Supraventricular tachycardia (SVT) is a common heart rhythm disorder characterized by an abnormally fast heartbeat that originates above the heart’s ventricles. This condition can lead to various symptoms, including palpitations, dizziness, and even fainting. One area of interest in the study of SVT is its potential relationship with dehydration. This article explores the nature of SVT, its symptoms, causes, and the implications of dehydration on this condition.
What Is Supraventricular Tachycardia?
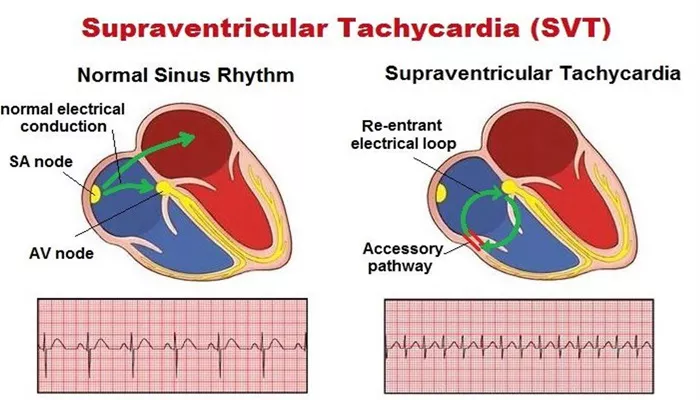
Supraventricular tachycardia refers to a group of arrhythmias that result in a rapid heart rate, typically exceeding 100 beats per minute. The term encompasses several types of tachycardia, including atrioventricular nodal reentrant tachycardia (AVNRT) and atrial fibrillation. SVT occurs when electrical signals in the heart become disrupted, causing the heart to beat too quickly.
Types of SVT
Atrioventricular Nodal Reentrant Tachycardia (AVNRT): This is the most common form of SVT, often triggered by a reentrant circuit within the AV node.
Atrial Fibrillation: This irregular and often rapid heart rate occurs when the atria experience chaotic electrical signals.
Atrial Flutter: Similar to atrial fibrillation, but with a more organized rhythm.
Paroxysmal Supraventricular Tachycardia (PSVT): This type is characterized by episodes of rapid heart rate that start and stop suddenly.
Symptoms of Supraventricular Tachycardia
Patients with SVT may experience a range of symptoms, which can vary in intensity:
Palpitations: A sensation of a racing or pounding heart.
Dizziness or Lightheadedness: Due to reduced blood flow to the brain.
Chest Pain: Often described as a tight or heavy feeling.
Shortness of Breath: Difficulty in breathing, especially during episodes.
Fainting: Loss of consciousness can occur in severe cases.
While some individuals may not experience noticeable symptoms, others may find the episodes distressing and disruptive to daily life.
SEE ALSO: Can Too Much Serotonin Cause Heart Problems?
Causes of Supraventricular Tachycardia
Several factors can contribute to the development of SVT, including:
Structural Heart Disease: Conditions such as coronary artery disease or heart valve disorders.
Electrolyte Imbalances: Abnormal levels of potassium, magnesium, or calcium can affect heart rhythm.
Stimulants: Caffeine, nicotine, and certain medications can provoke episodes.
Stress and Anxiety: Emotional or physical stress can trigger SVT.
Dehydration: A significant area of concern, as dehydration can lead to electrolyte imbalances and increased heart rate.
The Role of Dehydration in Supraventricular Tachycardia
Dehydration occurs when the body loses more fluids than it takes in.
This can lead to a variety of physiological changes, including alterations in blood volume and electrolyte concentrations.
How Dehydration Affects The Heart
Increased Heart Rate: When dehydrated, the body compensates for reduced blood volume by increasing heart rate to maintain adequate circulation. This heightened demand on the heart can precipitate episodes of SVT.
Electrolyte Imbalance: Dehydration can lead to imbalances in key electrolytes such as potassium and sodium, which are crucial for maintaining normal heart rhythm. An imbalance can disrupt electrical signaling in the heart, potentially triggering SVT.
Thickened Blood: Dehydration can result in thicker blood, making it more difficult for the heart to pump effectively. This increased workload may lead to a faster heart rate and palpitations.
Can Dehydration Cause Supraventricular Tachycardia
Research indicates a significant connection between dehydration and the occurrence of SVT. A study highlighted that fluid depletion could improve atrial contraction and increase heart rate, suggesting a direct link between hydration status and heart rhythm disorders.
In clinical observations, patients with a history of dehydration often report episodes of palpitations or SVT. For instance, a case study noted that a patient with restricted water intake experienced an increase in heart rate and SVT episodes, which improved with rehydration therapy.
Moreover, dehydration is recognized as a potential trigger for paroxysmal SVT, particularly in individuals with pre-existing heart conditions or those who are more susceptible to arrhythmias.
Managing Supraventricular Tachycardia Related to Dehydration
Addressing dehydration is crucial in managing SVT episodes. Here are several strategies to consider:
Hydration: Ensuring adequate fluid intake is essential. Individuals should aim for at least 8-10 glasses of water daily, adjusting for activity level and climate.
Electrolyte Balance: Consuming electrolyte-rich fluids, such as sports drinks or oral rehydration solutions, can help maintain proper electrolyte levels.
Monitoring Symptoms: Patients experiencing frequent SVT episodes should monitor their hydration status and be aware of symptoms indicating dehydration, such as dry mouth, fatigue, and decreased urination.
Medical Intervention: In cases of severe dehydration or persistent SVT, medical intervention may be necessary. This could include intravenous fluids or medications to stabilize heart rhythm.
Lifestyle Adjustments: Reducing caffeine and alcohol intake, managing stress levels, and engaging in regular physical activity can also help mitigate the risk of SVT episodes.
Conclusion
Supraventricular tachycardia is a complex condition influenced by various factors, including dehydration. The relationship between dehydration and SVT underscores the importance of maintaining proper hydration for overall cardiovascular health. Patients experiencing symptoms of SVT should consider their hydration status and seek medical advice if episodes persist. By understanding the connection between dehydration and heart rhythm disorders, individuals can take proactive steps to manage their health and reduce the risk of SVT.