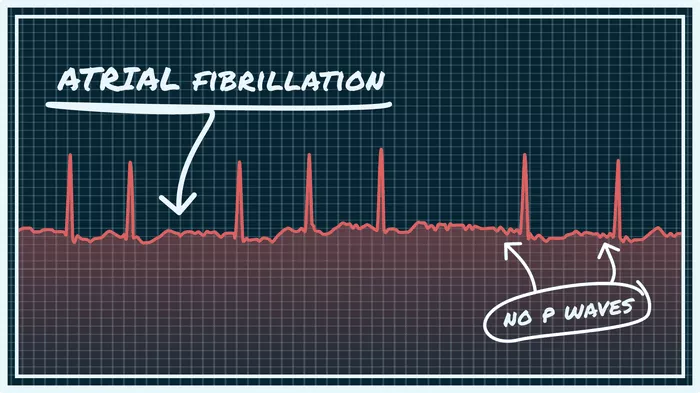
In recent years, the relationship between levothyroxine and atrial fibrillation (Afib) has garnered significant attention within the medical community. Atrial fibrillation (AFib) is a common heart rhythm disorder characterized by irregular and rapid heartbeats. It affects millions of people worldwide and is associated with an increased risk of stroke, heart failure, and other cardiovascular complications. Levothyroxine is a medication commonly used to treat hypothyroidism, a condition where the thyroid gland does not produce enough thyroid hormone. While levothyroxine is generally safe and effective when taken at the correct dose, there is concern that excessive use of this medication may lead to adverse effects, including the development of AFib.
Understanding Levothyroxine And Its Mechanism of Action
Levothyroxine is a synthetic form of thyroxine (T4), one of the main hormones produced by the thyroid gland. It plays a crucial role in regulating metabolism, energy production, and overall body function. When someone has hypothyroidism, their thyroid gland does not produce enough T4, leading to symptoms such as fatigue, weight gain, and cold intolerance.
Levothyroxine supplementation helps to restore normal thyroid hormone levels in the body, alleviating these symptoms and improving overall well-being.
The Link Between Hypothyroidism, Levothyroxine, And Atrial Fibrillation
Hypothyroidism has been associated with an increased risk of developing AFib. Thyroid hormones have a direct effect on the heart, influencing its rate and rhythm. In hypothyroidism, the reduced levels of thyroid hormones can lead to changes in the heart’s electrical activity, potentially predisposing individuals to arrhythmias such as AFib. By correcting hypothyroidism with levothyroxine therapy, the aim is to restore normal thyroid hormone levels and reduce the risk of cardiovascular complications.
However, there is a delicate balance when it comes to levothyroxine dosage. Taking too much levothyroxine can result in hyperthyroidism, a condition where thyroid hormone levels are elevated beyond the body’s requirements. Hyperthyroidism is also known to be a risk factor for developing AFib. Excessive thyroid hormone levels can lead to cardiac stress, altered heart function, and ultimately cardiac arrhythmias like AFib.
See Also: What Is Arrhythmia in Ecg
Clinical Evidence And Studies on Levothyroxine-Induced AFib
Several studies have investigated the relationship between levothyroxine use and the risk of developing AFib. One study published in the Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism found that among patients aged 65 years or older with newly diagnosed hypothyroidism, levothyroxine therapy was associated with a higher risk of AFib compared to those not receiving treatment. The study suggests that careful monitoring of thyroid hormone levels and appropriate dosing of levothyroxine are essential in this patient population to minimize the risk of AFib.
Another study published in the European Journal of Endocrinology highlighted the importance of individualized levothyroxine dosing based on factors such as age, weight, and underlying health conditions. The researchers found that older patients and those with pre-existing heart disease were more susceptible to developing AFib when exposed to excess thyroid hormone from levothyroxine therapy. Tailoring the dose of levothyroxine to each patient’s specific needs and regularly monitoring thyroid function parameters are crucial in preventing adverse cardiac events like AFib.
See Also: Can Heart Arrhythmia Cause Stroke
Clinical Management And Monitoring of Levothyroxine Therapy
For individuals taking levothyroxine for hypothyroidism, it is essential to work closely with a healthcare provider to determine the appropriate dosage and monitor thyroid hormone levels regularly. Healthcare providers may adjust the levothyroxine dose based on symptoms, thyroid function tests, and other clinical indicators to ensure that thyroid hormone levels remain within the normal range.
If there are concerns about the development of AFib or other cardiac issues while on levothyroxine therapy, further evaluation by a cardiologist may be necessary. An electrocardiogram (ECG) can help assess the heart’s electrical activity and detect any abnormal rhythms like AFib. Additionally, other cardiac tests such as echocardiography may be recommended to evaluate heart structure and function.
Conclusion
While levothyroxine is a valuable medication for treating hypothyroidism, excessive use of this medication can potentially increase the risk of developing AFib, especially in vulnerable populations such as older adults and those with underlying heart conditions. Close monitoring of thyroid hormone levels, individualized dosing, and collaboration between healthcare providers are essential in optimizing the benefits of levothyroxine therapy while minimizing the risk of cardiac complications like AFib. If you have any concerns about your levothyroxine treatment or experience symptoms suggestive of AFib, seek medical advice promptly for proper evaluation and management.