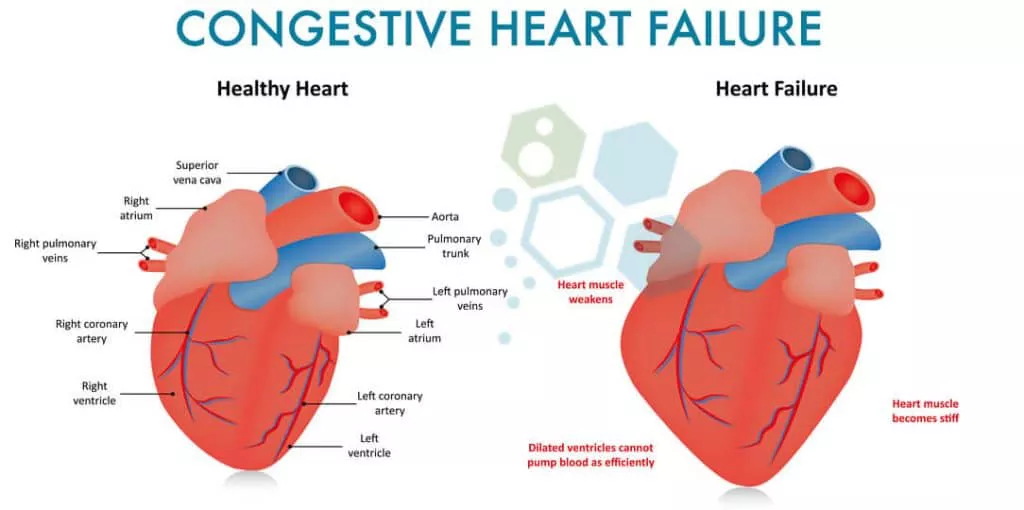
Left heart failure, also known as left ventricular failure, is a condition where the left side of the heart is unable to pump blood efficiently. This inefficiency leads to a buildup of blood and fluid in the lungs, causing a range of symptoms that can severely impact an individual’s quality of life. Recognizing these symptoms early is crucial for prompt diagnosis and treatment, which can help manage the condition and prevent further complications.
What Is A Symptom of Left Heart Failure?
Shortness of Breath
One of the most common and early symptoms of left heart failure is shortness of breath, also known as dyspnea. This occurs because the left ventricle fails to pump blood effectively, leading to a backlog of blood in the pulmonary veins. The increased pressure in these veins causes fluid to leak into the lungs, resulting in pulmonary congestion and difficulty breathing. Patients may experience shortness of breath during physical activity, at rest, or even while lying flat—a condition known as orthopnea.
See Also: How Does Exercise Help Heart Failure
Fatigue and Weakness
Fatigue and generalized weakness are significant symptoms of left heart failure. The heart’s inability to pump blood efficiently means that less oxygen-rich blood reaches the muscles and tissues throughout the body. This lack of adequate oxygen supply leads to a feeling of constant tiredness and reduced physical stamina, even during routine activities.
Persistent Cough and Wheezing
A persistent cough, especially one that produces frothy or blood-tinged sputum, is another hallmark symptom of left heart failure. This cough is often worse at night or when lying down, due to the accumulation of fluid in the lungs. Wheezing may also occur as the airways become constricted from the fluid buildup, leading to a whistling sound when breathing.
Swelling (Edema)
Swelling, or edema, particularly in the lower extremities such as the legs, ankles, and feet, is a common symptom of left heart failure. When the heart’s pumping ability is compromised, blood flow to the kidneys is reduced. This reduction triggers the kidneys to retain sodium and water, resulting in fluid buildup in the body’s tissues. Swelling may also be observed in the abdomen (ascites) and can lead to significant discomfort and weight gain.
Rapid or Irregular Heartbeat
Patients with left heart failure may experience a rapid or irregular heartbeat, known as arrhythmia. This symptom occurs as the heart tries to compensate for its decreased pumping capacity by beating faster. Palpitations, or the sensation of feeling your heart pounding or fluttering, can be alarming and may be accompanied by dizziness or lightheadedness.
