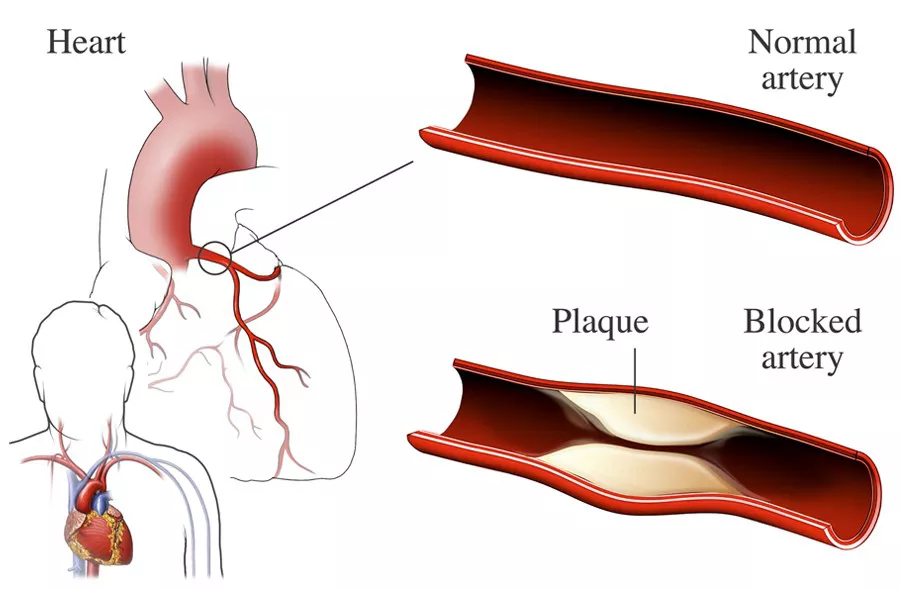
Clogged arteries, also known as atherosclerosis, occur when fatty deposits called plaques build up in the walls of arteries, leading to reduced blood flow. This condition is a major risk factor for heart disease and stroke, making it crucial to recognize its early signs and take preventive measures. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll delve into the early symptoms of clogged arteries, their causes, and strategies for prevention and treatment.
Understanding Clogged Arteries
Arteries are blood vessels that carry oxygen-rich blood from the heart to various parts of the body. When these arteries become clogged, it can disrupt the flow of blood and oxygen, leading to serious health complications. Atherosclerosis typically develops over time, starting with the accumulation of fatty substances, cholesterol, cellular waste, and calcium in the arterial walls.
Early Signs and Symptoms
1. Angina: One of the earliest signs of clogged arteries is angina, which manifests as chest pain or discomfort. This occurs when the heart muscle doesn’t receive enough oxygen due to reduced blood flow caused by narrowed arteries.
2. Shortness of Breath: As the arteries supplying blood to the lungs become narrowed, individuals may experience shortness of breath, especially during physical exertion or stress.
3. Fatigue: Reduced blood flow to vital organs can lead to generalized fatigue and weakness, as the body’s tissues and organs may not receive an adequate supply of oxygen and nutrients.
4. Leg Pain: Peripheral artery disease (PAD) is a common condition associated with clogged arteries in the legs. Symptoms include leg pain, cramping, numbness, or weakness, particularly during physical activity.
5. Cognitive Issues: Clogged arteries can also affect blood flow to the brain, leading to cognitive issues such as confusion, difficulty concentrating, memory problems, or even transient ischemic attacks (TIAs) or mini-strokes.
6. Erectile Dysfunction: In men, clogged arteries can contribute to erectile dysfunction (ED) due to impaired blood flow to the pelvic area.
7. Cold Extremities: Reduced circulation in the extremities, such as the hands and feet, can result in coldness, numbness, or tingling sensations.
Causes of Clogged Arteries
Several factors contribute to the development of clogged arteries, including:
1. High Cholesterol: Elevated levels of LDL cholesterol (“bad” cholesterol) can lead to the formation of plaques in the arteries.
2. High Blood Pressure: Hypertension puts added stress on arterial walls, promoting the accumulation of plaque.
3. Smoking: Tobacco smoke contains harmful chemicals that damage blood vessels and accelerate the progression of atherosclerosis.
4. Diabetes: Uncontrolled diabetes can lead to increased plaque formation and arterial damage.
5. Obesity: Excess body weight is associated with higher levels of cholesterol and inflammation, both of which contribute to clogged arteries.
6. Inactivity: Lack of physical activity can contribute to weight gain, high cholesterol, and other risk factors for atherosclerosis.
7. Poor Diet: A diet high in saturated fats, trans fats, and refined sugars can contribute to plaque buildup in the arteries.
Prevention and Treatment Strategies
1. Healthy Diet: Consuming a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats can help manage cholesterol levels and reduce the risk of clogged arteries.
2. Regular Exercise: Engaging in regular physical activity, such as brisk walking, jogging, cycling, or swimming, promotes cardiovascular health and helps maintain a healthy weight.
3. Smoking Cessation: Quitting smoking is one of the most effective ways to reduce the risk of atherosclerosis and its complications.
4. Blood Pressure Control: Monitoring and managing blood pressure through lifestyle changes and medication, if necessary, can help prevent arterial damage.
5. Cholesterol Management: Working with healthcare professionals to monitor cholesterol levels and using medications, if needed, can help control LDL cholesterol and prevent plaque formation.
6. Diabetes Management: Proper management of diabetes through medication, diet, exercise, and regular monitoring can reduce the risk of arterial damage.
7. Medication: In some cases, doctors may prescribe medications such as statins, blood thinners, or anti-hypertensive drugs to manage risk factors and prevent further progression of clogged arteries.
8. Surgical Interventions: In severe cases of clogged arteries, procedures such as angioplasty, stenting, or coronary artery bypass surgery may be necessary to restore blood flow to the affected areas.
Conclusion
Recognizing the early signs of clogged arteries is crucial for timely intervention and prevention of serious cardiovascular complications. By adopting a healthy lifestyle, managing risk factors, and seeking appropriate medical care, individuals can reduce their risk of developing atherosclerosis and improve their overall heart health. Regular monitoring, preventive screenings, and adherence to treatment plans are essential components of maintaining arterial health and well-being.