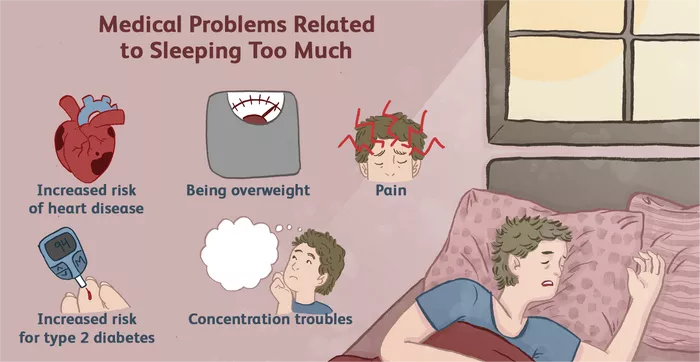
Sleep is a vital aspect of our overall health and well-being, with its quality and duration impacting various physiological functions. While adequate sleep is crucial for maintaining optimal health, excessive sleeping or hypersomnia can sometimes indicate underlying health issues, including potential heart problems. In this article, we delve into the connection between sleeping patterns and heart health, exploring the signs, causes, and implications of sleeping a lot in relation to heart conditions.
Understanding Hypersomnia and Its Potential Link to Heart Problems
Hypersomnia, characterized by excessive daytime sleepiness and prolonged nighttime sleep, can be a symptom of various medical conditions. When it comes to heart health, researchers have found associations between hypersomnia and cardiovascular diseases (CVDs), including coronary artery disease, heart failure, and hypertension. While not all instances of hypersomnia point directly to heart issues, understanding the potential link is crucial for early detection and intervention.
Exploring the Signs and Symptoms
1. Excessive Daytime Sleepiness (EDS): One of the primary symptoms of hypersomnia is EDS, where individuals may feel persistently sleepy during the day, regardless of how much they sleep at night. This can lead to difficulties in staying awake, concentrating, and completing daily tasks effectively.
2. Prolonged Nighttime Sleep: People with hypersomnia often sleep for extended periods at night, exceeding the recommended 7-9 hours for adults. Despite this prolonged sleep, they may not feel refreshed upon waking and may experience ongoing fatigue and drowsiness throughout the day.
3. Difficulty Waking Up: Another common sign is finding it challenging to wake up in the morning or feeling groggy even after sufficient hours of sleep. This can contribute to a cycle of oversleeping and daytime sleepiness, impacting overall productivity and well-being.
4. Increased Napping: Hypersomniacs may also exhibit a tendency to take frequent naps throughout the day, sometimes lasting for hours at a time. While napping can be beneficial in moderation, excessive daytime napping could indicate underlying sleep disorders or health issues.
The Role of Sleep Disorders in Heart Health
Several sleep disorders, such as obstructive sleep apnea (OSA) and insomnia, are known to influence heart health and contribute to hypersomnia-related symptoms. OSA, characterized by repeated interruptions in breathing during sleep, can lead to oxygen desaturation and increased stress on the cardiovascular system. Over time, untreated OSA raises the risk of developing hypertension, atrial fibrillation, and other heart conditions.
Insomnia, on the other hand, disrupts sleep continuity and quality, often resulting in fragmented sleep patterns and daytime sleepiness. Chronic insomnia has been linked to higher rates of CVDs, highlighting the intricate relationship between sleep disturbances and cardiovascular health.
Unpacking the Potential Causes of Hypersomnia in Heart Patients
While hypersomnia can manifest due to various factors, understanding the potential causes specific to heart patients is essential. Here are some key contributors to excessive sleepiness in individuals with heart problems:
1. Medication Side Effects: Certain medications prescribed for heart conditions, such as beta-blockers and diuretics, can cause drowsiness and fatigue as side effects. Patients experiencing excessive sleepiness should consult their healthcare providers to evaluate whether their medications contribute to hypersomnia.
2. Heart Failure and Reduced Cardiac Output: In heart failure patients, decreased cardiac output can lead to reduced oxygen delivery to tissues, including the brain. This can result in feelings of fatigue, lethargy, and increased sleep needs.
