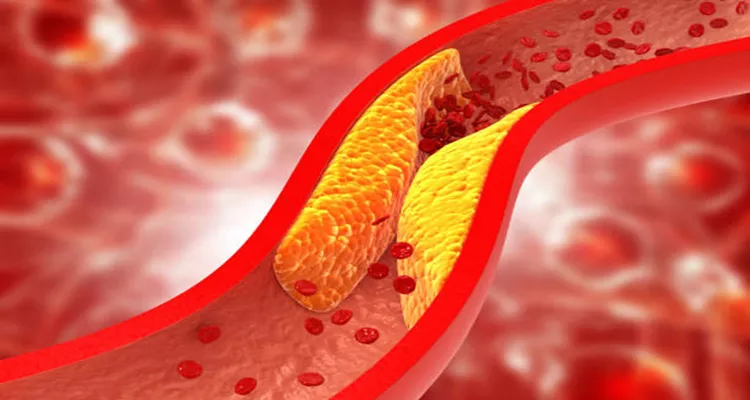
Coronary artery disease (CAD) is a leading cause of death worldwide, characterized by the narrowing or blockage of the coronary arteries due to plaque buildup. This condition can lead to serious health issues, including heart attacks and strokes. However, CAD is largely preventable through lifestyle modifications and medical interventions. This article will explore various strategies for preventing coronary artery disease, focusing on diet, exercise, smoking cessation, stress management, and medical treatments.
What Is Coronary Artery Disease?
Coronary artery disease occurs when the arteries supplying blood to the heart muscle become hardened and narrowed due to the buildup of cholesterol and other substances, known as plaque. This process, called atherosclerosis, can reduce blood flow to the heart, leading to chest pain (angina), shortness of breath, or more severe events like heart attacks.
How Can Coronary Artery Disease Be Prevented?
Healthy Diet: A Foundation for Prevention
A heart-healthy diet is crucial for preventing CAD. The following dietary guidelines can help maintain optimal cardiovascular health:
Reduce Saturated and Trans Fats: These fats, found in red meat, butter, cheese, and processed foods, can raise LDL (bad) cholesterol levels, contributing to plaque formation. Opt for healthier fats such as those found in fish, nuts, and olive oil.
Increase Fiber Intake: Soluble fiber, found in oats, beans, fruits, and vegetables, can help lower cholesterol levels. Aim for at least 25-30 grams of fiber daily.
see also: How to Prevent Coronary Artery Spasm
Limit Sodium Intake: High sodium levels can increase blood pressure, a risk factor for CAD. The American Heart Association recommends consuming no more than 2,300 milligrams of sodium per day, with an ideal limit of 1,500 milligrams for most adults.
Consume More Fruits and Vegetables: These foods are rich in vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants that support heart health. Strive for at least five servings per day.
Choose Whole Grains: Whole grains like brown rice, quinoa, and whole wheat bread provide more nutrients and fiber than refined grains, helping to control cholesterol levels and improve heart health.
Regular Physical Activity: Strengthening the Heart
Regular exercise is another key component in preventing coronary artery disease. Physical activity helps manage weight, reduce blood pressure, lower cholesterol levels, and improve overall cardiovascular health. Here are some exercise guidelines:
Aerobic Exercise: Activities such as walking, running, swimming, and cycling can improve heart health. Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity or 75 minutes of vigorous-intensity aerobic exercise per week.
Strength Training: Incorporating strength training exercises at least two days a week can help build muscle mass, boost metabolism, and support cardiovascular health.
Flexibility and Balance Exercises: Activities like yoga and tai chi can improve flexibility, balance, and reduce stress, contributing to overall well-being and heart health.
Smoking Cessation: A Crucial Step
Smoking is a major risk factor for coronary artery disease. The chemicals in tobacco smoke damage the heart and blood vessels, leading to the development of atherosclerosis. Quitting smoking can significantly reduce the risk of CAD and improve overall health. Here are some strategies to help quit smoking:
Seek Professional Help: Counseling and support groups can provide the necessary motivation and strategies to quit smoking.
Nicotine Replacement Therapy: Products such as nicotine patches, gum, and lozenges can help reduce withdrawal symptoms and cravings.
Medications: Prescription medications like varenicline (Chantix) and bupropion (Zyban) can assist in smoking cessation.
Behavioral Techniques: Identifying and avoiding triggers, practicing stress management techniques, and setting a quit date can enhance the likelihood of successfully quitting smoking.
Managing Stress: Maintaining Emotional and Physical Health
Chronic stress can contribute to the development of coronary artery disease by increasing blood pressure, raising cholesterol levels, and promoting unhealthy behaviors such as overeating and smoking. Effective stress management is essential for maintaining heart health. Consider the following techniques:
Relaxation Techniques: Practices such as deep breathing, meditation, and progressive muscle relaxation can help reduce stress levels.
Physical Activity: Regular exercise not only benefits the heart but also helps manage stress by releasing endorphins, the body’s natural stress relievers.
Healthy Sleep Habits: Ensuring adequate and quality sleep is crucial for stress management and overall health. Aim for 7-9 hours of sleep per night.
Social Support: Connecting with friends, family, or support groups can provide emotional support and help manage stress.
Time Management: Prioritizing tasks and setting realistic goals can reduce stress and improve productivity.
Medical Interventions: Montoring and Managing Health
In addition to lifestyle changes, medical interventions play a critical role in preventing and managing coronary artery disease. Regular check-ups and screenings can help identify risk factors and allow for timely intervention. Here are some medical strategies for CAD prevention:
Regular Health Screenings: Routine check-ups with a healthcare provider can monitor blood pressure, cholesterol levels, and blood sugar levels, helping to detect any abnormalities early.
Medications: For individuals with high blood pressure, high cholesterol, or diabetes, medications such as statins, antihypertensives, and antidiabetic drugs can help manage these conditions and reduce the risk of CAD.
Aspirin Therapy: For some individuals, low-dose aspirin therapy may be recommended to reduce the risk of heart attacks by preventing blood clots.
Managing Other Health Conditions: Conditions such as obesity, sleep apnea, and metabolic syndrome can increase the risk of CAD. Effective management of these conditions through lifestyle changes and medical treatment is essential.
Preventive Care: The Role of Healthcare Providers
Healthcare providers play a crucial role in the prevention of coronary artery disease. They can provide personalized advice, support, and treatment plans tailored to individual risk factors and health status. Key actions by healthcare providers include:
Risk Assessment: Evaluating individual risk factors such as family history, age, gender, and lifestyle habits to determine the risk of CAD.
Patient Education: Educating patients about the importance of lifestyle changes and providing resources and support for making these changes.
Monitoring and Follow-Up: Regular follow-up appointments to monitor progress, adjust treatment plans, and address any new health concerns.
Encouraging Preventive Measures: Emphasizing the importance of preventive measures such as vaccinations (e.g., flu shots) and regular screenings for other health conditions.
Conclusion
Preventing coronary artery disease requires a multifaceted approach that includes a healthy diet, regular physical activity, smoking cessation, stress management, and medical interventions. By adopting these strategies, individuals can significantly reduce their risk of CAD and improve their overall health and well-being. It is important to work closely with healthcare providers to develop a personalized prevention plan and stay proactive in managing heart health.