Cardiovascular health is a significant concern in modern society, where sedentary lifestyles and poor dietary choices contribute to the prevalence of heart disease. One common question that arises in the context of maintaining and improving heart health is whether aerobic exercise, often referred to as “cardio,” can help clean arteries. This article delves into the science behind cardiovascular exercise and its effects on arterial health, exploring the mechanisms through which cardio may benefit the cardiovascular system.
Understanding Arterial Health
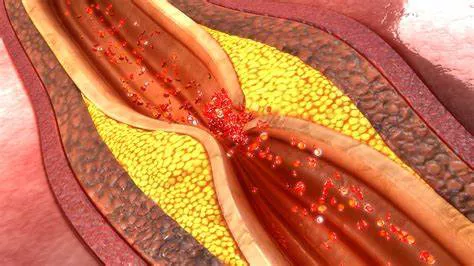
Arteries are blood vessels that carry oxygen-rich blood from the heart to the rest of the body. Healthy arteries are flexible, strong, and elastic, with smooth inner walls that allow blood to flow freely. However, over time, arteries can become clogged with a substance called plaque, which consists of fat, cholesterol, calcium, and other substances found in the blood. This condition, known as atherosclerosis, can lead to reduced blood flow and increase the risk of heart attack and stroke.
The Science Behind Aerobic Exercise
Aerobic exercise, commonly referred to as cardio, includes activities that increase the heart rate and improve the efficiency of the cardiovascular system. Examples of aerobic exercises include walking, running, cycling, swimming, and dancing. These activities require the body to use more oxygen and engage large muscle groups in a rhythmic manner.
see also: How Long Can Someone Live With Angina?
Benefits of Aerobic Exercise for Cardiovascular Health
Engaging in regular aerobic exercise has numerous benefits for cardiovascular health, including:
Improved Heart Function: Aerobic exercise strengthens the heart muscle, allowing it to pump blood more efficiently.
Increased Blood Flow: Exercise promotes the dilation of blood vessels, improving blood flow and oxygen delivery to tissues.
Lower Blood Pressure: Regular aerobic exercise can help reduce high blood pressure, a major risk factor for heart disease.
Improved Cholesterol Levels: Exercise can increase levels of HDL cholesterol (the “good” cholesterol) and reduce levels of LDL cholesterol.
Weight Management: Aerobic exercise helps maintain a healthy weight, reducing the risk of obesity-related cardiovascular problems.
Reduced Inflammation: Exercise has anti-inflammatory effects that can help prevent arterial damage.
Aerobic Exercise And Arterial Health
While aerobic exercise is well-known for its cardiovascular benefits, the question remains: Does cardio clean arteries? The answer is complex and involves several mechanisms through which aerobic exercise can positively impact arterial health.
Mechanisms of Arterial Improvement Through Aerobic Exercise
Reduction of Plaque Formation
Regular aerobic exercise can help reduce the factors that contribute to plaque formation in the arteries. For instance, exercise helps regulate blood lipid levels, reducing LDL cholesterol and increasing HDL cholesterol. Lower LDL cholesterol levels mean less material available to form plaque, while higher HDL cholesterol helps remove cholesterol from the bloodstream, preventing it from depositing on arterial walls.
Enhancement of Endothelial Function
The endothelium is the inner lining of the blood vessels, and its health is crucial for preventing atherosclerosis. Aerobic exercise enhances endothelial function by increasing the production of nitric oxide, a molecule that helps dilate blood vessels and improve blood flow. Improved endothelial function reduces the likelihood of plaque formation and arterial stiffness.
Reduction of Inflammation
Chronic inflammation is a significant contributor to atherosclerosis. Aerobic exercise has anti-inflammatory effects that can reduce the inflammatory processes involved in plaque formation. By lowering levels of inflammatory markers such as C-reactive protein (CRP), exercise helps protect the arteries from damage and plaque buildup.
Improvement of Insulin Sensitivity
Insulin resistance and high blood sugar levels can contribute to arterial damage and atherosclerosis. Aerobic exercise improves insulin sensitivity, helping the body regulate blood sugar levels more effectively. This reduction in blood sugar levels decreases the risk of plaque formation and arterial damage.
