Myocarditis is an inflammatory condition of the heart muscle (myocardium) that can significantly affect the heart’s ability to pump blood effectively. It can result from various causes, including infections, autoimmune diseases, and exposure to toxins. Diagnosing myocarditis can be challenging, as its symptoms often overlap with other cardiac conditions.
Echocardiography (echo) plays a crucial role in the diagnostic process, providing detailed images of the heart’s structure and function. This article delves into the echocardiographic findings associated with myocarditis, elucidating what this condition looks like on an echo.
Understanding Myocarditis
Myocarditis involves inflammation of the heart muscle, leading to myocardial damage and impaired cardiac function. The inflammation can be diffuse or focal, depending on the underlying cause and the extent of the disease. Common symptoms of myocarditis include chest pain, fatigue, shortness of breath, and arrhythmias. Severe cases may progress to heart failure or sudden cardiac death.
SEE ALSO: 8 Symptoms of COVID-19 Myocarditis
Echocardiography in Diagnosing Myocarditis
Echocardiography is a non-invasive imaging technique that uses ultrasound waves to create detailed images of the heart. It is a vital tool in the assessment of patients with suspected myocarditis. Echo provides real-time visualization of the heart’s structure and function, allowing for the detection of abnormalities that suggest myocardial inflammation and damage.
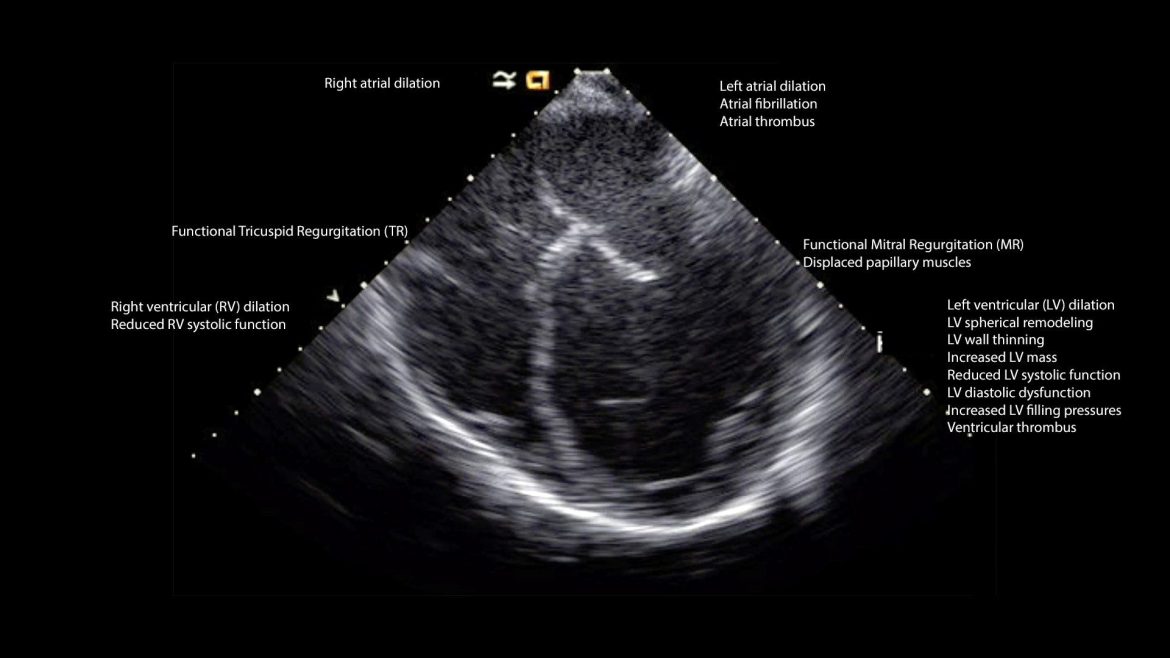
Key Echocardiographic Findings in Myocarditis
The echocardiographic appearance of myocarditis can vary widely, depending on the severity and extent of the inflammation. However, several key findings are commonly associated with this condition:
1. Left Ventricular Systolic Dysfunction
One of the hallmark features of myocarditis on echo is left ventricular (LV) systolic dysfunction. This manifests as a reduced ejection fraction (EF), indicating that the heart’s ability to pump blood is compromised. The extent of LV dysfunction can range from mild to severe, depending on the severity of the inflammation.
2. Regional Wall Motion Abnormalities
Myocarditis often leads to regional wall motion abnormalities, where specific areas of the heart muscle exhibit impaired movement. These abnormalities can be diffuse or localized, reflecting the areas affected by inflammation. On echo, this is seen as hypokinesis (reduced movement), akinesis (lack of movement), or dyskinesis (abnormal movement) of the affected myocardial segments.
