Coronary artery disease (CAD) is a major health concern worldwide, often leading to severe complications if not identified and managed early. Recognizing the warning signs is crucial for timely intervention and prevention of life-threatening events such as heart attacks. This article delves into the four primary warning signs of coronary artery disease, providing detailed insights into each symptom, their implications, and the importance of seeking medical attention promptly.
Introduction to Coronary Artery Disease
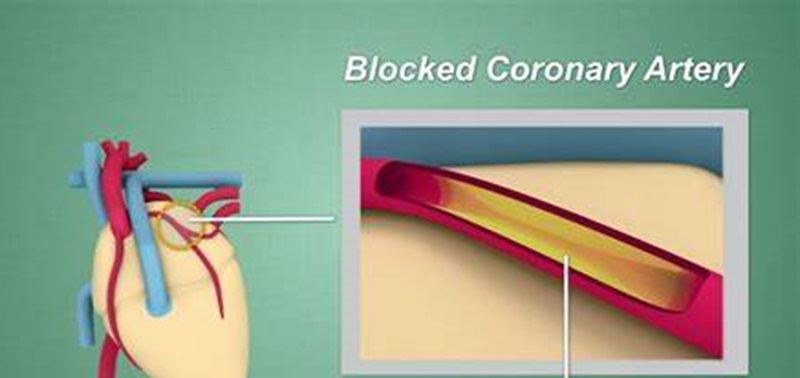
Coronary artery disease (CAD) is characterized by the narrowing or blockage of the coronary arteries, primarily due to atherosclerosis—a condition where plaque builds up on the artery walls. This buildup reduces blood flow to the heart muscle, which can lead to chest pain (angina), shortness of breath, or even a heart attack. Understanding the warning signs of CAD is essential for early detection and management, which can significantly improve outcomes and quality of life for those affected.
SEE ALSO: How Is CHD Caused?
4 Warning Signs of Coronary Artery Disease
1. Chest Pain (Angina)
Description
Chest pain, or angina, is one of the most common and recognizable warning signs of CAD. Angina occurs when the heart muscle does not get enough oxygen-rich blood. This condition can manifest as a feeling of pressure, tightness, or squeezing in the chest, and it may also extend to the shoulders, arms, neck, jaw, or back.
Types of Angina
Stable Angina: This type of angina typically occurs during physical exertion or stress and follows a predictable pattern. It usually lasts for a few minutes and can be relieved by rest or medication.
Unstable Angina: Unlike stable angina, unstable angina can occur unexpectedly, even at rest. It is more severe and lasts longer. This type of angina is a medical emergency as it indicates a higher risk of heart attack.
Variant (Prinzmetal) Angina: This is a rare type of angina caused by a spasm in the coronary arteries. It usually occurs at rest and can be severe.
Significance
The presence of angina indicates that the heart muscle is not receiving enough blood, which is a clear sign of narrowed or blocked coronary arteries. Prompt medical evaluation and treatment are essential to prevent the progression to a heart attack.
Management
Treatment for angina may include lifestyle changes, medications (such as nitrates, beta-blockers, and calcium channel blockers), and in some cases, surgical interventions like angioplasty or coronary artery bypass grafting (CABG).
2. Shortness of Breath
Description
Shortness of breath, also known as dyspnea, can be an early warning sign of CAD. It occurs when the heart is unable to pump sufficient blood to meet the body’s needs, resulting in fluid buildup in the lungs (congestive heart failure) or reduced oxygen delivery to tissues.
Symptoms
- Difficulty breathing during physical activity or at rest.
- A feeling of being unable to catch your breath.
- Wheezing or gasping for air.
- Waking up breathless during the night.
Significance
Shortness of breath can indicate that the heart’s pumping efficiency is compromised due to reduced blood flow from narrowed coronary arteries. This symptom should not be ignored, as it may precede more severe cardiac events.
