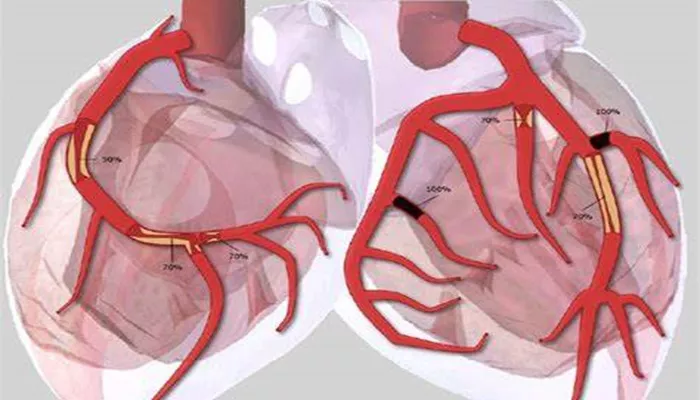
Coronary artery disease (CAD) is one of the most common forms of heart disease and a leading cause of death worldwide. It occurs when the coronary arteries, which supply blood to the heart muscle, become narrowed or blocked due to the buildup of plaque. This plaque is primarily composed of cholesterol, fatty substances, and other materials that accumulate in the artery walls, a process known as atherosclerosis. As the arteries narrow, blood flow to the heart is restricted, leading to various symptoms and complications. This article will discuss the characteristics of coronary artery disease and outline five key symptoms associated with this condition.
What Causes Coronary Artery Disease?
Several factors contribute to the development of coronary artery disease. These include:
High Cholesterol Levels: Elevated levels of low-density lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol can lead to plaque buildup in the arteries.
High Blood Pressure: Hypertension can damage the arteries over time, making them more susceptible to plaque formation.
Smoking: Tobacco use is a significant risk factor for CAD. It damages blood vessels and reduces oxygen supply to the heart.
Diabetes: High blood sugar levels can damage blood vessels and increase the risk of atherosclerosis.
Obesity: Excess body weight contributes to other risk factors, such as high blood pressure and diabetes.
Sedentary Lifestyle: Lack of physical activity can lead to weight gain and increase the risk of heart disease.
Family History: A family history of heart disease can increase an individual’s risk of developing CAD.
Age: The risk of CAD increases with age, particularly for men over 45 and women over 55.
see also: What Does Acute Coronary Syndrome Include
Symptoms of Coronary Artery Disease
Many people with coronary artery disease may not experience symptoms until the condition has progressed significantly.
However, as the disease advances, several symptoms may become apparent. Here are five key symptoms to be aware of:
1. Chest Pain (Angina)
Chest pain, often referred to as angina, is the most common symptom of coronary artery disease. It can present in various ways, including:
Pressure or Tightness: Many patients describe a feeling of pressure or tightness in the chest, similar to having a heavy weight on their chest.
Squeezing or Burning Sensation: Some individuals may experience a squeezing or burning sensation in the chest.
Radiating Pain: Angina can also radiate to other areas, such as the shoulders, arms, neck, jaw, or back.
Angina typically occurs during physical exertion or emotional stress when the heart requires more oxygen. It usually subsides with rest or the use of nitroglycerin, a medication that helps relieve chest pain.
2. Shortness of Breath
Shortness of breath, or dyspnea, is another common symptom of coronary artery disease. It may occur during physical activity or even at rest in more advanced cases. Patients may feel breathless or unable to catch their breath, particularly during exertion. This symptom arises because the heart struggles to pump enough blood to meet the body’s demands, leading to inadequate oxygen supply.
3. Fatigue
Unexplained fatigue is a symptom that can be associated with coronary artery disease. Patients may feel unusually tired or weak, even with minimal physical activity. This fatigue can result from the heart’s reduced ability to pump blood effectively, leading to decreased oxygen delivery to the body’s tissues. It is essential to note that fatigue may not always be linked to heart disease, but it can be a warning sign, especially when combined with other symptoms.
