Arrhythmia refers to an irregular heartbeat where the heart may beat too fast, too slow, or with an irregular rhythm. It encompasses various conditions, including atrial fibrillation, bradycardia, and tachycardia, among others. Individuals with arrhythmia often experience symptoms such as palpitations, dizziness, shortness of breath, and fatigue. Sleep disturbances are common among those with arrhythmia, which can further exacerbate the condition and negatively impact overall health.
The Importance of Quality Sleep
Quality sleep is crucial for everyone, but it is especially important for individuals with arrhythmia. Poor sleep can lead to an increased risk of heart disease, hypertension, and stroke. Additionally, lack of sleep can worsen arrhythmia symptoms, creating a vicious cycle of poor sleep and deteriorating heart health. Therefore, it is essential for people with arrhythmia to adopt strategies that promote restful sleep and manage their condition effectively.
Managing Arrhythmia for Better Sleep
Medication and Treatment Adherence
One of the primary steps in managing arrhythmia is adhering to prescribed medications and treatments. Medications such as beta-blockers, calcium channel blockers, and antiarrhythmic drugs can help regulate heart rhythm and reduce symptoms.
It is important to take these medications as prescribed and consult with a healthcare provider if any side effects or issues arise.
SEE ALSO: The 5 Best Sleeping Position for Patients with Arrhythmia
Regular Medical Check-ups
Regular check-ups with a cardiologist are essential for monitoring arrhythmia and adjusting treatment plans as needed.
These visits provide an opportunity to discuss any sleep-related issues and explore potential adjustments to medications or therapies that might improve sleep quality.
Creating A Sleep-Conducive Environment
Comfortable Sleeping Space
Creating a comfortable and relaxing sleeping environment can significantly impact sleep quality. Ensure that your bedroom is cool, quiet, and dark. Invest in a comfortable mattress and pillows that provide adequate support. Using blackout curtains and white noise machines can help eliminate external disturbances.
Establishing a Sleep Routine
Maintaining a consistent sleep schedule is beneficial for regulating the body’s internal clock. Try to go to bed and wake up at the same time every day, even on weekends. Establishing a pre-sleep routine, such as reading a book, taking a warm bath, or practicing relaxation techniques, can signal to your body that it is time to wind down and prepare for sleep.
Limiting Screen Time
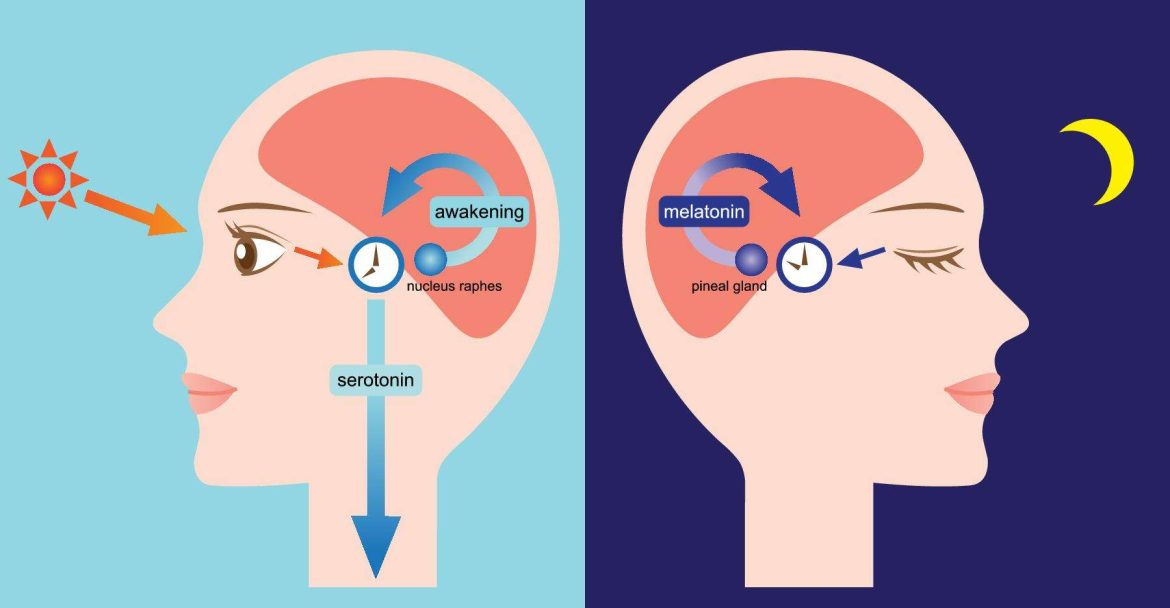
Exposure to screens before bedtime can interfere with the production of melatonin, the hormone responsible for regulating sleep. Limit screen time at least an hour before bed, and consider using blue light filters on electronic devices during the evening.