Difficulty Sleeping and Sleep Apnea
Left heart failure can disrupt normal sleep patterns. Difficulty sleeping, frequent waking at night due to shortness of breath, and sleep apnea—a condition where breathing repeatedly stops and starts during sleep—are common in individuals with left heart failure. Paroxysmal nocturnal dyspnea, a sudden severe shortness of breath that awakens a person from sleep, is particularly distressing and is a classic symptom of this condition.
Decreased Exercise Capacity
Individuals with left heart failure often notice a significant decrease in their ability to exercise or perform physical activities. This decreased exercise capacity is due to the heart’s reduced efficiency in pumping blood, which limits the oxygen supply to muscles during exertion. Even mild activities can lead to exhaustion and shortness of breath.
Chest Pain or Discomfort
Although less common, some patients with left heart failure may experience chest pain or discomfort. This symptom is particularly concerning as it may indicate the presence of coronary artery disease, which often coexists with heart failure.
Any chest pain should be evaluated promptly by a healthcare professional to rule out other serious conditions such as a heart attack.
Confusion and Impaired Thinking
Cognitive impairment, including confusion and difficulty concentrating, can occur in individuals with left heart failure. This symptom arises from reduced cardiac output, which decreases blood flow to the brain. The resulting lack of oxygen and nutrients can impair brain function, leading to memory problems and a reduced ability to perform mental tasks.
Loss of Appetite and Nausea
Left heart failure can affect the digestive system, leading to symptoms such as loss of appetite, nausea, and a feeling of fullness. The liver and intestines may become congested with blood, affecting their normal function and leading to gastrointestinal discomfort. This can result in unintended weight loss and malnutrition.
Anxiety and Depression
Living with left heart failure can take a significant emotional toll. Many patients experience anxiety and depression due to the chronic nature of the condition and the impact it has on their daily lives. The physical symptoms, coupled with the stress of managing a serious illness, can lead to feelings of hopelessness and emotional distress.
Frequent Urination at Night
Frequent urination, particularly at night (nocturia), is another symptom of left heart failure. When a person with heart failure lies down, fluid that has accumulated in the lower extremities is reabsorbed into the bloodstream and filtered by the kidneys, leading to increased urine production. This can disrupt sleep and contribute to overall fatigue.
Weight Gain
Unexplained weight gain can be an indicator of left heart failure. This weight gain is primarily due to fluid retention rather than fat accumulation. Monitoring weight regularly can help in identifying sudden increases, which may signal worsening heart failure and the need for medical intervention.
Diagnosis and Treatment
Recognizing the symptoms of left heart failure is the first step toward effective management. A thorough medical evaluation, including a physical examination, chest X-ray, electrocardiogram (ECG), echocardiogram, and blood tests, is essential for diagnosis. Treatment typically involves lifestyle changes, medications, and in some cases, surgical interventions to improve heart function and alleviate symptoms.
Medications
Common medications prescribed for left heart failure include diuretics to reduce fluid buildup, beta-blockers to slow the heart rate, ACE inhibitors or ARBs to relax blood vessels, and digitalis to strengthen heart contractions. Managing comorbid conditions such as hypertension and diabetes is also crucial.
Lifestyle Changes
Lifestyle modifications play a significant role in managing left heart failure. Patients are often advised to follow a low-sodium diet, limit fluid intake, engage in regular physical activity, avoid alcohol and tobacco, and monitor their weight daily. These changes can help reduce symptoms and improve overall heart health.
Surgical and Device-Based Treatments
In severe cases, surgical interventions such as coronary artery bypass grafting (CABG), heart valve repair or replacement, and the implantation of devices like pacemakers or defibrillators may be necessary. These procedures can help improve heart function and prevent life-threatening complications.
Conclusion
Left heart failure is a serious condition with a wide range of symptoms that can significantly impact an individual’s life.
Early recognition and prompt medical intervention are key to managing the disease and improving outcomes. By understanding the symptoms and seeking appropriate care, individuals with left heart failure can work with their healthcare providers to develop a comprehensive treatment plan that addresses their specific needs and enhances their quality of life.