Cardiovascular disease (CVD) remains a leading cause of morbidity and mortality globally, emphasizing the critical need for effective prevention and treatment strategies. Central to this effort is the management of plaque buildup in arteries, a process known as atherosclerosis. In this article, we delve into the mechanisms of plaque formation, explore risk factors for atherosclerosis, and discuss evidence-based approaches for reducing plaque buildup to promote cardiovascular health.
Understanding Atherosclerosis And Plaque Formation
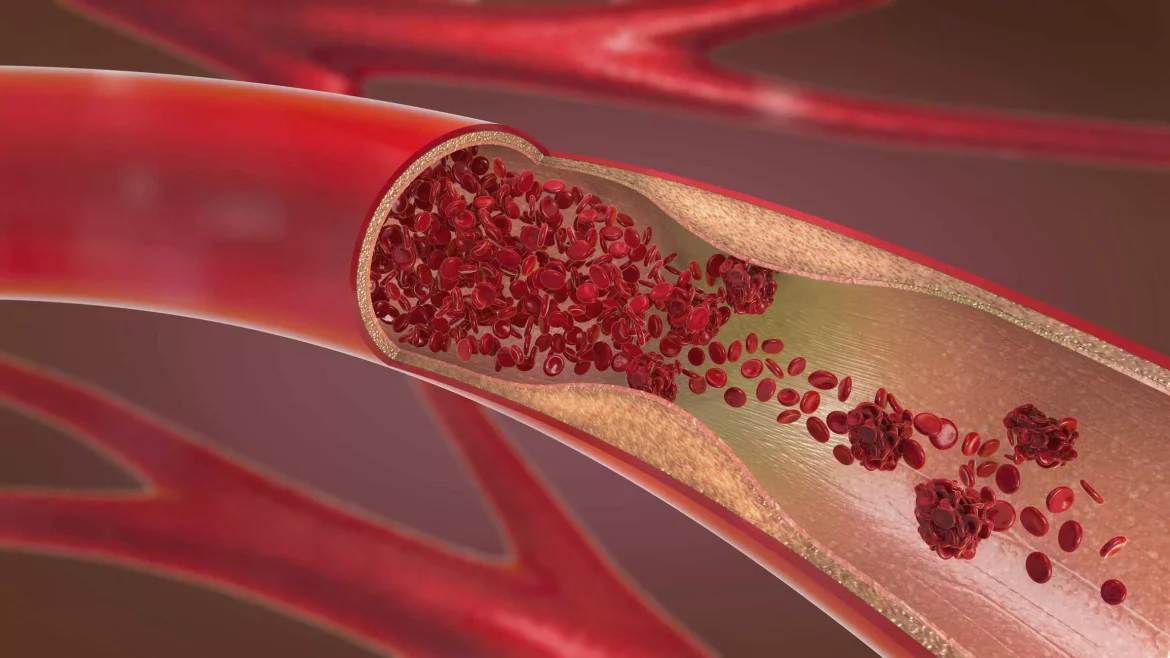
Atherosclerosis is a complex, progressive disease characterized by the deposition of fatty substances, cholesterol, cellular waste products, and calcium in the inner lining of arteries. This process leads to the formation of plaques that can narrow and stiffen arteries, restricting blood flow and increasing the risk of cardiovascular events such as heart attacks and strokes.
The key steps in plaque formation include:
Endothelial Dysfunction: Damage to the endothelium, the inner lining of blood vessels, leads to inflammation and the recruitment of immune cells.
LDL Cholesterol Infiltration: Low-density lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol penetrates the damaged endothelium and becomes oxidized, triggering an immune response.
Foam Cell Formation: Macrophages engulf oxidized LDL, transforming into foam cells that accumulate within the arterial wall.
Plaque Development: Foam cells, along with smooth muscle cells and connective tissue, form atherosclerotic plaques, which may protrude into the arterial lumen.
SEE ALSO:How to Prevent Coronary Artery Disease Through Exercise
Risk Factors for Atherosclerosis
Numerous risk factors contribute to the development and progression of atherosclerosis. These include:
High LDL Cholesterol: Elevated levels of LDL cholesterol, especially when oxidized, promote plaque formation.
