Introduction to Heart Failure
Heart failure (HF) is a disease caused by abnormal pumping function of the heart, resulting in the heart’s inability to meet the basic metabolic needs of the whole body. Common triggers include myocardial infarction, cardiomyopathy, myocarditis, etc.
Who Are The Most Susceptible Groups to Heart Failure?
Patients with hypertension, coronary heart disease, diabetes, chronic kidney disease, obesity, and patients with cardiomyopathy gene mutations or family history of myocardium are all high-risk groups for heart failure. Data show that nearly two-thirds of heart failure patients have a history of hypertension; 40% to 50% of heart failure patients have chronic kidney disease; about 30% of heart failure patients have type 2 diabetes, and once type 2 diabetes patients Symptoms of heart failure appear, the disease progresses quickly, the prognosis is poor, and the mortality rate is high
Explanation of The Different Types of Heart Failure
what Signs and Symptoms of Left-Sided Heart Failure:
- Shortness of breath (dyspnea), especially during
Key signs and symptoms specific to left-sided heart failure, including: - exertion or when lying flat.
- Persistent coughing or wheezing, often accompanied by pink, frothy sputum (pulmonary edema).Fatigue and weakness due to reduced cardiac output.Fluid retention leading to swelling in the legs, ankles, feet (edema), and sometimes in the abdomen (ascites).
- Rapid or irregular heartbeat (arrhythmias) due to changes in heart function.
what Signs and Symptoms of Right-Sided Heart Failure and Key signs and symptoms specific to right-sided heart failure, including:
- Swelling in the legs, ankles, feet, and abdomen (ascites) due to fluid retention
- Fatigue and weakness, often exacerbated by physical activity.
- Increased need to urinate at night (nocturia) due to fluid redistribution when lying down.
- Enlarged liver (hepatomegaly) and distended neck veins (jugular venous distension) due to impaired blood flow.
- Shortness of breath and difficulty breathing, particularly when lying flat (orthopnea) or during exertion.
How to Diagnostic And Evaluation
Overview of diagnostic tests and evaluations used to diagnose heart failure, including:
- Physical examination and medical history review.
- Echocardiogram (ultrasound of the heart) to assess heart structure and function.
- Chest X-ray to evaluate heart size and detect fluid buildup in the lungs.
- Blood tests to assess kidney function, electrolyte level
Management Strategies
Lifestyle modifications, including dietary changes (low-sodium diet), fluid restriction, and regular exercise.
Medications such as ACE inhibitors, beta-blockers, diuretics, and aldosterone antagonists to improve heart function and manage symptoms.
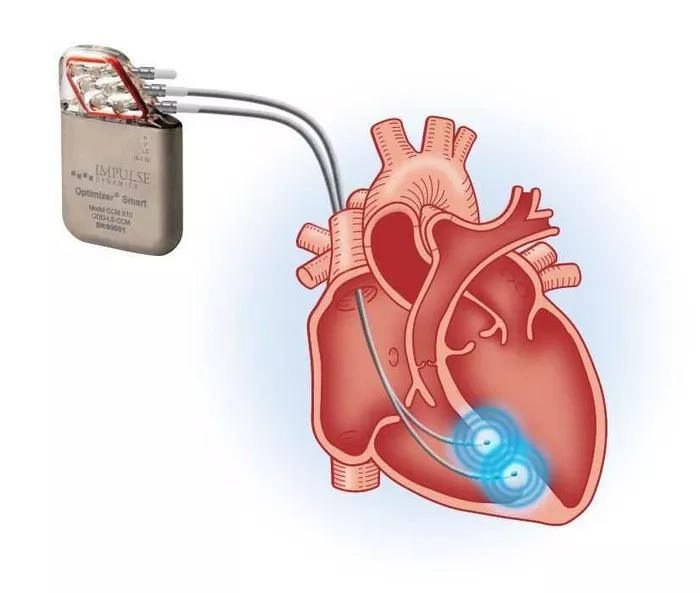
Device therapies (e.g., pacemakers, implantable cardioverter-defibrillators) and surgical interventions (e.g., heart valve repair or replacement) for specific cases.
Monitoring and follow-up care to track progress and adjust treatment plans as needed.
Educational Resources And Support
Information on patient education resources, support groups, and lifestyle management programs for individuals living with heart failure.
Importance of regular medical follow-ups and communication with healthcare providers for optimal heart failure management.
Conclusion
Summary of key points regarding signs, symptoms, diagnosis, and management of left and right-sided heart failure.
Encouragement for individuals to seek timely medical evaluation and ongoing support for heart failure management.
FAQs
How long can one live with first-stage heart failure?
Life expectancy in first-stage heart failure can vary significantly depending on various factors such as the underlying cause, overall health, lifestyle modifications, and adherence to treatment plans. With appropriate medical care and lifestyle changes, many individuals with first-stage heart failure can live for many years and maintain a good quality of life.
Can heart failure be cured?
Heart failure is a chronic condition that typically cannot be cured in the traditional sense. However, with proper management, including medications, lifestyle changes, and sometimes surgical interventions, the symptoms and progression of heart failure can be controlled and quality of life can be improved significantly.
What are the symptoms of heart failure?
Shortness of breath (dyspnea), especially during exertion or when lying flat.
Persistent coughing or wheezing, often with pink, frothy sputum.
Fatigue and weakness.
Swelling in the legs, ankles, feet, and sometimes in the abdomen (edema).
Rapid or irregular heartbeat (arrhythmias).
Difficulty concentrating or feeling confused.
Decreased exercise tolerance.
How do you know if you have symptoms of heart disease?
Chest pain, discomfort, or pressure (angina);Shortness of breath, especially during exertion;Irregular heartbeat (arrhythmias);Dizziness or lightheadedness.
Pain, numbness, or tingling in the arms, shoulders, neck, jaw, or back.Cold sweats.
How do you know if your blood vessels are blocked?
Signs of blocked blood vessels (atherosclerosis) may include:
Chest pain or discomfort (angina) that may worsen with physical activity or stress.
Shortness of breath.Pain, numbness, or weakness in the legs or arms, especially during physical activity.