4. Heart Palpitations
Heart palpitations refer to the sensation of an irregular or rapid heartbeat. Patients may describe this feeling as their heart racing, fluttering, or pounding in their chest. Palpitations can occur due to various factors, including stress, anxiety, or caffeine intake. However, in the context of coronary artery disease, they may indicate that the heart is not receiving enough blood and oxygen, leading to abnormal heart rhythms.
5. Dizziness or Lightheadedness
Dizziness or lightheadedness can occur in individuals with coronary artery disease, especially during physical activity or when standing up quickly. This symptom may be caused by reduced blood flow to the brain due to impaired heart function.
In some cases, it can lead to fainting or near-fainting episodes, which require immediate medical attention.
When to Seek Medical Attention
If you experience any of the symptoms associated with coronary artery disease, it is essential to seek medical attention promptly. This is particularly important if you experience:
Chest Pain: If chest pain lasts more than a few minutes or is accompanied by other symptoms such as shortness of breath, sweating, or nausea, call emergency services immediately.
Severe Shortness of Breath: If you have difficulty breathing, especially at rest or with minimal exertion, seek medical help.
Dizziness or Fainting:
If you experience sudden dizziness, lightheadedness, or fainting, it is important to consult a healthcare professional.
Diagnosis of Coronary Artery Disease
Diagnosing coronary artery disease typically involves a combination of medical history, physical examination, and diagnostic tests. Your healthcare provider may perform the following:
Medical History Review: Your doctor will ask about your symptoms, risk factors, and family history of heart disease.
Physical Examination: A physical exam may include checking your blood pressure, heart rate, and listening to your heart and lungs.
Electrocardiogram (ECG): This test records the electrical activity of your heart and can help identify irregularities in heart rhythm.
Stress Test: A stress test evaluates how your heart functions during physical activity. It may involve walking on a treadmill or pedaling a stationary bike while your heart is monitored.
Echocardiogram: This ultrasound test provides images of the heart’s structure and function, helping to assess any abnormalities.
Coronary Angiography: In some cases, a coronary angiogram may be performed. This test involves injecting a contrast dye into the coronary arteries to visualize blockages using X-ray imaging.
Treatment Options for Coronary Artery Disease
While coronary artery disease cannot be cured, various treatment options can help manage the condition and reduce the risk of complications. These include:
Lifestyle Changes: Adopting a heart-healthy lifestyle is crucial for managing CAD. This includes:
Eating a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins.
Engaging in regular physical activity, such as walking, swimming, or cycling.
Quitting smoking and avoiding secondhand smoke.
Managing stress through relaxation techniques, such as yoga or meditation.
Medications: Several medications may be prescribed to manage coronary artery disease, including:
Antiplatelet Agents: Medications like aspirin can help prevent blood clots from forming in narrowed arteries.
Statins: These drugs help lower cholesterol levels, reducing the risk of plaque buildup.
Beta-Blockers: These medications can lower heart rate and blood pressure, reducing the heart’s workload.
ACE Inhibitors: These help relax blood vessels and lower blood pressure, improving blood flow to the heart.
Diuretics: These medications help reduce fluid buildup in the body, easing symptoms of heart failure.
Surgical Procedures: In more severe cases, surgical interventions may be necessary, such as:
Coronary Angioplasty and Stenting: This procedure involves using a balloon to open narrowed arteries and placing a stent to keep them open.
Coronary Artery Bypass Grafting (CABG): This surgery creates a new pathway for blood to flow to the heart by bypassing blocked arteries.
Conclusion
Coronary artery disease is a prevalent and serious condition that can significantly impact an individual’s health and quality of life. Recognizing the symptoms, such as chest pain, shortness of breath, fatigue, heart palpitations, and dizziness, is crucial for early diagnosis and management.
While coronary artery disease cannot be cured, effective treatment options are available to manage symptoms and reduce the risk of complications. Lifestyle changes, medications, and surgical interventions can help individuals lead healthier lives.