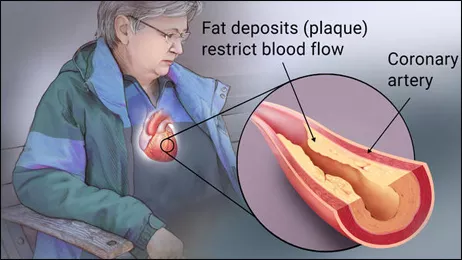
Ischemic heart disease (IHD), also known as coronary artery disease (CAD), is a condition characterized by reduced blood supply to the heart muscle, primarily due to the narrowing or blockage of coronary arteries. This can lead to angina, heart attacks, and other serious complications. As a leading cause of death globally, it is essential to understand the strategies for preventing IHD. Prevention involves lifestyle modifications, medical interventions, and regular health monitoring. This article explores various ways to prevent ischemic heart disease and improve overall cardiovascular health.
Risk Factors for Ischemic Heart Disease
Several risk factors contribute to the development of ischemic heart disease, including:
- High blood pressure
- High cholesterol levels
- Smoking
- Diabetes
- Obesity
- Physical inactivity
- Unhealthy diet
- Family history of heart disease
- Age and gender (men and older adults are at higher risk)
Understanding these risk factors is crucial for developing effective prevention strategies.
see also: What Are The Symptoms of First Degree Heart Block
How to Prevent Ischemic Heart Disease?
Healthy Diet
A balanced and nutritious diet is fundamental in preventing ischemic heart disease. Key dietary recommendations include:
Increase fruits and vegetables: Rich in vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants, they help reduce inflammation and improve heart health.
Whole grains: Foods like oats, brown rice, and whole wheat provide essential nutrients and fiber, aiding in cholesterol management.
Healthy fats: Incorporate sources of unsaturated fats such as olive oil, nuts, seeds, and fatty fish like salmon and mackerel, which are high in omega-3 fatty acids.
Limit saturated and trans fats: Found in red meat, full-fat dairy products, and processed foods, these fats can increase cholesterol levels and contribute to plaque buildup.
Reduce sodium intake: Excessive salt can raise blood pressure, a significant risk factor for IHD. Aim for less than 2,300 mg of sodium per day.
Moderate alcohol consumption: While moderate alcohol intake may have some heart benefits, excessive consumption can lead to high blood pressure and other health issues.
Regular Physical Activity
Engaging in regular physical activity is essential for maintaining cardiovascular health. Exercise helps control weight, lower blood pressure, reduce LDL (bad) cholesterol, and increase HDL (good) cholesterol. Recommendations include:
Aerobic exercise: Activities like walking, running, cycling, and swimming for at least 150 minutes per week of moderate-intensity or 75 minutes of high-intensity exercise.
Strength training: Incorporate muscle-strengthening activities at least two days per week to improve overall fitness and cardiovascular health.
Flexibility and balance exercises: Yoga and tai chi can enhance flexibility, balance, and stress management.
Weight Management
Maintaining a healthy weight is crucial in preventing ischemic heart disease. Excess body weight, especially around the abdomen, is associated with increased risk factors such as high blood pressure, high cholesterol, and diabetes. Strategies for weight management include:
Healthy eating habits: Focus on portion control, balanced meals, and avoiding processed and high-calorie foods.
Regular exercise: Combine aerobic and strength-training exercises to burn calories and build muscle.
Behavioral changes: Develop healthy habits, such as mindful eating and tracking food intake, to support long-term weight management.
Smoking Cessation
Smoking is a major risk factor for ischemic heart disease. Quitting smoking can significantly reduce the risk of heart disease and improve overall health. Tips for quitting smoking include:
Seek support: Join a smoking cessation program, use counseling services, or find a support group.
Medications: Consider nicotine replacement therapy (NRT) or prescription medications to help manage withdrawal symptoms.
Healthy habits: Replace smoking with healthy activities such as exercise, hobbies, or relaxation techniques.
Stress Management
Chronic stress can contribute to heart disease by increasing blood pressure, causing inflammation, and leading to unhealthy coping mechanisms such as overeating or smoking. Effective stress management techniques include:
Relaxation techniques: Practice deep breathing, meditation, or progressive muscle relaxation.
Physical activity: Exercise can reduce stress and improve mood.
Social support: Connect with friends, family, or support groups to share feelings and experiences.
Time management: Prioritize tasks and set realistic goals to reduce stress.
Medical Interventions for Preventing Ischemic Heart Disease
Regular Health Screenings
Regular health screenings are vital for early detection and management of risk factors for ischemic heart disease. Key screenings include:
Blood pressure: Monitor regularly to detect hypertension.
Cholesterol levels: Check lipid profiles to manage high cholesterol.
Blood sugar levels: Screen for diabetes or prediabetes.
Body mass index (BMI): Assess weight and identify obesity.
Electrocardiogram (ECG): Detect heart abnormalities.
Medications
For individuals with high risk or existing heart conditions, medications may be necessary to manage risk factors. Common medications include:
Antihypertensives: Lower blood pressure to reduce strain on the heart.
Statins: Lower cholesterol levels to prevent plaque buildup.
Aspirin: In low doses, it can reduce the risk of blood clots and heart attacks.
Diabetes medications: Control blood sugar levels to prevent complications.
Medical Procedures
In some cases, medical procedures may be necessary to prevent or treat ischemic heart disease. These include:
Angioplasty: A procedure to open narrowed or blocked coronary arteries.
Coronary artery bypass grafting (CABG): Surgery to create a new path for blood to flow around blocked arteries.
Stent placement: Inserting a stent to keep an artery open after angioplasty.
Preventive Measures for Specific Populations
Women
While ischemic heart disease is often associated with men, it is also a leading cause of death in women. Specific preventive measures for women include:
Awareness: Recognize that heart disease symptoms in women can differ from men, such as fatigue, nausea, and back or jaw pain.
Hormonal factors: Understand the impact of menopause and hormone replacement therapy on heart health.
Pregnancy-related conditions: Monitor and manage conditions like gestational diabetes and preeclampsia that increase heart disease risk.
Older Adults
As age is a significant risk factor, older adults should take extra precautions to prevent ischemic heart disease:
Regular check-ups: More frequent health screenings to monitor risk factors.
Medications: Adhere to prescribed medications and manage potential side effects.
Physical activity: Engage in low-impact exercises suitable for older adults to maintain heart health.
Individuals with Pre-existing Conditions
Those with pre-existing conditions such as diabetes, hypertension, or high cholesterol require tailored preventive strategies:
Close monitoring: Regularly check and manage blood pressure, cholesterol, and blood sugar levels.
Medications: Follow prescribed treatments and adjust as needed under medical supervision.
Lifestyle modifications: Adhere to a heart-healthy diet, exercise regimen, and stress management techniques.
Conclusion
Preventing ischemic heart disease involves a multifaceted approach that includes lifestyle modifications, medical interventions, and regular health monitoring. By adopting a healthy diet, engaging in regular physical activity, maintaining a healthy weight, quitting smoking, and managing stress, individuals can significantly reduce their risk of ischemic heart disease. Regular health screenings and appropriate medical treatments are also crucial in managing risk factors and preventing the progression of the disease. Tailoring preventive measures to specific populations such as women, older adults, and those with pre-existing conditions ensures comprehensive and effective heart disease prevention.