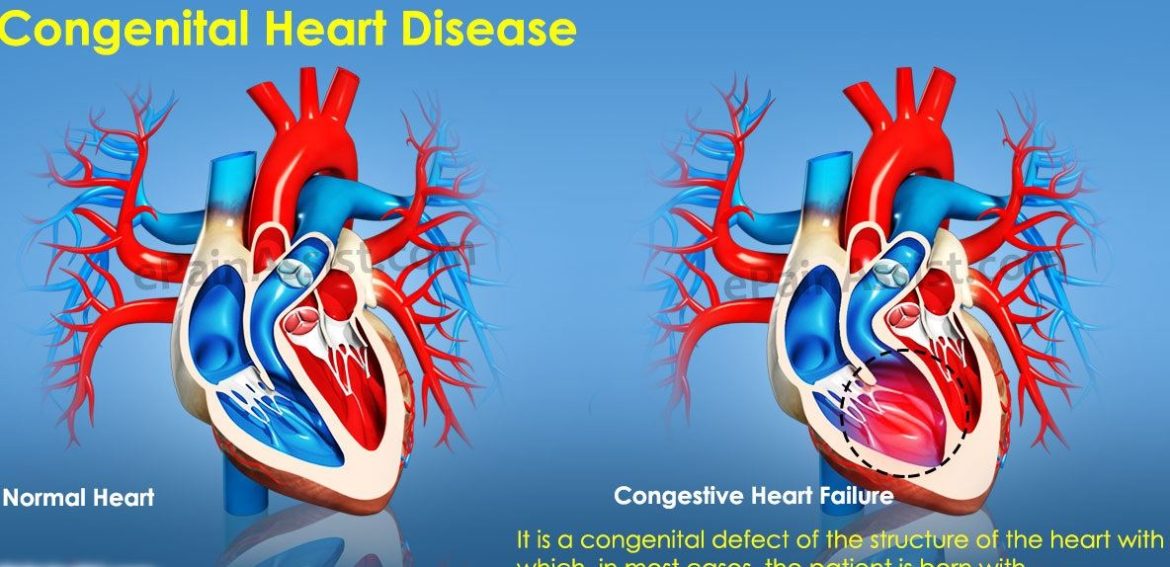
Congenital heart failure (CHF) is a complex condition that affects individuals from birth. It is characterized by structural abnormalities in the heart, leading to impaired function and potential complications over time. As a cardiologist specializing in heart failure, understanding the prognosis and life expectancy associated with CHF is crucial for patient care and management.
Understanding Congenital Heart Failure
Congenital heart defects encompass a wide range of abnormalities that can affect the heart’s structure and function. These defects may involve the heart valves, chambers, or major blood vessels. CHF occurs when these abnormalities result in the heart’s inability to pump blood effectively to meet the body’s needs.
Factors Influencing Life Expectancy
Several factors contribute to determining how long a person can live with congenital heart failure:
SEE ALSO: What Are The Treatments for Small Heart Blockages?
1. Severity of the Defect
The severity of the congenital heart defect plays a significant role in prognosis. Some defects are minor and may not significantly impact life expectancy, while others are more complex and require extensive medical intervention.
2. Timely Diagnosis and Treatment
Early diagnosis and appropriate management significantly improve outcomes for individuals with CHF. Timely interventions such as medications, surgical procedures, and lifestyle modifications can help mitigate complications and improve quality of life.
3. Associated Complications
CHF can lead to various complications such as arrhythmias, pulmonary hypertension, heart valve problems, and heart failure symptoms like fatigue and shortness of breath. Managing these complications effectively is crucial in enhancing longevity.
4. Overall Health Status
The patient’s overall health status, including factors like age, presence of other medical conditions (comorbidities), lifestyle habits, and adherence to treatment plans, also influence life expectancy.
Prognosis And Life Expectancy
It’s essential to note that the prognosis for individuals with congenital heart failure has improved significantly over the years due to advancements in medical technology and treatment strategies.
However, predicting an exact life expectancy can be challenging as it varies widely based on individual circumstances.
1. Mild to Moderate Defects
For individuals with mild to moderate congenital heart defects, life expectancy is often near-normal with appropriate management. This includes regular follow-ups with healthcare providers, adherence to medication regimens, lifestyle modifications (such as maintaining a healthy diet, staying physically active, avoiding smoking), and monitoring for any signs of worsening symptoms or complications.
2. Complex Defects
In cases of more complex congenital heart defects or those associated with significant complications, life expectancy may be reduced. However, advancements in surgical techniques, cardiac interventions, and medical therapies have improved outcomes even for these challenging cases.
3. Quality of Life Considerations
While life expectancy is an important aspect, focusing on improving the quality of life for individuals with CHF is equally crucial. This involves addressing symptoms, managing comorbidities effectively, providing psychological support, and promoting overall well-being.
Treatment Strategies for Congenital Heart Failure
The treatment approach for congenital heart failure aims to:
Manage Symptoms: Medications such as diuretics, ACE inhibitors, beta-blockers, and digitalis help alleviate symptoms like fluid retention, fatigue, and shortness of breath.
Surgical Interventions: Surgical procedures such as valve repair or replacement, atrial septal defect closure, ventricular septal defect repair, and implantation of devices like pacemakers or implantable cardioverter-defibrillators (ICDs) may be necessary depending on the specific defect and associated complications.
Lifestyle Modifications: Encouraging a heart-healthy lifestyle, including regular exercise (as recommended by healthcare providers), balanced nutrition, weight management, smoking cessation, and stress reduction, plays a vital role in managing CHF.
Regular Monitoring: Ongoing monitoring through clinical evaluations, imaging tests (such as echocardiograms), and laboratory assessments helps track disease progression, adjust treatment plans as needed, and detect any new complications early.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the prognosis for individuals with congenital heart failure has significantly improved with advancements in medical care and treatment modalities. While life expectancy varies based on factors such as the severity of the defect, timely diagnosis, treatment effectiveness, and overall health status, proactive management strategies can enhance both longevity and quality of life for patients living with CHF.
FAQs
How long can you live with congestive heart failure?
The life expectancy for individuals with congestive heart failure (CHF) varies widely depending on several factors such as the underlying cause of CHF, the severity of the condition, age, overall health status, and adherence to treatment plans.
With appropriate medical care, lifestyle modifications, and management of underlying conditions, many individuals with CHF can live for several years. However, it’s important to note that CHF is a chronic condition that requires ongoing monitoring and treatment to optimize outcomes.
Can you live a normal life with congenital heart disease?
Yes, many individuals with congenital heart disease (CHD) can live fulfilling and relatively normal lives with proper management and care. Advances in medical technology, surgical interventions, and cardiac therapies have significantly improved outcomes for people with CHD. However, the specific prognosis and ability to lead a normal life depend on factors such as the type and severity of the CHD, timely diagnosis and treatment, access to healthcare resources, lifestyle factors, and the presence of any associated complications.
Can heart failure go back to normal?
In some cases, heart failure can be managed effectively with medical treatments, lifestyle changes, and interventions such as surgery or device implantation, allowing individuals to experience significant improvement in symptoms and overall function. This improvement may lead to a state where the heart failure is well-controlled, and the individual can lead a relatively normal life.
However, it’s essential to recognize that heart failure is often a chronic condition that requires ongoing management and monitoring, even if symptoms improve. Compliance with treatment plans and regular follow-ups with healthcare providers are essential for optimizing outcomes in individuals with heart failure.