Irregular heartbeats, also known as arrhythmias, can be alarming and uncomfortable. They occur when the electrical impulses that coordinate your heartbeats don’t work properly, causing your heart to beat too fast, too slow, or irregularly.
It’s essential to understand what to do if you experience irregular heartbeats to ensure your health and peace of mind.
Symptoms of Irregular Heartbeats
Irregular heartbeats can present a range of symptoms, including:
Palpitations: A sensation that your heart is skipping beats, fluttering, or beating too hard or too fast.
Dizziness or Lightheadedness: Feeling faint or unsteady.
Shortness of Breath: Difficulty breathing or feeling like you can’t get enough air.
Chest Pain or Discomfort: Pain or pressure in your chest, which can be a sign of a more serious issue.
Fatigue: Feeling unusually tired or weak.
See Also: What Triggers AFib During Sleep?
Types of Irregular Heartbeats
There are several types of arrhythmias, each with different characteristics:
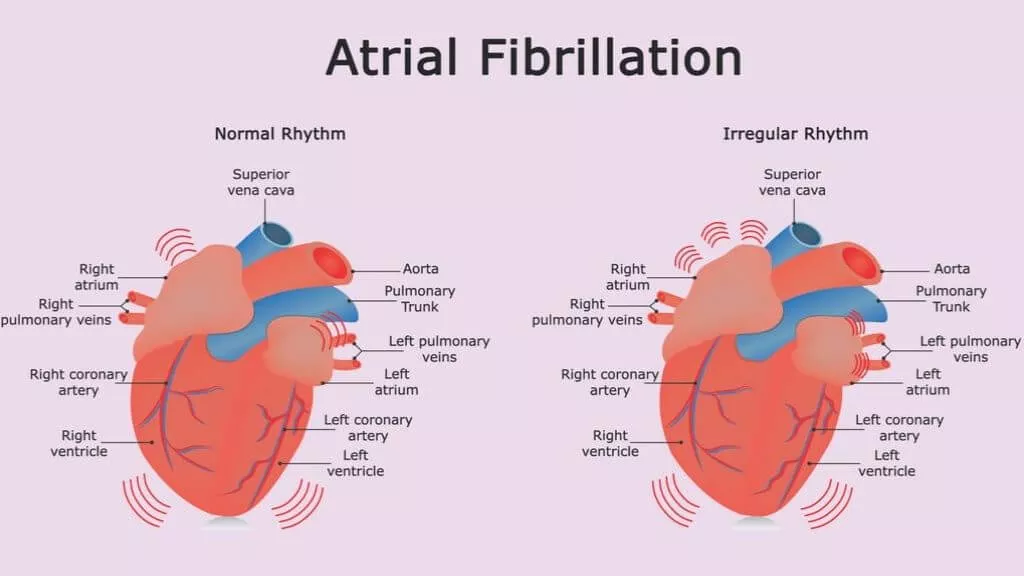
Atrial Fibrillation (AFib): Rapid, irregular beating of the upper chambers of the heart.
Atrial Flutter: Similar to AFib but with a more regular rhythm.
Supraventricular Tachycardia (SVT): Rapid heart rate originating above the heart’s ventricles.
Ventricular Tachycardia
Rapid heart rate originating in the heart’s lower chambers, which can be life-threatening.
Bradycardia: Slow heart rate, which can cause dizziness and fatigue.
Premature Heartbeats: Extra beats that occur before the next expected beat, causing a sensation of a skipped beat.
Understanding the type of arrhythmia you’re experiencing can help you and your healthcare provider determine the best course of action.
What to Do When Having Irregular Heartbeats?
Stay Calm
Experiencing an irregular heartbeat can be frightening, but staying calm is crucial. Anxiety and panic can exacerbate symptoms and make it harder to assess the situation accurately.
Monitor Your Symptoms
Keep track of your symptoms, including:
When they occur: Note the time of day and any activities you were doing.
Duration: How long the irregular heartbeat lasts.
Associated symptoms: Any additional symptoms like chest pain, shortness of breath, or dizziness.
Check Your Pulse
Checking your pulse can provide useful information about your heart rate and rhythm. To check your pulse:
Place your index and middle fingers on your wrist, just below the base of your thumb.
Press lightly until you feel your pulse.
Count the number of beats in 60 seconds.
A normal resting heart rate for adults ranges from 60 to 100 beats per minute. If your heart rate is significantly outside this range or if it’s irregular, note it down.
Perform Vagal Maneuvers
Vagal maneuvers can help slow down a rapid heartbeat by stimulating the vagus nerve. These techniques include:
Valsalva Maneuver: Hold your breath and bear down as if you are having a bowel movement.