3. Increased Echogenicity
In the acute phase of myocarditis, the inflamed myocardium may appear brighter (increased echogenicity) on the echocardiogram. This is due to the presence of inflammatory cells and edema within the heart muscle. Over time, as inflammation resolves, the echogenicity may return to normal.
4. Pericardial Effusion
Pericardial effusion, an accumulation of fluid in the pericardial sac surrounding the heart, is a common finding in myocarditis. On echo, pericardial effusion appears as an anechoic (dark) space between the pericardium and the myocardium. The presence of pericardial effusion can indicate ongoing inflammation and may be associated with more severe disease.
5. Dilated Cardiomyopathy
In chronic or severe cases of myocarditis, the heart may undergo remodeling, resulting in dilated cardiomyopathy. This is characterized by an enlarged left ventricle with a thinned and weakened myocardium.
On echo, this appears as a dilated LV cavity with reduced contractility and an impaired ejection fraction.
6. Intracardiac Thrombi
Myocarditis can increase the risk of thrombus (blood clot) formation within the heart chambers. Intracardiac thrombi are more likely to develop in areas of severe wall motion abnormalities or dilated cardiomyopathy. On echo, thrombi appear as echogenic masses within the heart chambers.
7. Diastolic Dysfunction
In addition to systolic dysfunction, myocarditis can also lead to diastolic dysfunction, where the heart’s ability to relax and fill with blood is impaired. Diastolic dysfunction can be assessed on echo through various parameters, including transmitral flow patterns, tissue Doppler imaging, and left atrial size.
Advanced Echocardiographic Techniques in Myocarditis
In addition to standard echocardiographic techniques, several advanced methods can provide further insights into the presence and severity of myocarditis:
1. Speckle Tracking Echocardiography
Speckle tracking echocardiography (STE) is a technique that analyzes the motion of speckles (natural acoustic markers) within the myocardium. STE can assess myocardial strain and strain rate, providing detailed information on regional and global myocardial function. In myocarditis, STE can detect subtle changes in myocardial mechanics that may not be apparent on conventional echo.
2. Three-Dimensional Echocardiography
Three-dimensional echocardiography (3D echo) allows for more comprehensive visualization of the heart’s st
ructure and function compared to traditional two-dimensional imaging. 3D echo can be particularly useful in assessing the extent of myocardial damage and remodeling in myocarditis, providing accurate measurements of ventricular volumes and ejection fraction.
3. Contrast-Enhanced Echocardiography
Contrast-enhanced echocardiography involves the use of intravenous contrast agents to improve the visualization of cardiac structures and blood flow. This technique can enhance the detection of wall motion abnormalities, intracardiac thrombi, and areas of myocardial necrosis or scarring in myocarditis.
Differential Diagnosis of Myocarditis on Echo
While echocardiography is a valuable tool in diagnosing myocarditis, it is essential to differentiate this condition from other cardiac diseases that may present with similar echocardiographic findings. Some conditions to consider in the differential diagnosis include:
1. Ischemic Heart Disease
Ischemic heart disease (IHD) can also cause regional wall motion abnormalities and LV dysfunction. However, IHD typically presents with a history of chest pain, risk factors for coronary artery disease, and findings of coronary artery stenosis on imaging studies. Myocarditis, on the other hand, may present with a viral prodrome, and coronary arteries are usually normal.
2. Dilated Cardiomyopathy
Dilated cardiomyopathy (DCM) is characterized by LV dilation and systolic dysfunction, similar to chronic myocarditis.
However, DCM is a chronic condition with a more gradual onset, whereas myocarditis often presents acutely. Additionally, myocarditis may show evidence of active inflammation or pericardial effusion, which are not typical features of primary DCM.
3. Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy
Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (HCM) involves abnormal thickening of the myocardium, which can be mistaken for myocarditis. However, HCM usually presents with asymmetric septal hypertrophy and preserved or hyperdynamic LV systolic function, unlike the global LV dysfunction seen in myocarditis.
4. Pericarditis
Pericarditis is inflammation of the pericardium, which can coexist with myocarditis (myopericarditis). Pericarditis typically presents with pericardial effusion and echocardiographic signs of pericardial inflammation, such as pericardial thickening and echogenic strands. Isolated pericarditis does not usually cause LV dysfunction or wall motion abnormalities.
Conclusion
Echocardiography is an indispensable tool in the diagnosis and management of myocarditis. The condition presents with a range of echocardiographic findings, including left ventricular systolic dysfunction, regional wall motion abnormalities, increased echogenicity, pericardial effusion, dilated cardiomyopathy, intracardiac thrombi, and diastolic dysfunction.
Advanced echocardiographic techniques such as speckle tracking, three-dimensional echocardiography, and contrast-enhanced echocardiography can provide additional insights into myocardial function and inflammation. Differentiating myocarditis from other cardiac conditions with similar echocardiographic features is crucial for accurate diagnosis and appropriate management.