Lifestyle Changes for Better Sleep
Regular Exercise
Engaging in regular physical activity can help improve overall heart health and reduce the frequency and severity of arrhythmia episodes. Aim for at least 30 minutes of moderate exercise most days of the week. However, avoid vigorous exercise close to bedtime, as it may interfere with your ability to fall asleep.
Healthy Diet
A heart-healthy diet can play a significant role in managing arrhythmia and promoting better sleep. Focus on consuming a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats. Limit the intake of caffeine, alcohol, and heavy meals, especially in the evening, as they can disrupt sleep patterns and trigger arrhythmia symptoms.
Stress Management
Stress and anxiety can exacerbate arrhythmia symptoms and contribute to sleep disturbances. Incorporate stress-reducing activities into your daily routine, such as yoga, meditation, deep breathing exercises, or engaging in hobbies you enjoy.
Seeking support from a therapist or counselor can also be beneficial for managing stress and anxiety related to arrhythmia.
Sleep Positions And Techniques
Left Side Sleeping
Sleeping on the left side is often recommended for individuals with heart conditions, including arrhythmia. This position can improve blood flow and reduce the pressure on the heart, potentially leading to fewer arrhythmia episodes during the night. Experiment with different sleeping positions to find the one that feels most comfortable and beneficial for your condition.
Elevating the Head
Elevating the head while sleeping can help reduce symptoms of arrhythmia, especially if you experience shortness of breath or palpitations at night. Use an adjustable bed or add extra pillows to elevate the head and upper body. This position can also help alleviate symptoms of acid reflux, which can further disrupt sleep.
Progressive Muscle Relaxation
Progressive muscle relaxation (PMR) is a technique that involves tensing and then relaxing different muscle groups in the body. This practice can help reduce stress and promote relaxation, making it easier to fall asleep. Incorporate
PMR into your nightly routine to help calm the mind and body before bed.
Dealing with Nighttime Arrhythmia Episodes
Recognizing Symptoms
It is important to recognize the symptoms of nighttime arrhythmia episodes, such as palpitations, chest discomfort, shortness of breath, or dizziness. Understanding these symptoms can help you respond appropriately and seek medical attention if necessary.
Deep Breathing Exercises
When experiencing arrhythmia symptoms at night, deep breathing exercises can help calm the heart and reduce anxiety.
Practice slow, deep breaths, inhaling through the nose and exhaling through the mouth. This technique can help regulate heart rate and promote relaxation.
Staying Calm
Remaining calm during an arrhythmia episode is crucial. Panic and anxiety can worsen symptoms and make it more difficult to return to sleep. Focus on slow, deep breaths and remind yourself that the episode will pass. If symptoms persist or worsen, seek medical assistance.
When to Seek Medical Attention
While many arrhythmia episodes are harmless, it is important to know when to seek medical attention. If you experience severe or persistent symptoms, such as chest pain, fainting, or difficulty breathing, contact a healthcare professional immediately. Additionally, if sleep disturbances due to arrhythmia are impacting your daily life, discuss these issues with your doctor to explore potential solutions.
Conclusion
Managing arrhythmia and achieving restful sleep can be challenging, but it is possible with the right strategies and lifestyle changes. By adhering to medication and treatment plans, creating a sleep-conducive environment, adopting healthy lifestyle habits, and seeking support when needed, individuals with arrhythmia can improve their sleep quality and overall well-being. Always consult with a healthcare professional for personalized advice and treatment options tailored to your specific condition.