Inflammation, atherosclerosis, and coronary artery disease (CAD) are interrelated conditions that significantly impact cardiovascular health.
Understanding these conditions, their connections, and their implications is crucial for comprehending the complexity of heart disease. This article will explore the definitions, causes, symptoms, and treatment options for these conditions, as well as their interrelationships.
Understanding Inflammation
Inflammation is a natural response of the body’s immune system to injury or infection. It is characterized by redness, heat, swelling, and pain at the site of injury. While acute inflammation is a protective mechanism, chronic inflammation can lead to various health problems, including cardiovascular diseases.
See Also: What Are The Symptoms of Heart Artery Blockage
Types of Inflammation
Acute Inflammation: This type is short-term and occurs as a response to injury or infection. It helps the body heal and fight off harmful stimuli.
Chronic Inflammation: This type is long-term and can persist for months or years. Chronic inflammation can result from persistent infections, autoimmune disorders, or exposure to harmful substances.
Causes of Chronic Inflammation
Infections: Persistent infections like hepatitis or tuberculosis can cause chronic inflammation.
Autoimmune Diseases: Conditions like rheumatoid arthritis and lupus lead to chronic inflammation as the immune system mistakenly attacks healthy tissue.
Lifestyle Factors: Poor diet, lack of exercise, smoking, and excessive alcohol consumption contribute to chronic inflammation.
Environmental Factors: Exposure to pollutants and toxins can trigger chronic inflammation.
- Symptoms of Chronic Inflammation
- Fatigue
- Fever
- Mouth sores
- Rashes
- Abdominal pain
- Chest pain
Chronic inflammation is often silent and may not cause noticeable symptoms until significant damage has occurred.
What Is Atherosclerosis?
Atherosclerosis is a condition characterized by the buildup of plaque within the arterial walls. Plaque is composed of fat, cholesterol, calcium, and other substances found in the blood. Over time, plaque hardens and narrows the arteries, restricting blood flow to vital organs and tissues.
Development of Atherosclerosis
Atherosclerosis develops gradually and can start as early as childhood.
The process involves several stages:
Endothelial Injury: The inner lining of the arteries (endothelium) becomes damaged due to factors like high blood pressure, smoking, or high cholesterol.
Fatty Streak Formation: Low-density lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol penetrates the damaged endothelium and accumulates in the arterial wall, forming fatty streaks.
Plaque Formation: The body attempts to repair the damage by sending white blood cells to the site. These cells ingest the LDL cholesterol, turning into foam cells and contributing to plaque formation.
Plaque Growth: Over time, the plaque grows and can become unstable. It may rupture, leading to the formation of a blood clot.
Risk Factors for Atherosclerosis
High Blood Pressure: Damages the arteries and accelerates plaque buildup.
High Cholesterol: Excess LDL cholesterol contributes to plaque formation.
Smoking: Damages the endothelium and promotes plaque accumulation.
Diabetes: Increases the risk of endothelial damage and atherosclerosis.
Obesity: Associated with higher levels of LDL cholesterol and inflammation.
Sedentary Lifestyle: Lack of exercise contributes to several risk factors for atherosclerosis.
Unhealthy Diet: Diets high in saturated fats, trans fats, and cholesterol promote plaque buildup.
Family History: Genetic factors can influence the risk of atherosclerosis.
see also: how long can you live with a faulty heart valve
Symptoms of Atherosclerosis
Atherosclerosis may not cause symptoms until the arteries are significantly narrowed or blocked. Symptoms depend on the affected arteries:
Coronary Arteries: Chest pain (angina), shortness of breath, heart attack.
Carotid Arteries: Sudden weakness, paralysis, confusion, vision problems, stroke.
Peripheral Arteries: Leg pain, numbness, difficulty walking, peripheral artery disease.
Renal Arteries: High blood pressure, kidney failure.
What Is Coronary Artery Disease?
Coronary artery disease (CAD) is a specific type of atherosclerosis that affects the coronary arteries, which supply blood to the heart muscle.
CAD is the leading cause of heart attacks and one of the most common forms of heart disease.
Pathophysiology of CAD
CAD develops when the coronary arteries become narrowed or blocked due to plaque buildup. This reduces blood flow to the heart muscle, leading to a condition known as ischemia. If the blood supply is severely restricted or completely blocked, it can result in a heart attack (myocardial infarction).
Symptoms of CAD
Angina: Chest pain or discomfort that occurs when the heart muscle does not get enough blood. It can feel like pressure, squeezing, or fullness in the chest.
Shortness of Breath: Due to reduced oxygen supply to the heart.
Heart Attack: Symptoms include chest pain or discomfort, upper body pain, shortness of breath, sweating, nausea, and lightheadedness.
Risk Factors for CAD
Age: The risk of CAD increases with age.
Gender: Men are at higher risk of CAD at an earlier age compared to women.
Family History: A family history of heart disease increases the risk.
Smoking: Damages the arteries and accelerates plaque buildup.