Coughing: Forceful coughing can also stimulate the vagus nerve.
Cold Water Splash: Splashing your face with cold water or immersing your face in cold water can sometimes help.
These maneuvers are generally safe but should be done with caution, especially if you have a history of heart conditions.
Avoid Triggers
Certain factors can trigger or worsen arrhythmias. Common triggers include:
Caffeine: Found in coffee, tea, soda, and energy drinks.
Alcohol: Excessive alcohol consumption can lead to arrhythmias.
Stress: Emotional and physical stress can trigger irregular heartbeats.
Medications: Some medications, including over-the-counter decongestants and weight loss pills, can affect heart rhythm.
Avoiding these triggers can help reduce the frequency and severity of irregular heartbeats.
When to Seek Medical Help
Immediate Medical Attention
Seek immediate medical attention if you experience:
Severe chest pain: This could be a sign of a heart attack.
Fainting or severe dizziness: These symptoms indicate a significant drop in blood flow to the brain.
Shortness of breath: Difficulty breathing could signify a serious heart or lung issue.
Rapid, irregular heartbeat lasting more than a few minutes: This may require urgent medical intervention.
Schedule a Doctor’s Appointment
If you experience frequent or persistent irregular heartbeats, make an appointment with your healthcare provider. They can perform a thorough evaluation to determine the cause and appropriate treatment.
Diagnostic Tests
Your doctor may recommend several tests to diagnose the cause of your irregular heartbeats, including:
Electrocardiogram (ECG or EKG): Measures the electrical activity of your heart.
Holter Monitor: A portable device worn for 24-48 hours to record heart activity.
Event Monitor: Similar to a Holter monitor but used for longer periods to capture irregular heartbeats.
Echocardiogram: An ultrasound of your heart to check for structural abnormalities.
Stress Test: Measures how your heart functions during physical activity.
These tests can help identify the type of arrhythmia and guide treatment decisions.
Treatment Options
Lifestyle Changes
Making lifestyle changes can help manage and prevent arrhythmias:
Healthy Diet: A heart-healthy diet includes fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats.
Regular Exercise: Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate exercise each week. Consult your doctor before starting a new exercise program.
Quit Smoking: Smoking increases the risk of heart disease and arrhythmias.
Limit Alcohol and Caffeine: Reducing intake of these substances can help prevent irregular heartbeats.
Stress Management: Techniques such as meditation, yoga, and deep breathing exercises can help reduce stress.
Medications
Medications can help control the heart rate and rhythm. Commonly prescribed medications include:
Beta-Blockers: Reduce the heart rate and decrease the workload on the heart.
Calcium Channel Blockers: Help relax the blood vessels and decrease the heart rate.
Antiarrhythmic Drugs: Help restore a normal heart rhythm.
Anticoagulants: Prevent blood clots, especially in conditions like atrial fibrillation.
It’s important to take medications as prescribed and discuss any side effects with your doctor.
Medical Procedures
In some cases, medical procedures may be necessary to treat arrhythmias:
Cardioversion: An electrical shock is delivered to the heart to restore a normal rhythm.
Catheter Ablation: A procedure that destroys small areas of heart tissue causing the arrhythmia.
Pacemaker: A small device implanted under the skin to help control abnormal heart rhythms.
Implantable Cardioverter-Defibrillator (ICD): A device that monitors the heart rhythm and delivers shocks if a life-threatening arrhythmia is detected.
Surgical Options
For severe cases, surgery may be required:
Maze Procedure: A surgical technique that creates scar tissue to redirect electrical signals in the heart.
Coronary Bypass Surgery: Improves blood flow to the heart in cases of severe coronary artery disease.
Long-Term Management
Regular Check-Ups
Regular follow-ups with your healthcare provider are essential for managing arrhythmias. These appointments allow your doctor to monitor your condition, adjust treatments as needed, and address any new symptoms.
Monitoring Your Condition
Keeping a log of your symptoms and triggers can help your doctor fine-tune your treatment plan. Devices such as home blood pressure monitors and portable ECG devices can provide valuable information between appointments.
Support and Education
Educating yourself about arrhythmias and joining support groups can help you manage the emotional and psychological aspects of the condition. Support from family, friends, and healthcare professionals is crucial for long-term management.
Conclusion
Irregular heartbeats can be concerning, but with the right knowledge and actions, you can manage the condition effectively.
Staying calm, monitoring your symptoms, avoiding triggers, and seeking medical help when necessary are key steps. With appropriate lifestyle changes, medications, and possibly medical procedures, you can maintain a healthy and active life.
Regular check-ups and support will ensure you stay on top of your condition and live well despite arrhythmias.