arrhythmias, including AVNRT. Addressing sleep quality and implementing strategies to improve sleep hygiene may help reduce triggers for AVNRT.
Management Strategies
Managing AVNRT involves a multifaceted approach that addresses both trigger identification and arrhythmia management. Strategies may include:
1. Trigger Avoidance: Educating patients about common triggers and lifestyle modifications, such as stress management techniques, dietary changes, and smoking cessation, can help reduce the frequency of AVNRT episodes.
2. Medication Management: Antiarrhythmic medications or beta-blockers may be prescribed to help control heart rate and rhythm in patients with recurrent AVNRT episodes. Individualized medication regimens and close monitoring are essential for optimal outcomes.
3. Catheter Ablation: In cases where medications are ineffective or not well-tolerated, catheter ablation may be recommended. This minimally invasive procedure targets and eliminates the abnormal electrical pathways responsible for AVNRT, offering a potential cure for eligible patients.
4. Lifestyle Modifications: Encouraging healthy lifestyle habits, such as regular exercise, balanced nutrition, adequate sleep, and stress management, can support overall cardiovascular health and reduce the likelihood of AVNRT triggers.
Conclusion
AVNRT is a common arrhythmia with various triggers that can precipitate episodes in susceptible individuals. Identifying and addressing these triggers are crucial steps in effective management and prevention of AVNRT-related morbidity. By understanding the mechanisms behind AVNRT triggers and implementing targeted management strategies, healthcare providers can improve patient outcomes and enhance quality of life for individuals living with this condition.