Irregular heartbeat, also known as arrhythmia, is a condition that affects the rhythm of your heart. While occasional irregular heartbeats are common and usually harmless, persistent or severe arrhythmias can be dangerous and even life-threatening. In this article, we’ll explore why irregular heartbeat is dangerous and the potential risks associated with this condition.
Understanding Arrhythmia
Before delving into the dangers of irregular heartbeat, let’s first understand what arrhythmia is and how it affects the heart.
Arrhythmia refers to any abnormality in the rhythm of your heartbeat. Your heart has an electrical system that controls its rhythm, ensuring that it beats at a steady and regular pace. However, in arrhythmia, this electrical system malfunctions, causing the heart to beat too fast, too slow, or irregularly.
Types of Arrhythmias
There are several types of arrhythmias, each with its own characteristics and potential risks. Some common types include:
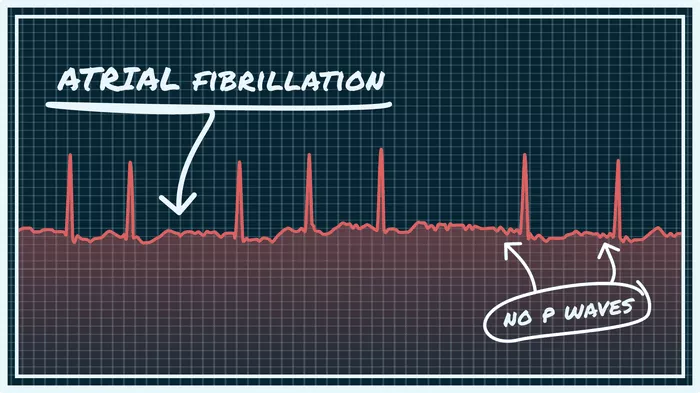
Atrial Fibrillation (AFib): This is one of the most common types of arrhythmia, characterized by rapid and irregular heartbeat originating in the atria, the heart’s upper chambers.
Bradycardia: This occurs when the heart beats too slowly, leading to insufficient blood flow to the body.
Tachycardia: This refers to a heart rate that is excessively fast, which can also disrupt normal blood flow.
Why Irregular Heartbeat Is Dangerous
Now, let’s delve into why irregular heartbeat can be dangerous and pose serious health risks:
Reduced Blood Flow: In arrhythmias where the heart beats too fast or too slow, there can be a decrease in the efficiency of blood flow throughout the body. This reduced blood flow can lead to symptoms such as dizziness, fatigue, and shortness of breath. In severe cases, it can result in organ damage due to inadequate oxygen supply.
Blood Clot Formation: Certain types of arrhythmias, such as atrial fibrillation (AFib), can cause blood to pool in the heart’s chambers, increasing the risk of blood clot formation. If a blood clot travels to vital organs such as the brain, it can cause a stroke, which is a medical emergency with potentially devastating consequences.
Heart Failure: Prolonged irregular heartbeat can weaken the heart muscle over time, leading to a condition known as heart failure. In heart failure, the heart is unable to pump blood effectively, causing fluid buildup in the lungs and other parts of the body. This can result in symptoms like swelling of the legs, difficulty breathing, and fatigue.
Sudden Cardiac Arrest: In some cases, certain types of arrhythmias can trigger a sudden and life-threatening condition called cardiac arrest. During cardiac arrest, the heart’s electrical activity becomes chaotic, leading to a cessation of blood flow to the body. Without immediate medical intervention such as CPR and defibrillation, cardiac arrest can be fatal within minutes.
Increased Risk of Stroke: As mentioned earlier, certain arrhythmias, particularly atrial fibrillation, significantly increase the risk of stroke due to blood clot formation. Strokes can cause permanent neurological damage and have long-term consequences on a person’s quality of life.
Risk Factors for Irregular Heartbeat
Several factors can contribute to the development of irregular heartbeat and increase the associated risks. These risk factors include:
Age: The risk of arrhythmias increases with age, especially for those over 65 years old.
Heart Disease: Conditions such as coronary artery disease, heart valve disorders, and prior heart attacks can predispose individuals to arrhythmias.
High Blood Pressure: Hypertension can strain the heart and disrupt its electrical system, leading to arrhythmias.
Diabetes: Uncontrolled diabetes can damage blood vessels and nerves, affecting the heart’s electrical function.
Lifestyle Factors: Smoking, excessive alcohol consumption, and a sedentary lifestyle can contribute to the development of arrhythmias.
Family History: A family history of heart rhythm disorders can increase your risk of experiencing irregular heartbeats.
Diagnosis And Treatment
If you experience symptoms of irregular heartbeat such as palpitations, dizziness, chest pain, or fainting spells, it’s crucial to seek medical attention promptly. A healthcare provider can perform various tests, including electrocardiograms (ECGs), Holter monitoring, and echocardiograms, to diagnose arrhythmias and determine their underlying causes.
Treatment for irregular heartbeat depends on the type and severity of the arrhythmia but may include:
Medications: Antiarrhythmic drugs can help regulate heart rhythm and reduce the risk of complications.
Cardioversion: This procedure involves restoring normal heart rhythm using electrical shocks or medications.
Catheter Ablation: In cases of certain arrhythmias, catheter ablation can be performed to destroy abnormal heart tissue causing the irregular rhythm.
Implantable Devices: Devices such as pacemakers or implantable cardioverter-defibrillators (ICDs) may be recommended to regulate heart rhythm and prevent sudden cardiac arrest.
Conclusion
Irregular heartbeat, or arrhythmia, can be a serious and potentially life-threatening condition if left untreated. It can lead to complications such as reduced blood flow, blood clot formation, heart failure, and even sudden cardiac arrest. Recognizing the symptoms of arrhythmias, understanding the associated risks, and seeking prompt medical evaluation and treatment are crucial steps in managing this condition and reducing its impact on your health and well-being. If you have concerns about your heart rhythm or experience any related symptoms, consult your healthcare provider for guidance and appropriate care.
FAQs
Is irregular heartbeat a heart attack?
An irregular heartbeat, also known as arrhythmia, is not the same as a heart attack. A heart attack occurs when blood flow to part of the heart muscle is blocked, usually by a blood clot. On the other hand, arrhythmia refers to abnormal heart rhythms, which can include beats that are too fast, too slow, or irregular.
What does it feel like to have an irregular heartbeat?
The sensation of an irregular heartbeat can vary depending on the individual and the specific type of arrhythmia. Some people may not notice any symptoms, while others may experience palpitations (a sensation of fluttering or pounding in the chest), dizziness, shortness of breath, chest discomfort, or fatigue.
Can I exercise if I have an irregular heartbeat?
Whether you can exercise with an irregular heartbeat depends on the type and severity of the arrhythmia, as well as your overall health. In many cases, moderate exercise is safe and even beneficial for people with certain types of arrhythmias.
However, it’s essential to consult with your healthcare provider to determine the appropriate level of physical activity for your condition. They may recommend specific exercises or precautions based on your individual situation