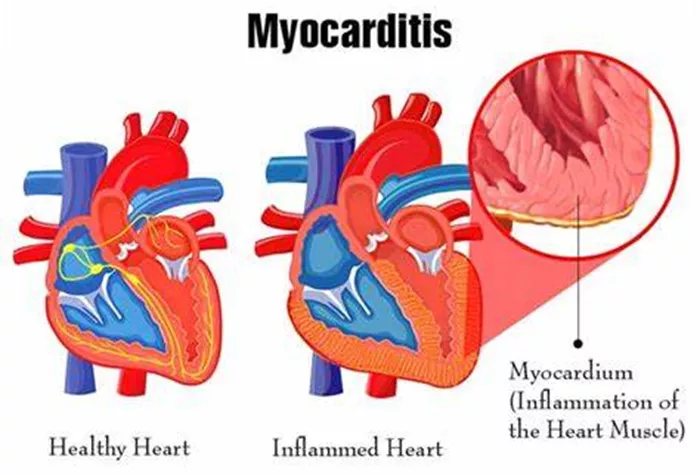
Myocarditis is an inflammation of the heart muscle (myocardium), often caused by viral infections, bacterial infections, autoimmune diseases, or exposure to toxins. This condition can disrupt the heart’s electrical system, reducing its ability to pump and causing rapid or abnormal heart rhythms (arrhythmias). Understanding the symptoms and experiences associated with myocarditis is essential for early detection and effective treatment.
The Onset of Myocarditis Symptoms
The symptoms of myocarditis can vary widely depending on the severity of the inflammation and the underlying cause. In some cases, individuals may be asymptomatic, while others may experience severe, life-threatening symptoms. Generally, the onset of myocarditis symptoms can be acute, subacute, or chronic, with varying intensities.
Early Symptoms
1. Fatigue and Weakness
One of the earliest signs of myocarditis is a persistent feeling of fatigue and weakness. This is often due to the body’s response to inflammation and infection, which can cause a general sense of malaise. Patients may feel unusually tired even after minimal physical exertion, and this fatigue does not improve with rest.
2. Chest Pain
Chest pain is a common symptom of myocarditis and can be mistaken for a heart attack. The pain is usually sharp or stabbing and may be exacerbated by deep breaths, coughing, or physical activity. It is essential to differentiate this pain from other types of chest pain by considering its duration and associated symptoms.
3. Shortness of Breath
Shortness of breath (dyspnea) is another early sign of myocarditis. This symptom can occur at rest or during physical activity. The inflammation of the heart muscle can reduce its ability to pump blood efficiently, leading to fluid accumulation in the lungs (pulmonary congestion) and subsequent difficulty breathing.
4. Palpitations and Arrhythmias
Patients with myocarditis often experience palpitations, which are sensations of a rapid or irregular heartbeat. This occurs because inflammation can disrupt the heart’s electrical signals, leading to arrhythmias. These palpitations can be uncomfortable and may be accompanied by dizziness or lightheadedness.
Progressive Symptoms
As myocarditis progresses, the symptoms can become more severe and may include:
5. Swelling (Edema)
Swelling in the legs, ankles, and feet (edema) can occur due to fluid retention. This happens when the heart’s pumping efficiency is compromised, leading to a buildup of fluid in the body’s tissues. Edema is often accompanied by a feeling of heaviness and discomfort in the affected areas.
6. Persistent Cough
A persistent cough can develop due to fluid accumulation in the lungs. This cough is often worse at night or when lying down and may be accompanied by pink, frothy sputum if pulmonary congestion is severe.
7. Abdominal Pain and Nausea
In some cases, myocarditis can cause abdominal pain, nausea, and a feeling of fullness. This can result from fluid retention in the abdomen or reduced blood flow to the digestive organs. These symptoms can also lead to a loss of appetite and unintentional weight loss.
8. Fever and Chills
Since myocarditis is often caused by an infection, it is common for patients to experience fever and chills. These symptoms are part of the body’s immune response to fight off the infection causing the inflammation.
Chronic Myocarditis Symptoms
In cases where myocarditis becomes chronic, the symptoms can persist for months or even years, leading to long-term complications. Chronic myocarditis can result in dilated cardiomyopathy, a condition where the heart becomes enlarged and weakened, leading to chronic heart failure.
9. Chronic Fatigue
Patients with chronic myocarditis often experience ongoing fatigue and weakness. This can severely impact their quality of life, making it difficult to perform daily activities and maintain an active lifestyle.
10. Exercise Intolerance
Chronic myocarditis can lead to exercise intolerance, where patients find it challenging to engage in physical activities without experiencing significant symptoms such as shortness of breath, chest pain, or fatigue. This can limit their ability to participate in sports, work, or recreational activities.
11. Persistent Edema
Long-term fluid retention can lead to persistent swelling in the legs, ankles, and feet. This can cause discomfort and difficulty wearing shoes or walking. In severe cases, the swelling can extend to the abdomen (ascites).
12. Cognitive Impairment
Chronic myocarditis can also affect cognitive function due to reduced blood flow to the brain. Patients may experience memory problems, difficulty concentrating, and a general sense of mental fog.
Diagnosis And Treatment of Myocarditis
Diagnostic Tests
Diagnosing myocarditis involves a combination of medical history, physical examination, and diagnostic tests. Common tests include:
Electrocardiogram (ECG): Detects abnormal heart rhythms and electrical activity.
Echocardiogram: Uses sound waves to create images of the heart, showing its size, structure, and function.
Blood Tests: Measure markers of inflammation and infection.
Cardiac MRI: Provides detailed images of the heart, helping to identify inflammation and damage.
Endomyocardial Biopsy: Involves taking a small sample of heart tissue to examine under a microscope.
Treatment Options
The treatment of myocarditis depends on the underlying cause and severity of the condition. Options include:
Medications: Anti-inflammatory drugs, antiviral medications, and antibiotics to treat infections.
Heart Medications: Beta-blockers, ACE inhibitors, and diuretics to manage symptoms and improve heart function.
Lifestyle Changes: Rest, avoiding strenuous activities, and following a heart-healthy diet.
Advanced Therapies: In severe cases, patients may require mechanical support devices or a heart transplant.
Recovery And Long-Term Outlook
The recovery process for myocarditis varies from person to person. Some individuals recover fully with proper treatment, while others may develop chronic conditions such as dilated cardiomyopathy or heart failure. Regular follow-up with a cardiologist is essential to monitor heart function and manage any ongoing symptoms.
Preventing Myocarditis
While it is not always possible to prevent myocarditis, certain measures can reduce the risk:
Vaccination: Stay up-to-date with vaccinations, especially for influenza and COVID-19.
Good Hygiene: Practice good hand hygiene to reduce the risk of infections.
Healthy Lifestyle: Maintain a healthy lifestyle with a balanced diet, regular exercise, and avoiding smoking and excessive alcohol consumption.
Prompt Treatment: Seek medical attention for any signs of infection or heart-related symptoms.
Conclusion
Myocarditis is a serious condition that can significantly impact an individual’s health and quality of life. Understanding the symptoms and experiences associated with myocarditis is crucial for early detection and effective treatment. If you experience any symptoms such as chest pain, shortness of breath, fatigue, or palpitations, it is essential to seek medical attention promptly. With proper diagnosis and treatment, many individuals with myocarditis can recover and lead healthy lives.