Management
Addressing shortness of breath involves treating the underlying CAD and improving heart function. This may include medications to reduce fluid buildup (diuretics), improve heart function (ACE inhibitors, beta-blockers), and lifestyle changes such as weight management, smoking cessation, and regular physical activity.
3. Fatigue
Description
Unexplained fatigue is a less recognized but significant warning sign of CAD. Fatigue in the context of heart disease is often due to reduced blood flow to the heart and other organs, leading to decreased oxygen and nutrient delivery.
Symptoms
- Persistent tiredness despite adequate rest.
- Difficulty performing everyday activities.
- Feeling exhausted after minimal exertion.
Significance
Fatigue may be a subtle and early indicator of CAD, especially in women. It reflects the heart’s struggle to supply adequate blood flow, impacting overall energy levels and physical endurance.
Management
Managing fatigue involves comprehensive treatment of CAD through medications, lifestyle modifications, and addressing contributing factors such as sleep disorders or anemia. Regular exercise, a balanced diet, and stress management techniques can also help improve energy levels.
4. Heart Palpitations
Description
Heart palpitations are sensations of irregular or rapid heartbeats. While occasional palpitations can be harmless, frequent or severe palpitations may indicate underlying heart problems, including CAD.
Symptoms
A feeling of fluttering, pounding, or racing heart.
Skipped or extra heartbeats.
A sensation of the heart beating too hard or fast.
Significance
Palpitations can occur due to reduced blood flow to the heart muscle, causing electrical instability and abnormal heart rhythms (arrhythmias). This symptom warrants medical evaluation to rule out serious conditions like atrial fibrillation or ventricular tachycardia.
Management
Treatment for palpitations may involve medications to control heart rate and rhythm (beta-blockers, antiarrhythmics), lifestyle changes to avoid triggers (caffeine, stress), and in some cases, procedures like catheter ablation to correct abnormal heart rhythms.
Risk Factors for Coronary Artery Disease
Understanding the risk factors for CAD is crucial for prevention and early intervention. Common risk factors include:
High Blood Pressure: Elevated blood pressure can damage the arteries, making them more susceptible to plaque buildup.
High Cholesterol: High levels of LDL cholesterol contribute to plaque formation in the arteries.
Smoking: Smoking damages the lining of the arteries and accelerates atherosclerosis.
Diabetes: Diabetes increases the risk of CAD by contributing to high blood sugar levels, which can damage blood vessels.
Obesity: Excess weight, especially around the abdomen, is associated with increased risk of CAD.
Sedentary Lifestyle: Lack of physical activity contributes to obesity, high blood pressure, and high cholesterol.
Family History: A family history of heart disease increases the likelihood of developing CAD.
Age and Gender: Men are at higher risk of CAD at a younger age, while women’s risk increases after menopause.
Prevention And Early Detection
Preventing CAD involves addressing modifiable risk factors through lifestyle changes and medical management. Key strategies include:
Healthy Diet: Consuming a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats.
Regular Exercise: Engaging in at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise per week.
Smoking Cessation: Quitting smoking to improve heart health and reduce CAD risk.
Weight Management: Maintaining a healthy weight through diet and exercise.
Blood Pressure and Cholesterol Control: Regular monitoring and management of blood pressure and cholesterol levels.
Diabetes Management: Keeping blood sugar levels under control through diet, exercise, and medications.
Early detection of CAD through regular check-ups, screening tests (such as cholesterol levels and blood pressure), and diagnostic procedures (like stress tests and coronary angiography) is vital for timely intervention and better outcomes.
Conclusion
Coronary artery disease is a serious condition that requires vigilance and proactive management. Recognizing the warning signs—chest pain, shortness of breath, fatigue, and heart palpitations—can lead to early diagnosis and treatment, potentially preventing severe complications such as heart attacks. By addressing risk factors and adopting a heart-healthy lifestyle, individuals can significantly reduce their risk of developing CAD and improve their overall cardiovascular health. If you or someone you know experiences these warning signs, seeking medical attention promptly is crucial for ensuring optimal heart health and longevity.