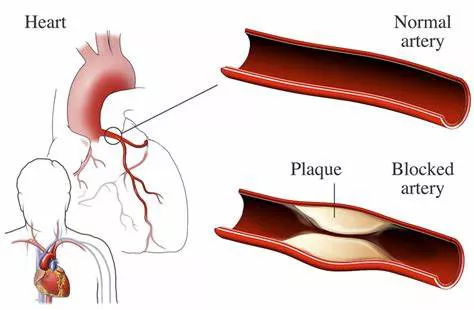
Heart blockage, also known as coronary artery disease (CAD), is a serious medical condition where the arteries that supply blood to the heart become narrowed or blocked. This can lead to severe health complications, including heart attacks and other cardiovascular diseases. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for heart blockage is crucial for managing and preventing this condition.
How Do You Get Heart Blockage?
Heart blockage typically results from a combination of lifestyle factors, genetic predisposition, and underlying health conditions. Here are the primary causes of heart blockage:
1. Atherosclerosis
Atherosclerosis is the most common cause of heart blockage. It occurs when fatty deposits, cholesterol, and other substances build up on the artery walls, forming plaques. Over time, these plaques can harden and narrow the arteries, restricting blood flow to the heart.
2. High Cholesterol
High levels of low-density lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol, often referred to as “bad” cholesterol, contribute significantly to plaque formation in the arteries. LDL cholesterol can infiltrate the artery walls, leading to atherosclerosis and increasing the risk of heart blockage.
3. High Blood Pressure
Hypertension, or high blood pressure, can damage the inner lining of the arteries, making them more susceptible to plaque buildup. Consistently high blood pressure forces the heart to work harder, which can further strain the cardiovascular system and contribute to heart blockage.
4. Smoking
Smoking is a major risk factor for heart blockage. The chemicals in tobacco smoke damage the blood vessels, promote plaque buildup, and increase the risk of blood clots. Smoking also lowers the levels of high-density lipoprotein (HDL) cholesterol, known as “good” cholesterol, which helps remove LDL cholesterol from the bloodstream.
5. Diabetes
Diabetes, particularly type 2 diabetes, is closely linked to heart blockage. High blood sugar levels can damage the arteries and promote plaque formation. Additionally, diabetes often coexists with other risk factors for heart blockage, such as high blood pressure and high cholesterol.
6. Obesity
Excess body weight, especially when concentrated around the abdomen, increases the risk of heart blockage. Obesity is often associated with high blood pressure, high cholesterol, and diabetes, all of which are significant risk factors for coronary artery disease.
7. Sedentary Lifestyle
Lack of physical activity contributes to the development of heart blockage. Regular exercise helps maintain a healthy weight, lower blood pressure, improve cholesterol levels, and enhance overall cardiovascular health.
8. Unhealthy Diet
A diet high in saturated fats, trans fats, cholesterol, and sodium can contribute to the development of heart blockage.
Consuming excessive amounts of processed foods, red meat, and sugary beverages increases the risk of atherosclerosis and coronary artery disease.
9. Family History
Genetics play a role in the risk of heart blockage. A family history of heart disease increases the likelihood of developing coronary artery disease. If close relatives have experienced heart attacks or other cardiovascular events, it is essential to be vigilant about heart health.
10. Age and Gender
The risk of heart blockage increases with age. Men are generally at higher risk of developing coronary artery disease earlier in life compared to women. However, after menopause, the risk for women increases and can eventually surpass that of men.
Symptoms of Heart Blockage
Recognizing the symptoms of heart blockage is critical for early intervention and treatment. Common symptoms include:
1. Chest Pain (Angina)
Chest pain or discomfort, often described as pressure, tightness, or squeezing, is a hallmark symptom of heart blockage.
This pain may radiate to the shoulders, arms, neck, jaw, or back and is typically triggered by physical activity or stress.
