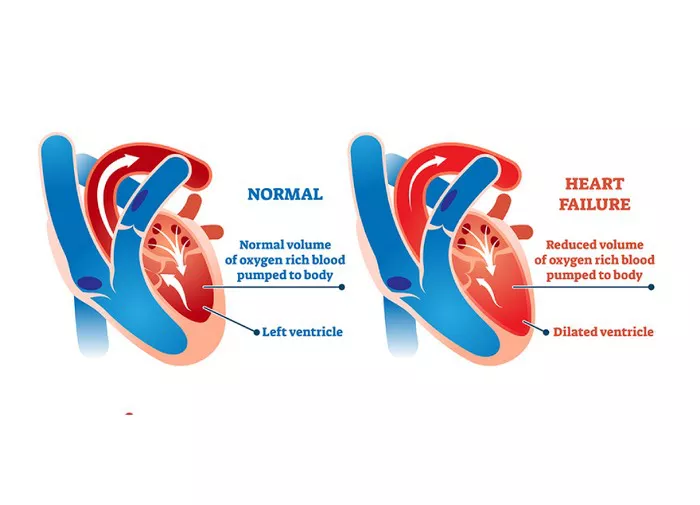
Preserved left ventricular systolic function refers to the ability of the left ventricle of the heart to contract and pump blood effectively while maintaining normal levels of ejection fraction (EF). This condition is significant in cardiovascular health as it indicates the heart’s ability to function optimally despite certain challenges or conditions. In this comprehensive article, we will delve into the specifics of preserved left ventricular systolic function, its clinical relevance, diagnostic criteria, causes, management, and implications for patient care.
Understanding Left Ventricular Systolic Function
Before diving into preserved left ventricular systolic function, it’s crucial to understand the role of the left ventricle in the cardiovascular system. The left ventricle is responsible for pumping oxygen-rich blood from the lungs to the rest of the body. Systolic function refers to the contraction phase of the cardiac cycle when the heart pumps blood out into circulation. This phase is essential for maintaining adequate cardiac output and tissue perfusion.
Left ventricular systolic function is typically assessed using echocardiography or other imaging modalities. One of the key parameters used to evaluate systolic function is the ejection fraction (EF), which measures the percentage of blood pumped out of the left ventricle with each contraction. A normal EF ranges between 50% and 70%, indicating good systolic function.
Defining Preserved Left Ventricular Systolic Function
Preserved left ventricular systolic function, also known as preserved ejection fraction (PEF) or diastolic heart failure with preserved ejection fraction (HFpEF), refers to a condition where the left ventricle maintains a normal or near-normal EF despite underlying cardiovascular issues. Unlike reduced EF, which is commonly seen in heart failure with reduced ejection fraction (HFrEF), preserved EF implies that the heart’s pumping ability is not significantly impaired.
Diagnostic Criteria for Preserved Left Ventricular Systolic Function
Diagnosing preserved left ventricular systolic function involves a comprehensive evaluation of cardiac structure, function, and hemodynamics. Key diagnostic criteria include:
1. Echocardiography: A crucial imaging tool used to assess left ventricular dimensions, wall thickness, EF, and diastolic function.
2. Clinical Symptoms: Patients may present with symptoms of heart failure such as dyspnea, fatigue, exercise intolerance, and fluid retention.
3. Laboratory Tests: Blood tests may reveal elevated levels of natriuretic peptides (BNP or NT-proBNP), indicating cardiac stress or dysfunction.
4. Cardiac Imaging: Other imaging modalities like cardiac MRI or CT may provide additional insights into cardiac structure and function.
5. Invasive Procedures: In certain cases, invasive tests such as cardiac catheterization may be performed to assess hemodynamics and coronary artery status.
Causes and Risk Factors
Preserved left ventricular systolic function can result from various underlying conditions and risk factors, including:
1. Hypertension: Chronic high blood pressure can lead to left ventricular hypertrophy and diastolic dysfunction, contributing to preserved EF.
2. Aging: The natural aging process can affect cardiac function, leading to diastolic dysfunction and preserved EF in older individuals.
3. Obesity and Metabolic Syndrome: Conditions like obesity, diabetes, and metabolic syndrome are associated with cardiac remodeling and diastolic dysfunction.
4. Coronary Artery Disease (CAD): Chronic coronary artery disease can impair diastolic function and contribute to preserved EF.
5. Valvular Heart Disease: Conditions such as aortic stenosis or mitral regurgitation can impact diastolic function and EF.
6. Cardiomyopathies: Certain types of cardiomyopathies, including hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (HCM) or restrictive cardiomyopathy, can lead to preserved EF.
7. Other Factors: Chronic kidney disease, atrial fibrillation, and pulmonary hypertension are additional factors that can contribute to preserved left ventricular systolic function.
Clinical Implications and Management
Preserved left ventricular systolic function has important clinical implications for patient management and outcomes. Some key points to consider include:
1. Treatment Challenges: Managing heart failure with preserved EF can be challenging as traditional heart failure therapies aimed at improving systolic function may not be as effective.
2. Focus on Diastolic Dysfunction: Since diastolic dysfunction plays a significant role in preserved EF, management strategies often focus on optimizing diastolic function and addressing underlying causes.
3. Lifestyle Modifications: Encouraging lifestyle changes such as weight management, regular exercise, and dietary modifications (e.g., low-sodium diet) can help improve overall cardiovascular health.
4. Medication Management: While certain medications like beta-blockers, ACE inhibitors, or ARBs may be used to manage symptoms and comorbidities, their efficacy in improving outcomes in HFpEF remains debated.
5. Comprehensive Care: Collaborative care involving cardiologists, primary care providers, and other healthcare professionals is essential for holistic management of patients with preserved left ventricular systolic function.
6. Monitoring and Follow-Up: Regular monitoring of symptoms, cardiac function, and comorbidities is crucial to assess treatment response and adjust management strategies accordingly.
Conclusion
Preserved left ventricular systolic function is a clinically significant condition characterized by the maintenance of normal or near-normal ejection fraction despite underlying cardiovascular issues. Understanding the diagnostic criteria, causes, risk factors, and management strategies for preserved EF is essential for healthcare professionals involved in the care of patients with heart failure and preserved EF. By addressing diastolic dysfunction, optimizing lifestyle factors, and providing comprehensive care, healthcare teams can improve outcomes and quality of life for individuals with preserved left ventricular systolic function.