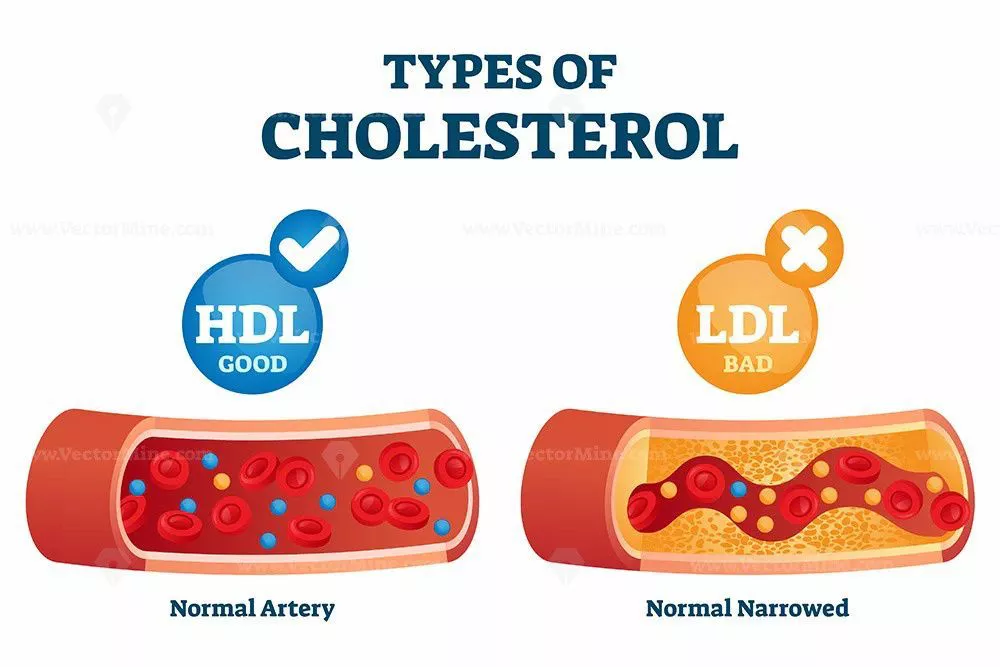
As individuals age, their bodies undergo various physiological changes that can impact their health in different ways. One notable change that occurs with aging is the increase in low-density lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol levels. LDL cholesterol, often referred to as “bad” cholesterol, plays a crucial role in cardiovascular health and is a significant risk factor for heart disease. Understanding why LDL levels tend to rise as people age is essential for managing cardiovascular health and reducing the risk of related complications.
The Role of LDL Cholesterol
Before delving into why LDL levels increase with age, it’s crucial to understand the role of LDL cholesterol in the body.
Cholesterol is a waxy substance produced by the liver and is essential for building cell membranes, producing hormones like estrogen and testosterone, and aiding in the digestion of fats. Cholesterol travels through the bloodstream in lipoproteins, which are classified based on their density. LDL cholesterol is one type of lipoprotein that carries cholesterol from the liver to cells throughout the body.
While cholesterol is necessary for various bodily functions, too much LDL cholesterol can lead to the buildup of plaque in the arteries, a condition known as atherosclerosis. Over time, this buildup can narrow the arteries and restrict blood flow, increasing the risk of heart attack and stroke.
SEE ALSO: Who Treats Hyperlipidemia
What Are Factors Influencing LDL Levels
Several factors contribute to the increase in LDL cholesterol levels with age. These factors can be categorized into intrinsic (related to aging itself) and extrinsic (related to lifestyle and environmental factors).
Intrinsic Factors:
Hormonal Changes: Hormonal shifts that occur with age, particularly in women during menopause, can affect cholesterol levels. Estrogen, which helps maintain healthy cholesterol levels, decreases during menopause, leading to an increase in LDL cholesterol.
Reduced Metabolic Rate: As people age, their metabolic rate tends to slow down. This can result in reduced efficiency in processing and clearing cholesterol from the bloodstream, contributing to higher LDL levels.
Genetics: Genetic factors also play a significant role in cholesterol levels. Some individuals may have a genetic predisposition to higher LDL cholesterol levels, which can become more pronounced with age.
Extrinsic Factors:
Dietary Habits: Poor dietary choices, such as consuming foods high in saturated and trans fats, can significantly impact LDL cholesterol levels. Over time, a diet rich in these unhealthy fats can lead to elevated LDL levels.
Lack of Physical Activity: Sedentary lifestyles, which are more common in older adults, can contribute to higher LDL cholesterol levels. Regular physical activity helps maintain healthy cholesterol levels by promoting the production of high-density lipoprotein (HDL) cholesterol, often referred to as “good” cholesterol.
Smoking and Alcohol Consumption: Smoking tobacco and excessive alcohol consumption are detrimental to cardiovascular health and can contribute to higher LDL cholesterol levels.
Managing LDL Cholesterol in Older Adults
While the increase in LDL cholesterol with age is a natural process, it is essential to manage cholesterol levels effectively to reduce the risk of cardiovascular disease. Here are some strategies for managing LDL cholesterol in older adults:
Healthy Diet: Encourage a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats such as those found in nuts, seeds, and avocados. Limit intake of saturated fats, trans fats, and cholesterol-rich foods.
Regular Exercise: Encourage regular physical activity, such as brisk walking, swimming, or cycling, to help maintain a healthy weight and improve cholesterol levels.
Smoking Cessation: Encourage smoking cessation programs and support for individuals who smoke, as quitting smoking can significantly improve cardiovascular health.
Medication: In some cases, medication may be necessary to manage LDL cholesterol levels effectively. Statins and other cholesterol-lowering medications may be prescribed by healthcare professionals based on individual risk factors and cholesterol levels.
Regular Monitoring: Encourage regular cholesterol screenings and monitoring, especially for individuals with a family history of high cholesterol or cardiovascular disease.
Conclusion
In conclusion, LDL cholesterol levels tend to increase with age due to a combination of intrinsic factors such as hormonal changes and reduced metabolic rate, as well as extrinsic factors like dietary habits and lifestyle choices. Managing LDL cholesterol levels through healthy lifestyle choices, regular physical activity, and, if necessary, medication, is crucial for reducing the risk of cardiovascular disease in older adults.
By understanding the factors contributing to elevated LDL levels and taking proactive steps to address them, individuals can maintain optimal cardiovascular health as they age.