Reduction of Blood Pressure
High blood pressure can damage the arterial walls and promote plaque formation. Regular aerobic exercise helps lower blood pressure by improving the efficiency of the cardiovascular system. Lower blood pressure reduces the strain on the arteries and decreases the risk of atherosclerosis.
Promotion of Weight Loss
Obesity is a significant risk factor for atherosclerosis. Aerobic exercise is an effective way to burn calories and promote weight loss. Maintaining a healthy weight reduces the burden on the cardiovascular system and lowers the risk of plaque formation in the arteries.
Scientific Evidence Supporting The Benefits of Aerobic Exercise
Numerous studies have investigated the effects of aerobic exercise on arterial health. The following sections highlight key findings from scientific research that support the role of aerobic exercise in maintaining and improving arterial health.
Study 1: Aerobic Exercise and Endothelial Function
A study published in the journal “Circulation” examined the effects of aerobic exercise on endothelial function in middle-aged and older adults. The researchers found that regular aerobic exercise improved endothelial function by increasing nitric oxide production, leading to better blood vessel dilation and blood flow. These improvements in endothelial function help prevent plaque formation and arterial stiffness, contributing to overall cardiovascular health.
Study 2: Aerobic Exercise and Cholesterol Levels
Research published in the “Journal of the American Medical Association” investigated the effects of aerobic exercise on cholesterol levels in sedentary adults. The study found that participants who engaged in regular aerobic exercise experienced significant reductions in LDL cholesterol and increases in HDL cholesterol. These changes in cholesterol levels are associated with a lower risk of plaque formation and improved arterial health.
Study 3: Aerobic Exercise and Inflammation
A study published in “Medicine & Science in Sports & Exercise” examined the anti-inflammatory effects of aerobic exercise in overweight and obese adults. The researchers found that regular aerobic exercise reduced levels of inflammatory markers, including C-reactive protein (CRP). By reducing inflammation, aerobic exercise helps protect the arteries from damage and plaque buildup, promoting better cardiovascular health.
Practical Recommendations for Aerobic Exercise
To maximize the cardiovascular benefits of aerobic exercise and promote arterial health, it is essential to follow practical recommendations for incorporating exercise into daily life. The following guidelines can help individuals achieve optimal results:
Frequency: Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic exercise per week, spread over at least five days.
Alternatively, 75 minutes of vigorous-intensity aerobic exercise per week can provide similar benefits.
Intensity: Moderate-intensity aerobic exercise includes activities such as brisk walking, cycling, and swimming. Vigorous-intensity aerobic exercise includes activities such as running, high-intensity interval training (HIIT), and aerobics.
Duration: Each aerobic exercise session should last at least 30 minutes. For those new to exercise, starting with shorter sessions and gradually increasing duration can be beneficial.
Variety: Incorporating a variety of aerobic activities can help prevent boredom and maintain motivation. Examples include walking, jogging, cycling, swimming, dancing, and group fitness classes.
Progression: Gradually increasing the intensity and duration of aerobic exercise can help improve fitness levels and achieve better cardiovascular benefits. It is essential to listen to the body and avoid overexertion.
Consistency: Regular, consistent aerobic exercise is crucial for maintaining cardiovascular health and promoting arterial health. Sporadic or infrequent exercise may not provide the same benefits.
Consultation: Before starting a new exercise program, especially for individuals with existing health conditions, it is essential to consult a healthcare provider or fitness professional. They can provide personalized recommendations and ensure that the exercise program is safe and effective.
conclution
Aerobic exercise, or cardio, offers numerous benefits for cardiovascular health and arterial health. While it may not “clean” arteries in the literal sense, regular aerobic exercise can reduce the factors that contribute to plaque formation, improve endothelial function, reduce inflammation, enhance insulin sensitivity, lower blood pressure, and promote weight loss.
These mechanisms collectively contribute to healthier arteries and a lower risk of atherosclerosis and cardiovascular disease.