High Blood Pressure: Strains the heart and damages the arteries.
High Cholesterol: Contributes to plaque formation.
Diabetes: Increases the risk of CAD.
Obesity: Associated with higher cholesterol levels, high blood pressure, and diabetes.
Physical Inactivity: Contributes to several risk factors for CAD.
Unhealthy Diet: Diets high in saturated fats, trans fats, and cholesterol promote plaque buildup.
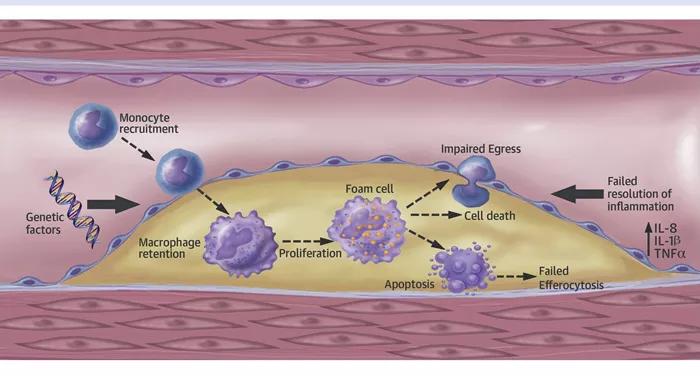
Interconnection Between Inflammation, Atherosclerosis, And CAD
Inflammation plays a crucial role in the development and progression of atherosclerosis and CAD. Here’s how they are interconnected:
Initiation of Atherosclerosis: Inflammation can damage the endothelium, leading to the initiation of atherosclerosis.
Factors like high blood pressure, smoking, and high cholesterol contribute to endothelial injury and inflammation.
Plaque Formation: Inflammatory cells, such as macrophages, play a significant role in plaque formation. These cells ingest LDL cholesterol, turning into foam cells and contributing to plaque growth.
Plaque Progression and Rupture: Chronic inflammation can cause plaque instability and rupture. When a plaque ruptures, it triggers the formation of a blood clot, which can block blood flow and lead to a heart attack.
CAD Development: The progression of atherosclerosis in the coronary arteries leads to CAD. Inflammation exacerbates the narrowing and blockage of these arteries, reducing blood flow to the heart muscle and increasing the risk of heart attacks.
Diagnosis of Atherosclerosis And CAD
Diagnosing atherosclerosis and CAD involves several tests and procedures:
Blood Tests: Measure cholesterol levels, blood sugar levels, and markers of inflammation.
Electrocardiogram (ECG): Records the electrical activity of the heart and detects abnormalities.
Stress Testing: Evaluates the heart’s response to physical stress, often using exercise or medication to simulate exertion.
Imaging Tests: Include echocardiography, CT scans, and MRI to visualize the heart and arteries.
Coronary Angiography: A specialized X-ray test that uses contrast dye to visualize the coronary arteries and detect blockages.
Treatment Options
Lifestyle Changes
Adopting a healthy lifestyle is crucial for managing atherosclerosis and CAD:
Healthy Diet: Emphasize fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats. Limit saturated fats, trans fats, cholesterol, salt, and added sugars.
Regular Exercise: Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic activity or 75 minutes of vigorous-intensity activity each week.
Quit Smoking: Smoking cessation significantly reduces the risk of atherosclerosis and CAD.
Weight Management: Maintain a healthy weight to reduce the risk of associated conditions like high blood pressure and diabetes.
Stress Management: Techniques like yoga, meditation, and deep breathing exercises can help manage stress and reduce inflammation.
Medications
Several medications can help manage atherosclerosis and CAD:
Statins: Lower cholesterol levels and reduce inflammation.
Antiplatelet Agents: Prevent blood clots by inhibiting platelet aggregation.
ACE Inhibitors: Lower blood pressure and reduce strain on the heart.
Beta-Blockers: Reduce heart rate and blood pressure, decreasing the heart’s oxygen demand.
Calcium Channel Blockers: Relax blood vessels and reduce blood pressure.
Nitroglycerin: Relieves angina by dilating blood vessels.
Surgical Procedures
In some cases, surgical interventions may be necessary:
Angioplasty and Stenting: A catheter is used to open blocked arteries, and a stent is placed to keep them open.
Coronary Artery Bypass Grafting (CABG): A surgical procedure that uses a graft to bypass blocked coronary arteries and improve blood flow to the heart.
Endarterectomy: Surgical removal of plaque from the arteries.
Conclusion
Inflammation, atherosclerosis, and coronary artery disease are closely interconnected conditions that significantly impact cardiovascular health. Chronic inflammation can initiat e and accelerate the progression of atherosclerosis, leading to the development of CAD. Understanding these conditions, their risk factors, symptoms, and treatment options is essential for preventing and managing heart disease. By adopting a healthy lifestyle, adhering to medical treatments, and staying informed, individuals can reduce their risk of atherosclerosis and CAD, ultimately promoting better heart health.