2. Shortness of Breath
Shortness of breath, especially during exertion, can indicate heart blockage. As the heart struggles to pump blood efficiently due to blocked arteries, it can lead to respiratory difficulties.
3. Fatigue
Unexplained fatigue or a significant decrease in energy levels can be a symptom of heart blockage. Reduced blood flow to the heart and muscles can cause persistent tiredness.
4. Heart Palpitations
Irregular heartbeats or palpitations, where the heart feels like it is racing, fluttering, or skipping beats, can be associated with heart blockage.
5. Nausea and Dizziness
Nausea, lightheadedness, or dizziness can occur, particularly in women, as symptoms of heart blockage. These symptoms may accompany chest pain or occur independently.
6. Sweating
Excessive sweating, especially cold sweats, can be a sign of heart blockage. This symptom often occurs alongside chest pain or discomfort.
Treatment Options for Heart Blockage
Treating heart blockage involves lifestyle changes, medications, and sometimes surgical interventions. Here are the main treatment options:
1. Lifestyle Changes
Adopting a heart-healthy lifestyle is essential for managing and preventing heart blockage. Key lifestyle changes include:
Diet: A diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats can help reduce cholesterol levels and prevent plaque buildup.
Exercise: Regular physical activity, such as walking, swimming, or cycling, improves cardiovascular health and helps maintain a healthy weight.
Smoking Cessation: Quitting smoking is crucial for reducing the risk of heart blockage and improving overall heart health.
Weight Management: Achieving and maintaining a healthy weight can reduce the risk of heart disease and alleviate the strain on the heart.
2. Medications
Several medications can help manage heart blockage and prevent complications:
Statins: Statins lower LDL cholesterol levels and reduce the risk of plaque formation.
Antiplatelet Agents: Medications like aspirin reduce the risk of blood clots and improve blood flow.
Beta-Blockers: Beta-blockers lower blood pressure and heart rate, reducing the heart’s workload.
ACE Inhibitors: Angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors help relax blood vessels and lower blood pressure.
Calcium Channel Blockers: These medications relax and widen blood vessels, improving blood flow and reducing blood pressure.
3. Surgical Interventions
In severe cases of heart blockage, surgical procedures may be necessary:
Angioplasty and Stent Placement: Angioplasty involves inserting a catheter with a balloon into the blocked artery. The balloon is inflated to open the artery, and a stent is placed to keep it open.
Coronary Artery Bypass Grafting (CABG): CABG surgery involves creating a bypass around the blocked artery using a healthy blood vessel from another part of the body. This allows blood to flow around the blockage.
Prevention of Heart Blockage
Preventing heart blockage involves proactive measures to maintain cardiovascular health:
1. Regular Health Screenings
Regular check-ups with a healthcare provider can help monitor risk factors like blood pressure, cholesterol levels, and blood sugar. Early detection and management of these factors can prevent heart blockage.
2. Healthy Diet
A balanced diet that limits saturated fats, trans fats, and sodium while emphasizing fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins is vital for heart health.
3. Physical Activity
Engaging in at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic activity per week, along with muscle-strengthening exercises, promotes cardiovascular health.
4. Stress Management
Chronic stress can contribute to heart disease. Practicing stress-reducing techniques such as meditation, yoga, or deep breathing can improve heart health.
5. Avoiding Tobacco
Avoiding smoking and exposure to secondhand smoke is crucial for preventing heart blockage and maintaining overall cardiovascular health.
Conclusion
Heart blockage is a serious condition that requires prompt diagnosis and management. By understanding the causes and symptoms of heart blockage, individuals can take proactive steps to reduce their risk and seek appropriate treatment.
Adopting a heart-healthy lifestyle, taking prescribed medications, and, if necessary, undergoing surgical interventions can significantly improve outcomes and enhance quality of life. Regular health screenings and a commitment to maintaining cardiovascular health are essential for preventing heart blockage and ensuring a healthy heart.