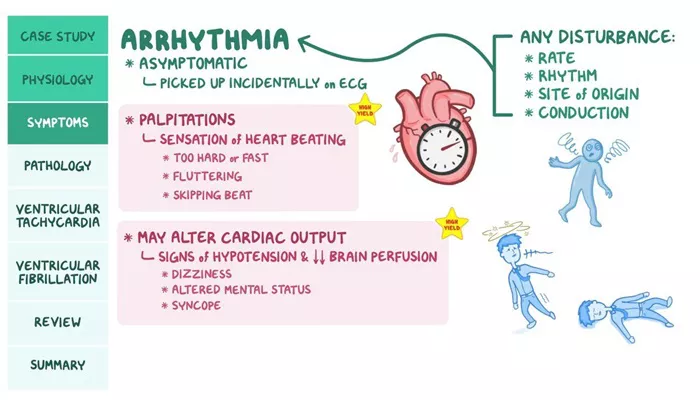
Arrhythmias are irregular heartbeats that can significantly impact a person’s health. They can manifest as a heart that beats too fast (tachycardia), too slow (bradycardia), or in an irregular pattern. Understanding the clinical significance of arrhythmias is crucial for effective diagnosis, management, and treatment.
What Is Arrhythmias?
Arrhythmias arise from issues in the electrical conduction system of the heart. This system controls the heart rate and rhythm, ensuring that the heart pumps blood efficiently throughout the body. When this system malfunctions, it can lead to various types of arrhythmias, each with its own implications for health.
The prevalence of arrhythmias is notable; studies suggest that between 1.5% to 5% of the general population may experience some form of arrhythmia, with atrial fibrillation being the most common type.
While some arrhythmias may be benign, others can lead to severe complications, including stroke and sudden cardiac death.
Types of Arrhythmias
Several types of arrhythmias exist, each with unique characteristics and clinical significance:
Atrial Fibrillation (AF): The most prevalent type, characterized by rapid and irregular beating of the atria. It increases the risk of stroke by five times compared to individuals with a normal rhythm.
Supraventricular Tachycardia (SVT): Involves episodes of abnormally fast heart rates originating above the ventricles. It can lead to symptoms such as palpitations and dizziness.
Bradycardia: Defined as a slower than normal heart rate (below 60 beats per minute). While it may be harmless in well-conditioned athletes, it can cause significant symptoms in others.
Heart Block: A condition where the electrical signals are delayed or blocked, potentially leading to fainting or sudden cardiac arrest.
Ventricular Fibrillation: A life-threatening condition where the heart quivers instead of pumping effectively. Immediate medical intervention is required to restore a normal rhythm.
SEE ALSO: Is Multifocal Atrial Tachycardia Dangerous?
Clinical Significance of Arrhythmias
The clinical significance of arrhythmias can be categorized into several key areas:
1. Risk of Stroke
Atrial fibrillation significantly increases the risk of stroke due to the formation of blood clots in the atria. These clots can dislodge and travel to the brain, causing a stroke. Patients with AF often require anticoagulant therapy to mitigate this risk.
2. Sudden Cardiac Death
Certain arrhythmias, particularly ventricular fibrillation and tachycardia, are associated with sudden cardiac death. This is especially prevalent in individuals with underlying heart disease. Prompt recognition and treatment are vital for preventing fatal outcomes.
3. Heart Failure
Arrhythmias can exacerbate existing heart failure or contribute to its development. For instance, rapid ventricular rates during AF can lead to decreased cardiac output and worsening symptoms in heart failure patients.
4. Quality of Life
Patients with symptomatic arrhythmias often experience reduced quality of life due to palpitations, fatigue, and anxiety related to their condition. Effective management through lifestyle changes or medical interventions is essential for improving their overall well-being.
5. Complications from Underlying Conditions
Arrhythmias can signal underlying health issues such as coronary artery disease or cardiomyopathy. Identifying and treating these conditions is crucial for managing arrhythmias effectively.
Diagnosis of Arrhythmias
Diagnosing arrhythmias involves a combination of patient history, physical examination, and specific diagnostic tests:
Electrocardiogram (ECG): The primary tool for diagnosing arrhythmias; it records the electrical activity of the heart and identifies abnormal rhythms.
Holter Monitoring: A portable ECG device worn for 24 hours or longer to capture intermittent arrhythmic events during daily activities.
Electrophysiological Studies: Invasive tests that map electrical signals within the heart to identify specific arrhythmic pathways.
Echocardiogram: An ultrasound test that evaluates heart structure and function, helping to identify any underlying abnormalities contributing to arrhythmias.
Treatment Options
The treatment for arrhythmias varies based on type, severity, and underlying causes:
1. Medications
Antiarrhythmic drugs are commonly prescribed to control heart rate or restore normal rhythm. These include:
Beta-blockers: Help slow down heart rate.
Calcium channel blockers: Reduce heart workload and control rhythm.
Anticoagulants: Used primarily in AF patients to prevent stroke.
2. Electrical Interventions
For certain types of arrhythmias, electrical interventions may be necessary:
Cardioversion: A procedure that uses electricity to reset the heart’s rhythm.
Catheter Ablation: A minimally invasive procedure that destroys small areas of heart tissue causing abnormal electrical signals.
3. Devices
Implantable devices may be required for long-term management:
Pacemakers: Used for bradycardia or certain types of blockages; they help maintain an adequate heart rate.
Implantable Cardioverter-Defibrillators (ICDs): Designed for patients at high risk of life-threatening arrhythmias; they monitor heart rhythms and deliver shocks if dangerous rhythms are detected.
Lifestyle Modifications
In addition to medical treatments, lifestyle changes play a crucial role in managing arrhythmias:
Dietary Changes: Reducing caffeine and alcohol intake can help minimize triggers for some patients.
Regular Exercise: Engaging in regular physical activity supports overall cardiovascular health but should be tailored based on individual tolerance.
Stress Management: Techniques such as yoga or meditation can help reduce stress-induced arrhythmic episodes.
Conclusion
Understanding the clinical significance of arrhythmias is essential for both patients and healthcare providers. With proper diagnosis and treatment, many individuals with arrhythmias can lead normal lives while minimizing their risk for serious complications such as stroke or sudden cardiac death. Continuous advancements in medical technology and treatment options offer hope for improved outcomes in managing these complex conditions.
Related topics:
- Will Atrial Fibrillation Shorten My Life
- Can Not Eating Enough Cause Heart Arrhythmia?
- How Do Doctors Treat Heart Palpitations?