3. Sleep-Disordered Breathing: As mentioned earlier, conditions like obstructive sleep apnea are prevalent among individuals with heart disease. The repetitive nighttime awakenings and oxygen desaturations associated with sleep apnea can contribute to daytime sleepiness and hypersomnia.
4. Psychological Factors: Chronic stress, anxiety, and depression commonly coexist with heart problems and can significantly impact sleep quality and quantity. Mental health conditions may contribute to hypersomnia through altered sleep-wake patterns and heightened arousal during sleep.
Assessing the Risk and Impact of Hypersomnia on Heart Health
While occasional instances of oversleeping may not raise significant concerns, persistent hypersomnia warrants medical evaluation, especially for individuals with known heart conditions or risk factors. Here’s how healthcare professionals assess the risk and impact of hypersomnia on heart health:
Diagnostic Tools and Tests
1. Sleep Studies: Polysomnography (PSG) and home sleep apnea tests (HSATs) are valuable tools for diagnosing sleep disorders like sleep apnea and identifying patterns of hypersomnia. These studies measure various parameters during sleep, including breathing patterns, oxygen levels, and brain activity.
2. Cardiac Monitoring: For patients with suspected heart-related hypersomnia, cardiac monitoring tools such as electrocardiograms (ECGs) and Holter monitors may be used to assess heart rhythm, detect arrhythmias, and evaluate cardiac function during sleep.
3. Blood Tests: Laboratory tests, including lipid profiles, inflammatory markers, and brain natriuretic peptide (BNP) levels, can provide insights into cardiovascular risk factors and the presence of heart-related conditions contributing to hypersomnia.
Collaborative Care Approach
Managing hypersomnia in individuals with heart problems often requires a multidisciplinary approach involving cardiologists, sleep specialists, and mental health professionals. Treatment strategies may include:
1. Optimizing Medication Regimens: Adjusting medication doses or switching to alternative therapies with fewer sedative effects can help alleviate hypersomnia symptoms.
2. Continuous Positive Airway Pressure (CPAP) Therapy: For patients with sleep apnea, CPAP therapy is highly effective in improving sleep quality, reducing daytime sleepiness, and lowering cardiovascular risks.
3. Behavioral and Cognitive Therapies: Cognitive-behavioral therapy for insomnia (CBT-I) and stress-reduction techniques can address underlying psychological factors contributing to hypersomnia and promote healthier sleep habits.
4. Lifestyle Modifications: Encouraging regular exercise, maintaining a balanced diet, and practicing good sleep hygiene are integral components of managing hypersomnia and supporting overall heart health.
Navigating the Intersection of Sleep, Heart Health, and Overall Well-being
The relationship between sleep patterns, heart health, and overall well-being is complex and multifaceted. While excessive sleepiness can serve as a potential indicator of underlying heart problems, it’s essential to consider individual variations, medical history, and lifestyle factors when evaluating hypersomnia in clinical settings.
Empowering Patients Through Education and Awareness
Educating patients about the importance of healthy sleep habits, recognizing warning signs of sleep disorders, and fostering open communication with healthcare providers are crucial steps in promoting proactive heart care. By raising awareness and addressing sleep-related concerns early on, individuals can take proactive steps to optimize their sleep, manage heart risks, and enhance their quality of life.
Research Advances and Future Directions
Ongoing research efforts continue to explore the intricate connections between sleep, heart health, and disease prevention. Advancements in technology, such as wearable devices and telemedicine platforms, offer new avenues for monitoring sleep patterns, conducting virtual consultations, and delivering personalized interventions for patients with sleep-related issues and cardiovascular conditions.
Conclusion
In conclusion, while sleeping a lot can sometimes be a sign of heart problems, it is essential to approach hypersomnia within the broader context of an individual’s health and medical history. Collaborative efforts among healthcare professionals, patients, and caregivers play a pivotal role in identifying, managing, and addressing hypersomnia and its potential implications for heart health. By staying informed, proactive, and engaged in comprehensive care, individuals can navigate the intersection of sleep, heart health, and overall well-being more effectively.