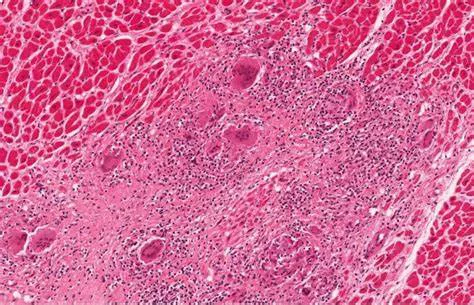
Myocarditis, an inflammation of the heart muscle (myocardium), can arise from various causes, including viral infections, autoimmune diseases, and exposure to certain toxins. This condition can affect anyone, regardless of age or gender, and its severity can range from mild to life-threatening. A pressing question for those diagnosed with myocarditis is whether the condition leaves permanent damage to the heart. This article delves into the causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and potential long-term effects of myocarditis, with a focus on understanding if it can result in lasting heart damage.
What Causes Myocarditis?
Myocarditis typically occurs when the heart muscle becomes inflamed due to an infection or autoimmune response. Common causes include:
Viral Infections
Viruses are the leading cause of myocarditis. The most common viruses associated with the condition are:
- Coxsackievirus B
- Adenovirus
- Parvovirus B19
- Epstein-Barr virus
- Hepatitis C
- Herpes simplex virus
- Influenza
These viruses can directly invade the heart muscle or trigger an immune response that inadvertently damages the heart.
See Also: Can An Echocardiogram Detect Myocarditis
Bacterial And Fungal Infections
Although less common, bacterial and fungal infections can also cause myocarditis. Notable examples include:
- Streptococcus
- Staphylococcus
- Borrelia burgdorferi (the bacteria that causes Lyme disease)
- Mycobacterium tuberculosis
- Histoplasma
- Candida
- Autoimmune Diseases
In some cases, the body’s immune system mistakenly attacks the heart muscle, leading to myocarditis. Conditions that can cause this autoimmune response include:
- Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE)
- Rheumatoid arthritis
- Sarcoidosis
- Giant cell myocarditis
- Toxins and Drugs
Certain toxins and medications can also cause myocarditis. Examples include:
- Alcohol
- Cocaine
- Certain chemotherapy drugs
- Exposure to heavy metals
Other Causes
Myocarditis can also result from radiation therapy, especially in treatments involving the chest area, or from other inflammatory diseases.
Diagnosing Myocarditis
Diagnosing myocarditis can be challenging due to its varied symptoms and overlap with other heart conditions. Common diagnostic methods include:
Physical Examination and Medical History
A doctor will start with a thorough physical examination and medical history review to identify any potential causes or risk factors.
Electrocardiogram (ECG or EKG)
An ECG records the electrical activity of the heart and can detect irregularities that suggest myocarditis.
Blood Tests
Blood tests can identify markers of inflammation, cardiac enzymes indicating heart muscle damage, and specific antibodies associated with infections or autoimmune responses.
Imaging Studies
Echocardiogram: An ultrasound of the heart that can reveal changes in heart size, shape, and function.
Cardiac MRI: Provides detailed images of the heart muscle, helping to identify inflammation and scarring.
Chest X-ray: Can show the size and shape of the heart and detect fluid buildup in the lungs.
Endomyocardial Biopsy
In some cases, a biopsy of the heart muscle may be necessary to confirm the diagnosis. This involves taking a small sample of heart tissue for microscopic examination.
Treatment of Myocarditis
The treatment of myocarditis depends on the underlying cause and severity of the condition. Common treatment approaches include:
Medications
Antiviral drugs: For viral infections.
Antibiotics or antifungal medications: For bacterial or fungal infections.
Anti-inflammatory drugs: To reduce inflammation and alleviate symptoms.
Heart medications: Such as beta-blockers, ACE inhibitors, or diuretics to manage heart failure symptoms and improve heart function.
Lifestyle Changes
Rest and reduced physical activity: To minimize strain on the heart.
Dietary modifications: To support heart health.
Avoiding alcohol and recreational drugs: To prevent further heart damage.
Medical Procedures
Implantable devices: Such as pacemakers or defibrillators for severe arrhythmias.
Mechanical circulatory support: In cases of severe heart failure, devices like ventricular assist devices (VADs) may be necessary.
Heart transplant: In extreme cases where the heart is severely damaged and other treatments are ineffective.
Potential Long-Term Effects of Myocarditis
The long-term effects of myocarditis depend on the severity of the initial inflammation, the underlying cause, and the effectiveness of the treatment. While some individuals recover fully, others may experience lasting heart damage. Here are the potential long-term outcomes:
Full Recovery
Many individuals with mild myocarditis recover fully without any long-term heart damage. This is especially true if the condition is diagnosed early and treated effectively.
Persistent Heart Muscle Damage
In some cases, myocarditis can cause persistent inflammation and damage to the heart muscle, leading to chronic heart problems. This can include:
Dilated cardiomyopathy: A condition where the heart muscle becomes weakened and enlarged, reducing its ability to pump blood effectively.
Heart failure: Chronic myocarditis can lead to heart failure, a condition where the heart cannot pump enough blood to meet the body’s needs.
Arrhythmias: Irregular heartbeats can persist even after the initial inflammation has resolved.
Scar Tissue Formation
The healing process after myocarditis can result in scar tissue formation in the heart muscle. This scar tissue can interfere with the heart’s electrical signals, leading to arrhythmias and reduced heart function.
Risk of Recurrence
In some cases, myocarditis can recur, especially if the underlying cause is not adequately addressed. Recurrent episodes of myocarditis can increase the risk of long-term heart damage.
Sudden Cardiac Death
Although rare, severe myocarditis can lead to sudden cardiac death, particularly if it causes severe arrhythmias or heart failure.
Managing And Preventing Long-Term Damage
Managing the long-term effects of myocarditis involves regular medical follow-up, lifestyle modifications, and adherence to prescribed treatments. Here are some strategies to help prevent and manage long-term heart damage:
Regular Medical Follow-Up
Regular check-ups with a cardiologist are essential to monitor heart function and detect any early signs of complications. This may include periodic ECGs, echocardiograms, and blood tests.
Adhering to Treatment Plans
Following the prescribed treatment plan, including medications and lifestyle changes, is crucial for preventing further heart damage and managing symptoms.
Healthy Lifestyle Choices
Adopting a heart-healthy lifestyle can help reduce the risk of long-term damage. This includes:
Eating a balanced diet: Rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats.
Exercising regularly: Engaging in moderate physical activity as recommended by a healthcare provider.
Avoiding smoking and excessive alcohol consumption: Both can exacerbate heart problems.
Managing stress: Through techniques like mindfulness, meditation, and regular physical activity.
Monitoring for Recurrence
Being vigilant about any new or recurring symptoms and seeking prompt medical attention if they occur can help manage recurrent myocarditis episodes.
Immunizations
Staying up-to-date with vaccinations, particularly for viruses known to cause myocarditis (like influenza), can help prevent infections that could trigger the condition.
Conclusion
Myocarditis is a serious condition that can have varying long-term effects depending on the severity of the inflammation and the effectiveness of treatment. While many individuals recover fully without lasting damage, others may experience chronic heart problems, including heart failure, arrhythmias, and dilated cardiomyopathy. Early diagnosis, appropriate treatment, and regular medical follow-up are crucial in managing the condition and preventing permanent heart damage.
Adopting a heart-healthy lifestyle and adhering to medical advice can also play a significant role in mitigating the long-term effects of myocarditis.