Hypertension: High blood pressure accelerates endothelial damage and contributes to plaque rupture.
Smoking: Tobacco smoke contains toxins that promote inflammation and oxidative stress, exacerbating atherosclerosis.
Diabetes: Uncontrolled diabetes is associated with glucose-related damage to blood vessels and increased atherosclerotic risk.
Obesity: Excess body weight, particularly abdominal adiposity, is linked to insulin resistance and dyslipidemia, contributing to atherosclerosis.
Physical Inactivity: Sedentary lifestyles contribute to obesity, hypertension, and dyslipidemia, all of which fuel plaque buildup.
Poor Diet: Diets high in saturated fats, trans fats, and refined sugars promote atherosclerosis, while diets rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains support cardiovascular health.
Strategies for Reducing Plaque Buildup
Effective management of atherosclerosis involves a multifaceted approach targeting modifiable risk factors and promoting cardiovascular wellness. Key strategies include:
Lifestyle Modifications:
Healthy Diet: Emphasize a Mediterranean-style diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats (e.g., omega-3 fatty acids from fish).
Regular Exercise: Engage in aerobic activities such as brisk walking, cycling, or swimming for at least 150 minutes per week, supplemented by strength training.
Smoking Cessation: Quitting smoking is crucial to reducing inflammation, improving vascular function, and lowering cardiovascular risk.
Weight Management: Achieve and maintain a healthy weight through calorie control, portion moderation, and ongoing physical activity.
Stress Management: Practice relaxation techniques such as meditation, yoga, deep breathing exercises, and mindfulness to reduce stress-related cardiovascular strain.
Medication Therapy:
Statins: These drugs lower LDL cholesterol and have anti-inflammatory effects, slowing plaque progression and reducing cardiovascular events.
Blood Pressure Medications: Antihypertensive agents help control blood pressure and protect against endothelial damage and arterial stiffness.
Antiplatelet Agents: Aspirin and other antiplatelet drugs may be prescribed to prevent blood clots and reduce the risk of heart attacks and strokes.
Antidiabetic Medications: For individuals with diabetes, optimizing glycemic control with medications such as metformin or insulin is crucial to managing atherosclerotic risk.
Interventional Procedures:
Angioplasty and Stenting: In cases of severe arterial narrowing (stenosis), angioplasty with or without stent placement can restore blood flow.
Atherectomy: This procedure involves removing plaque from arteries using specialized catheters, reducing the risk of occlusion.
Coronary Artery Bypass Grafting (CABG): For extensive coronary artery disease, CABG surgery may be necessary to bypass blocked or narrowed vessels and improve blood flow to the heart.
How to Reduce Plaque Buildup in Arteries: Practical Tips
Beyond medical interventions, individuals can take proactive steps to reduce plaque buildup and enhance cardiovascular health:
Monitor Cholesterol Levels: Regularly check your cholesterol levels and work with your healthcare provider to keep LDL cholesterol within target ranges.
Manage Blood Pressure: Monitor blood pressure at home and follow prescribed medications and lifestyle modifications to maintain optimal blood pressure levels.
Maintain a Healthy Weight: Aim for a body mass index (BMI) within the healthy range and focus on sustainable weight management strategies.
Limit Saturated and Trans Fats: Reduce intake of foods high in saturated fats and trans fats, opting instead for heart-healthy alternatives.
Engage in Regular Exercise: Incorporate aerobic and strength-training exercises into your routine to improve cardiovascular fitness and vascular health.
Manage Diabetes Effectively: Monitor blood glucose levels, adhere to prescribed medications, follow dietary guidelines, and maintain regular medical check-ups for diabetes management.
Practice Stress Reduction: Prioritize stress-relieving activities such as hobbies, social connections, relaxation techniques, and adequate sleep to support overall well-being.
Conclusion
Reducing plaque buildup in arteries is a cornerstone of cardiovascular disease prevention and treatment. By addressing modifiable risk factors, adopting a heart-healthy lifestyle, adhering to medication regimens as prescribed, and collaborating closely with healthcare providers, individuals can significantly reduce their atherosclerotic burden and improve long-term cardiovascular outcomes.